Abstract
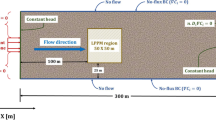
In this paper the efforts were made in the laboratory to construct a physical model and a simulated model with the help of computational fluid dynamic (CFD) techniques to provide the solutions of contaminant transport within the saturated porous media under a hydraulic structure. Brinkman equations with Forchheimer correction and species flow through porous media were considered together to describe the problem. Three categories factors were considered to be analyzed in this study. The first one is the hydraulic factors represented in the upstream water head (H). While, the second factor is the geometry of the hydraulic structures represented in the length of the base and the length of the sheet pile. The physical properties and chemical properties were the third investigated factors, in which the physical properties of the porous media include porosity and intrinsic permeability, while the chemical properties represented by the rate of generation and retardation caused by the adsorption. The physical properties have a slight effect on the concentrations because of the low flow velocity through the porous media. On the other hand, a considerable decrement on the concentrations were noticed when the rate of generation and retardation caused by adsorption was increased. Also, it was observed that the diffusion coefficient has no dramatic effect on the concentrations and contaminant moving. The results of the CFD simulated model and that of the physical model were verified with two cases for pressure head and one case for the contaminates transport. For the first case of pressure head, the maximum percentage error at five selected points was about 15% at worst point with average error of 10%. While, for the case two, the maximum percentage error is about 9% at worst one with an average error of 8%. For the simulation of the contaminates transport, reliable statistical indexes error indicted that the CFD simulated model gives a good agreement with all experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Concentration of contaminants
- C f :
-
Dimensionless friction coefficient
- c m :
-
Measured concentration
- \(\overline {{c_m}} \) :
-
The mean measured concentration
- C s :
-
Simulated concentration
- D = Dx = Dy :
-
Diffusion coefficient
- e :
-
Error
- H :
-
Up stream water head
- k :
-
Intrinsic permeability
- Kd :
-
Adsorption isotherm
- L b :
-
Length of base
- L s :
-
Length of the sheet pile
- MAE :
-
Mean absolute error
- MSE :
-
Mean squared error
- n :
-
Porosity
- p :
-
Pressure
- r :
-
Rate of generation
- R :
-
Retardation which is caused her by adsorption
- RMSE :
-
Root mean squared error
- RSE :
-
Relative squared error
- s:
-
Rate of external source, function of c
- u :
-
Velocity field in the x-direction
- v :
-
Velocity field in the y-direction
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density
References
Ahmed A, McLoughlin S, Johnston H (2015) 3D analysis of seepage under hydraulic structures with intermediate filters. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 141(1), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000944
Al-Madhhachi AT, Hasan MB (2018) Influence of in-situ scaling on variability of polluted soil erodibility parameter. Pollution 4(4):617–633, DOI: https://doi.org/10.22059/poll.2018.252263.393
Al-Madhhachi AT, Mutter GM, Hasan MB (2019) Predicting mechanistic detachment model due to lead-contaminated soil treated with Iraqi stabilizers. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 23(7):2898–2907, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-2312-3
Amiri A, Vafai K (1998) Transient analysis of incompressible flow through a packed bed. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 41(24):4259–4279, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(98)00120-3
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Hosseini SA (2005) Error analysis of finite difference methods for two dimensional advection-dispersion-reaction equation. Advances in Water Resources 28(8):793–806, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.02.003
Ballarini E, Bauer S, Eberhardt C, Beyer C (2012) Evaluation of transverse dispersion effects in tank experiments by numerical modeling: Parameter estimation, sensitivity analysis and revision of experimental design. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 134(1):22–36, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.04.001
Batty TA (2015) Examining the use of the partition coefficient in the quantifying sorption of heavy metals in permo-triassic sandstone aquifers. PhD Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
Brusseau ML (1994) Transport of reactive contaminants in heterogeneous porous media. AN AGUJournal 32(3):285–313, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/94RG00624
Carlier E, El Khattabi J, Potdevin JL (2006) Solute transport in sand and chalk: A probabilistic approach. Hydrological Processes 20(5):1047–1055, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.5931
Chao W, Pei-Fang W, Yong L (2003) Composite modelling approach and experimental study for subsurface transport of contaminants from land-disposal sites. Journal of Hydrodynamics 15(4):1–9
Clement TP (2001) Generalized solution to multispecies transport equations coupled with a first-order reaction network. Water Resources Research 37(1):157–163, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2000WR900239
Craig JR, Rabideau AJ (2006) Finite difference modelling of contaminant transport using analytic element flow solutions. Advances in Water Resources 29(7):1075–1087, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.08.010
Domenico PA (1987) An analytical model for multidimensional transport of a decaying contaminant species. Journal of Hydrology 91(1–2):49–58, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(87)90127-2
El-Zein A, Carter JP, Aire DW (2006) Three-dimensional finite elements for the analysis of soil contaminant using a multiple-porosity approach. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics 30(7):577–597, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.491
Fox PJ, Lee JG, Lenhart JJ (2011) Coupled consolidation and contaminant transport in compressible porous media. International Journal of Geomechanics 11(2):113–123, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000035
Guyonnet D, Neville C (2004) Dimensionless analysis of two analytical solutions for 3-D solute transport in groundwater. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 75(1–2):141–153, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2004.06.004
Hasan MB, Al-Madhhachi AT (2018) The influence of crude oil on mechanistic detachment rate parameters. Geosciences 8(9):332–348, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090332
Hrmann LL, Noseck U, Tix C (1998) Model of contaminant transport in porous media in the presence of colloids applied to actinide migration in column experiments. Water Resources Research 34(3):421–426, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/97WR03468
Li MH, Cheng HP, Yeh GT (2005) An adaptive multigrid approach for the simulation of contaminant transport in the 3D subsurface. Computers & Geosciences 31(8):1028–1041, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2005.03.010
Massimo R, David H, Gabriele C, Peter K (2012) Experimental investigation and pore-scale modelling interpretation of compound-specific transverse dispersion in porous media. Transport in Porous Media 93(3):347–362, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-9953-8
Merle CP, Wiggert DC, Midhat H (2010) Mechanics of fluids, fourth edition. Global Engineering, 670–720
Morillo E, Undabeytia T, Maqueda C, Ramos A (2000) Glyphosate adsorption on soils of different characteristics. Influence of copper addition. Chemosphere 40(1):103–107, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00255-6
Park E, Zhan H (2001) Analytical solutions of contaminant transport from finite one-, two- and three dimensional sources in a finite-thickness aquifer. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 53(1):41–61, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7722(01)00136-x
Patel SB, Chore HS (2014) Contaminant transport through porous media: An overview of experimental and numerical studies. Advances in Environmental Research 3(1):45–69, DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/aer.2014.3.1.045
Penrose W, Polzer RWL, Essington E, Nelson HD, Orlandini KA (1990) Mobility of plutonium and americium through a shallow aquifer in a semiarid region. Environmental Science & Technology 24(1):228–234, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/es500539t
Rao P, Medina MA (2005) A multiple domain algorithm for modelling one-dimensional transient contaminant transport flows. Applied Mathematics and Computation 167(1):1–15, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2004.06.064
Rao P, Medina MA (2006) A multiple domain algorithm for modelling two dimensional contaminant transport flows. Applied Mathematics and Computation 174(1):117–133, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.03.021
Remesikova M (2007) Numerical solution of two-dimensional convection-diffusion adsorption problems using an operator splitting scheme. Applied Mathematics and Computation 184(1):116–130, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.06.018
Sadiq SM, Sanaa ATA, Shaymaa AMA, Zainab TA (2020) CFD simulation and experimental study to predict the flowrate across a square edge broad crested weir depending on the end depth as a control section. Proceedings of 19th international conference in civil engineering AICCE’19, August 21–22, Penang, Malaysia
Satpute SS, Parkale S, Kashid LM (2015) Study of Sorption behavior of Atrazine toward soil. International Journal of Environmental Science 6(1):1–12, DOI: https://doi.org/10.6088/ijes.6001
Shackelford CD, Lee JM (2005) Analysing diffusion by analogy with consolidation. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering ASCE 13(11):1345–1359, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:11(1345)
Sharma PK, Sawant VA, Shukla SK, Khan Z (2013) Experimental and numerical simulation of contaminant transport through layered soil. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 8(4):345–351, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/1939787913Y.0000000014
Sharma PK, Umang D (2014) Contaminant transport through fractured-porous media: An experimental study. Journal of Hydro-environment Research 8(3):223–233.
Srinivasan V, Clement TP, Lee KK (2007) Domenico solution — Is it valid? Ground Water 45(2):136–146, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00281.x
Zimmermann S, Koumoutsakos P, Kinzelbach W (2001) Simulation of pollutant transport using a particle method. Journal of Computational Physics 173(1):322–347, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.2001.6879
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mustansiriyah University (www.uomustansiriyah.edu.iq) and college of engineering Baghdad-Iraq for its support in the present work and the Hydraulic and hydrology Laboratory staff in the College of Engineering for their support and helps through the period of the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhsun, S.S., Saleh, M.S. & Qassim, A.R. Physical and CFD Simulated Models to Analyze the Contaminant Transport through Porous Media under Hydraulic Structures. KSCE J Civ Eng 24, 3674–3691 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1767-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1767-6