Abstract
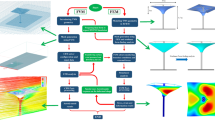
A high precision FE model is the key basis for cause analysis and overcoming of inner polygon defect of hot rolled seamless steel tubes. In this paper, the viscoelastic-plastic FEM is adopted in order to develop a high precision FE model for predicting the defect of inner polygon. Mechanical properties of tube material under rolling environment is obtained through five sets of high temperature compression tests, thus the viscoelastic-plastic constitutive equation of tube material is regressed and agrees with the tests results. Heat transfer boundary conditions, roll constant speed and contact friction boundary conditions are applied simultaneously on the FE model and thermo-mechanical coupled explicit algorithm is adopted for solution. The precision of the FE model is verified through industry experiments. Results shows the simulated inner wall shape is in good accordance with the experiment results, and the friction force, stress, strain and temperature distribution in the deformation zone are also discussed. It can be concluded that the viscoelastic-plastic FE model is of high precision and can be applied for better analysis of the hot rolling results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayoumi, L. S. (2003). “Analysis of flow and stresses in a tube stretch-reducing hot rolling schedule.” Int. J. Mech. Sci., Vol. 45, pp. 553–565, DOI: 10.1016/S0020-7403(03)00047-X.
Carretero, O. V., Bliznuk, V., and Sanchez, N. (2014). “Analysis of the strengthening mechanisms in pipeline steels as a function of the hot rolling parameters.” Materials Science & Engineering A, Vol. 604, pp. 46–56, DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.02.066.
Carvalho, R. N. (2007). “Simulation of the process of hot rolling of seamless tubes.” Proc. 5th international conference on processing and manufacturing of advanced materials, Vancouver, DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.539-543.4602.
Fuat, K., Josef, N., and Robert, A. L. (2010). “Effect of thickness variation on collapse pressure of seamless pipes.” Ocean Engineering, Vol. 37, pp. 11–12, DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.03.014.
Jiang, Y. Z. and Tang, H. P. (2015). “Method for improving transverse wall thickness precision of seamless steel tube based on tube rotation.” Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, Vol. 22, pp. 924–930, DOI: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15) 30091–1.
Jiang, Y. Z., Tang, H. P., Tang, H. H., Deng, S. B., and Peng, X. (2015). “Explicit FE modelling of tube stretch reduction and analysis of wall thickness variation.” Ironmaking & Steelmaking, Vol. 42, pp. 176–184, DOI: 10.1179/1743281214Y.0000000217.
Knysh, P. and Korkolis, Y. P. (2015). “Determination of the fraction of plastic work converted into heat in metals.” Mechanics of Materials, Vol. 86, pp. 71–80, DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2015.03.006.
Li, H., Yang, H., and Zhang, Z. (2014). “Hot tube-forming. In Comprehensive materials processing.” Edited by Saleem H, Gilmar FB, Chester JVT and Bekir Y, Elsevier, Oxford, pp. 321–350, DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-08-096532-1.00525-2.
Li, J. H. and Yu, H. (2012). “Numerical simulation of seamless Tube’s stretch reducing process.” Master. Sci. Forum, Vols. 704–705, pp. 155–159, DOI: 10.4028/MSF.704-705.155.
Li, S. Z., Bao, H. Y., and Zhang, Z. C. (2010). “Research on design method of polygonal roll pass for stretch reduced seamless tubes.” Master Sci Forum, Vol. 654–656, pp. 1614–1617, DOI: 10.4028/MSF.654–656.1614.
Li, S. Z., Zhang, Z. C., Bao, H. Y., and Zhou, Z. Y. (2010). “Influence of roll speed schedule on transverse wall thickness evenness of shell elongated by mandrel mill.” Materials Science Forum, Vol. 654–656, pp. 1311–1314, DOI: 10.4028/MSF.654-656.1311.
Pater, Z., Kazanecki, J., and Bartnicki, J. (2006). “Three dimensional thermo-mechanical simulation of the tube forming process in Diescher’s mill.” J. Mater. Process Technol., Vol. 177, pp. 167–170, DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.03.205.
Pirling, T., Carrado, A., and Palkowski, H. (2011). “Residual stress distribution in seamless tubes determined experimentally and by FEM.” In: Procedia Eng., pp. 3080–3085, DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.04.510.
Seyed, A. N., Elham, M., Mohammad, M. S., and Mohsen, M. (2016). “Mechanical response of buried High-Density Polyethylene pipelines under normal fault motions.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 20, No. 6, pp. 2253–2261, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-015-0695-3DO.
Shi, D. Q., Gao, G. L., Xiao, P., and Gao, Z. W. (2012). “Defects detection system for steel tubes based on electromagnetic acoustic technology.” Procedia Engineering, Vol. 29, pp. 252–256, DOI: 10.1016/proeng.2011.12.702.
Tu, W. B., Tang, Y., Hu, J. Y., Wang, Q. H., and Lu, L. S. (2015). “Heat transfer and friction characteristics of laminar flow through a circular tube with small pipe inserts.” International Journal of Thermal Sciences, Vol. 96, pp. 94–101, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.04.013.
Wang, F. J., Shuang, Y. H., and Hu, J. H. (2014). “Explorative study of tandem skew rolling process for producing seamless steel tubes.” JMPT, Vol. 214, pp. 1597–1604, DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.03.002.
Xu, Z. Q., Du, F. S., and Wang, M. T. (2007). “The simulation study of the linear mark generating process in the stretch reducing.” J. Mater. Process Technol., Vols. 187–188, pp. 373–377, DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.11.073.
Yin, Y. D., Li, S. Z., Xu, J., Li, Y. H., Long, G. M., and Deng, P. A. (2010). “Analysis of transverse wall thickness precision of steel tube rolled by semi-floating mandrel mill.” Materials Science Forum, Vols. 654–656, pp. 1510–1512, DOI: 10.4028 /AMR.97-101.3097.
Yu, H. L., Liu, X. H., Zhao, X. M., and Kusaba, Y. (2006). “FEM analysis for V-H rolling process by updating geometric method.” Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 180, pp. 323–327, DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.07.012.
Yu, H., Du, F. S., and Wang, F. X. (2011). “Finite element model development and application on stretch reducing process of seamless tube.” Chin J. Mech Eng., Vol. 47, pp. 74–79, DOI: 10.3901/JME.2011.22.074.
Zhao, C. J., Liu, Y. F., Bai, L., Wang, N., and Shuang, Y. H. (2016). “Stretch reduction of seamless steel tube by skew rolling and its numerical simulation.” Metallurgical Research and Technology, Vol. 113, No. 3, pp. 307–311, DOI: 10.1051/metal/2016009.
Zhou, Y., Chen, J. L., Zhao, C. J., and Shuang, Y. H. (2012). “Seamless tube in stretch reducing 3-d thermal-mechanical coupling analysis.” Adv Mater Res, Vol. 572, pp. 198–202, DOI: 10.4028 /AMR.572.198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, YZ., Li, XJ., Zhang, XP. et al. High Precision FE Modeling for Predicting Inner Polygon Defect of Hot Rolled Seamless Steel Tubes. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 4445–4453 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-1014-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-1014-6