Abstract
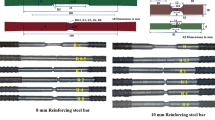
An experimental investigation on chloride diffusion in structural concrete under the cyclic impact loading is conducted. Effects of magnitudes and loading times are studied. Relationship between damage coefficients and chloride diffusion coefficients is obtained. The cyclic impact loading causes the initiation of new cracks and the propagation of existing cracks, which brings an obvious promotion for chloride diffusion. There should be a damage threshold. If the magnitude of the external loading is large enough to make the damage exceed the threshold, initiation and propagation of cracks become quite significant and chloride diffusion can be greatly promoted. With the increase of the damage coefficient, the chloride diffusion coefficient increases. The increasing rates decrease with long immersion times. Relationship curves of damage coefficients and chloride diffusion coefficients show a good correlation and can be well described with power functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M (2016) Marine concrete structures: Design, durability and performance, 1st edition. Woodhead Publishing, Amsterdam, Nederland
Anderson TL (2017) Fracture mechanics: Fundamentals and applications, 4th edition. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Beeby AW (1983) Cracking, cover, and corrostion of reinforcement. Concrete International 5(2):35–40
Beer FP, Johnston Jr. ER, DeWolf JT, Mazurek DF (2014) Mechanics of materials, 7th edition. McGraw-Hill Education, New York, NY, USA
Birnin-Yauri UA, Glasser FP (1998) Friedel’s salt, Ca2Al(OH)6(Cl,OH)·2H2O: Its solid solutions and their role in chloride binding. Cement and Concrete Research 28(12):1713–1723, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00162-8
Bompan KF, Haach VG (2018) Ultrasonic tests in the evaluation of the stress level in concrete prisms based on the acoustoelasticity. Construction and Building Materials 162:740–750, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.11.153
Carlson SR, Young RP (1993) Acoustic emission and ultrasonic velocity study of excavation-induced microcrack damage at the underground research laboratory. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts 30(7):901–907, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(93)90042-C
Climent MA, de Vera G, López JF, Viqueira E, Andrade C (2002) A test method for measuring chloride diffusion coefficients through nonsaturated concrete: Part I. The instantaneous plane source diffusion case. Cement and Concrete Research 32(7):1113–1123, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)00750-0
Dhir RK, Jones MR, Ahmed HEH, Seneviratne AMG (1990) Rapid estimation of chloride diffusion coefficient in concrete. Magazine of Concrete Research 42(152):177–185, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.1990.42.152.177
Djerbi A, Bonnet S, Khelidj A, Baroghel-bouny V (2008) Influence of traversing crack on chloride diffusion into concrete. Cement and Concrete Research 38(6):877–883, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.10.007
Eric JH and Victor ES (1999) Numerical simulation of reinforced concrete deterioration: Part 2 — Steel corrosion and concrete cracking. Materials Journal 96(3), DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/630
Fu Chuanqing, Jin Xianyu, Jin Nanguo (2010) Modeling of chloride ions diffusion in cracked concrete. Earth and Space 2010, 3579–3589, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/41096(366)343
Hu JS, Li Q (2006) Relevant problems concerning port structure reliability design. Port & Waterway Engineering 394(10):70–73, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16233/j.cnki.issn1002-4972.2006.10.012
JTS 167–2018 (2018) Code for design of wharf structure. Ministry of Transportation of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing, China
Liu C, Teng B, Zhang J (2011) Impact velocity of a moored ship. Journal of Waterway and Harbor 32(3):161–167, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2011.03.002
Liu H, Wang M, Zhang Q (2014) Virtual design of shaking table test in sine-swept vibration. Journal of Natural Disasters 23(1):252–257, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13577/j.jnd.2014.0134
Luo QZ, Huang ZB (2010) Mechanical model and lateral transient responses of bridge piers in collision with ship. Journal of the China Railway Society 32(6):84–89, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.06.014
Mangat PS, Molloy BT (1994) Prediction of long term chloride concentration in concrete. Materials and Structures 27(6):338, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473426
Marsavina L, Audenaert K, De Schutter G, Faur N, Marsavina D (2009) Experimental and numerical determination of the chloride penetration in cracked concrete. Construction and Building Materials 23(1): 264–274, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.12.015
Meglis IL, Chow T, Martin CD, Young RP (2005) Assessing in situ microcrack damage using ultrasonic velocity tomography. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 42(1):25–34, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.06.002
Philipse AP (2018) Continuity, gradients and fick’s diffusion laws. In: Brownian Motion, Springer, Berlin, Germany, 61–70
Saetta AV, Vitaliani RV (2004) Experimental investigation and numerical modeling of carbonation process in reinforced concrete structures: Part I: Theoretical formulation. Cement and Concrete Research 34(4):571–579, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.09.009
Šomodíková M, Strauss A, Zambon I, Teplý B (2018) Quantification of parameters for modeling of chloride ion ingress into concrete. Structural Concrete, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.201800049
Stigh U (1987) Influence of damage on ultrasonic velocity and strength — Analysis and experiments. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 28(1):1–12, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(87)90114-7
Sun C, Yuan L, Zhai X, Qu F, Li Y, Hou B (2018) Numerical and experimental study of moisture and chloride transport in unsaturated concrete. Construction and Building Materials 189:1067–1075, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.158
Tang L (1996) Chloride transport in concrete — Measurement and prediction thèse. Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden
Tang L (1999) Concentration dependence of diffusion and migration of chloride ions: Part 2. Experimental evaluations. Cement and Concrete Research 29(9):1469–1474, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(99)00120-9
Thomas MDA, Bamforth PB (1999) Modelling chloride diffusion in concrete: Effect of fly ash and slag. Cement and Concrete Research 29(4):487–495, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00192-6
TJT270-98 (1998) Test specification for concrete of waterway engineering. Ministry of Transportation of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing, China
Truc O, Ollivier J-P, Nilsson L-O (2000) Numerical simulation of multi-species transport through saturated concrete during a migration test — MsDiff code. Cement and Concrete Research 30(10):1581–1592, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(00)00305-7
Ye T, Xianyu JIN, Nanguo JIN (2018) Investigation on the transport properties of chlorides in concrete II Numerical simulation. MATEC Web of Conferences 199:02014, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201819902014
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shanghai SASAC Special support fund for technological innovation and level upgrading of enterprises.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Py., Zheng, Yl., Luo, Wb. et al. Experimental Study on Chloride Diffusion in Structural Concrete considering the Effect of Damages Induced by the Cyclic Impact Loading. KSCE J Civ Eng 24, 187–194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0477-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0477-4