Abstract
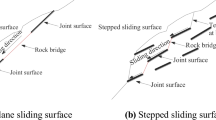
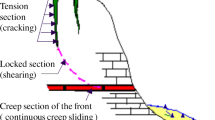
To study the stability evaluation method and failure mode of reserved rock masses, the Yueyang landslide project was taken as the research object. First, based on the limit equilibrium method and elastic mechanics, the formulas for calculating the stability of a reserved rock mass were analyzed. Second, the failure modes of the reserved rock mass were tested by the experiment model. The results show that the failure modes of the reserved rock mass can be divided into three modes: upward sliding failure, downward sliding failure and tensile crack failure, which are mainly related to the strength and width of the reserved rock mass. Therefore, it is unreasonable to regard a reserved rock mass as a unified failure form in the design of anti-slide pile reinforcement. In addition, although both moderate-strength and strong-strength reserved rock masses exhibit tensile crack failure, moderate-strength rock masses under triangular loading are prone to tension-sliding failure, while strong-strength rock masses under parabolic loading are prone to tension-overturning failure. Finally, the displacement and stress monitoring results in the experiment are basically consistent with the theoretical analysis, indicating that the theoretical analysis results have high reliability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Action height of the triangle load
- a 1, a 2, a 3 :
-
Coefficient of the parabolic load function
- B :
-
Angle between the slide surface and anti-slide pile (≤90°)
- B :
-
Width of the reserved rock mass in front of the anti-slide pile
- B :
-
Width of the anti-slide pile
- B p :
-
Influence width of the anti-slide pile
- B pa :
-
Critical width of reserved rock mass at parabolic load
- B tr :
-
Critical width of the reserved rock mass at triangular load
- c :
-
Cohesion of the reserved rock mass
- F s :
-
Factor of safety
- F s1 :
-
Driving force
- F s2 :
-
Resisting force
- F 1 :
-
Friction force between the anti-slide pile and reserved rock mass
- F 2, F 3 :
-
Lateral shearing force on the sliding wedge
- H :
-
Height of the reserved rock mass in front of the anti-slide pile
- h :
-
Plastic zone height
- γ :
-
Unit weight of the reserved rock mass
- δ :
-
Friction angle between the anti-slide pile and reserved rock mass
- λ 1, λ 2, λ 3, λ 4 :
-
Assumed parameters
- [σ R]:
-
Compressive strength of the reserved rock mass
- [σ τ]:
-
Tensile strength of the reserved rock mass
- σ x, σ x, τ xy :
-
Stress of the reserve rock mass
- ϕ :
-
Internal friction angle of the reserved rock mass
References
Bo Z, Yunsheng W, Yu W, Tong S, Yongchao Z (2017) Retaining mechanism and structural characteristics of h type anti-slide pile (hTP pile) and experience with its engineering application. Engineering Geology 222:29–37, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.018
Cai J, Du G, Xia H, Sun C (2021) Model test and numerical simulation study on bearing characteristics of pervious concrete pile composite foundation. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 25(10):3679–3690, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1522-7
Dai Z, Zhang X, Zhou S, Lu C, Zhen Y (2010) Field modeling of laterally distributed landslide thrusts over anti-slide piles. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 32(10):1513–1518 (in Chinese)
Ding Z, Song C, Chen L, Shi K (2020) Dynamic analysis of laterally loaded single piles in sandy soils considering sliding and debonding on the pile-soil interface. Ocean Engineering 217:107720, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107720
Fan G, Zhang J, Qi S, Wu J (2019) Dynamic response of a slope reinforced by double-row anti-sliding piles and pre-stressed anchor cables. Journal of Mountain Science 16(1):226–241, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5041-z
Gong W, Li J, Li L (2018) Limit analysis on seismic stability of anisotropic and nonhomogeneous slopes with anti-slide piles. Science China Technological Sciences 61(1):140–146, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9147-8
He C, Hu X, Liu D, Xu C, Wu S, Wang X, Zhang H (2020) Model tests of the evolutionary process and failure mechanism of a pile-reinforced landslide under two different reservoir conditions. Engineering Geology 277:105811, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105811
Hu X, Zhou C, Xu C, Liu D, Wu S, Li L (2019) Model tests of the response of landslide-stabilizing piles to piles with different stiffness. Landslides 16(11):2187–2200, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01233-4
Huang Y, Xu X, Liu J, Mao W (2020) Centrifuge modeling of seismic response and failure mode of a slope reinforced by a pile-anchor structure. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 131:106037, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106037
Jun X, Chenghua W (2006) Pre-stressed rope reinforced anti-sliding pile. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences 11(4):887–891, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02830182
Li C, Tang H, Hu X, Wang L (2013) Numerical modelling study of the load sharing law of anti-sliding piles based on the soil arching effect for Erliban landslide, China. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 17(6):1251–1262, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-013-0074-x
Li C, Wang X, Tang H, Lei G, Yan J, Zhang Y (2017) A preliminary study on the location of the stabilizing piles for colluvial landslides with interbedding hard and soft bedrocks. Engineering Geology 224:15–28, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.020
Liang X, He H, Zhang Y (2019) Optimization design of micro-piles in landslide safety protection based on machine learning. Safety Science 118:861–867, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.06.021
Liu X, Cai G, Liu L, Zhou Z (2020a) Investigation of internal force of anti-slide pile on landslides considering the actual distribution of soil resistance acting on anti-slide piles. Natural Hazards 102(3):1369–1392, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03971-4
Liu D, Hu X, Zhou C, Xu C, He C, Zhang H, Wang Q (2020b) Deformation mechanisms and evolution of a pile-reinforced landslide under long-term reservoir operation. Engineering Geology 275:105747, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105747
Liu X, Kou M, Feng H, Zhou Y (2018) Experimental and numerical studies on the deformation response and retaining mechanism of h-type anti-sliding piles in clay landslide. Environmental Earth Sciences 77(5):163, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7360-3
Ma N, Wu H, Ma H, Wu X, Wang G (2019) Examining dynamic soil pressures and the effectiveness of different pile structures inside reinforced slopes using shaking table tests. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 116:293–303, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.10.005
Meng FZ, Li SJ, Zhang ZH (2012) Determination of mechanical parameters of reservoir landslide based on back analysis using evolutionary artificial network. Applied Mechanics and Materials 170–173:729–734, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.170-173.729
Min Z, Lei N, Yan X, Shulin D (2015) A thrust load-caused landslide triggered by excavation of the slope toe: A case study of the Chaancun landslide in Dalian city, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 8(9):6555–6565, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1710-6
Nie Z, Zhang Z, Zheng H, Lin S (2020) Stability analysis of landslides using BEM and variational inequality based contact model. Computers and Geotechnics 123:103575, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103575
Qiu P (2019) Contrastive analysis of indoor model test and numerical test on pull-out failure of fully-embedded anti-slide pile. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 283:012035, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/283/1/012035
Rao P, Zhao L, Chen Q, Nimbalkar S (2019) Three-dimensional limit analysis of slopes reinforced with piles in soils exhibiting heterogeneity and anisotropy in cohesion. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 121:194–199, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.02.030
Shadunts KS, Matsii SI (1997) Interaction between pile rows and sliding soil. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering 34(2):35, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02465015
Stark TD, Arellano WD, Hillman RP, Hughes RM, Joyal N, Hillebrandt D (2005) Effect of toe excavation on a deep bedrock landslide. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities 19(3):244–255, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3828(2005)19:3(244)
Tang H, Hu X, Xu C, Li C, Yong R Wang L (2014) A novel approach for determining landslide pushing force based on landslide-pile interactions. Engineering Geology 182:15–24, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.024
Toupin RA (1965) Saint-Venant’s principle. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 18(2):83–96, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282253
Vijaywargiya R, Green I (2007) A finite element study of the deformations, forces, stress formations, and energy losses in sliding cylindrical contacts. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics 42(7): 914–927, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2007.03.017
Wang J, Liang Y, Zhang H, Wu Y, Lin X (2014) A loess landslide induced by excavation and rainfall. Landslides 11(1):141–152, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0418-0
Wang L, Sun D, Yao Y, Tan Y (2019) Seismic stability of 3D piled unsaturated earth slopes using kinematic limit analysis. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 126:105821, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.105821
Wang L, Sun D, Yao Y, Wu L, Xu Y (2020a) Kinematic limit analysis of three-dimensional unsaturated soil slopes reinforced with a row of piles. Computers and Geotechnics 120:103428, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103428
Wang H, Wang P, Qin H, Yue J, Zhang J (2020b) Method to control the deformation of anti-slide piles in zhenzilin landslide. Applied Sciences 10(8):2831, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082831
Wu F, Chen B, Zou Q, Zhai C, Liu W, Chen J, Ni G (2019) Range estimation of horizontal stress of deep rock based on Mohr-Coulomb criterion. Results in Physics 12:2107–2111, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.02.061
Xie Q, Cao Z, Shi X, Fu X, Ban Y Wu Z (2021) Model test of interaction between load-caused landslide and double-row anti-slide piles by transparent soil material. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 46:4841–4856, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05256-1
Xu Z (2018) A concise course in elasticity, fifth edition. Higher Education Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Xu M, Tang Y, Liu X, Yang H, Luo B (2018) A shaking table model test on a rock slope anchored with adaptive anchor cables. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 112:201–208, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.10.021
Zhang H, Li C, Hu X, Fu Z, Chen W, Yao W, Zhang Y, Jiang X (2020) Deformation response and triggering factors of the reservoir landslide-pile system based upon geographic detector technology and uncertainty of monitoring data. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment 35:1481–1498, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01889-8
Zhang Q, Hu J, Du Y, Gao Y, Li J (2021) A laboratory and field-monitoring experiment on the ability of anti-slide piles to prevent buckling failures in bedding slopes. Environmental Earth Sciences 80(2):44, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09288-6
Zhang Y, Hu X, Tannant DD, Zhang G, Tan F (2018) Field monitoring and deformation characteristics of a landslide with piles in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Landslides 15(3):581–592, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0945-9
Zhang G, Wang L (2017) Simplified evaluation on the stability level of pile-reinforced slopes. Soils and Foundations 57(4):575–586, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2017.03.009
Zheng Y (2010) Engineering treatment of slope & landslide. China Communications Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 41302256) and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Geological Hazards on Three Gorges Reservoir Area (China Three Gorges University), Ministry of Education (Grant Number 2020KDZ06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, D., He, L. & Qin, L. Stability of the Rock Mass Reserved in front of Anti-slide Piles. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 569–583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-0315-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-0315-3