Abstract
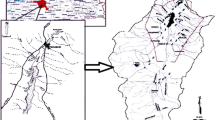
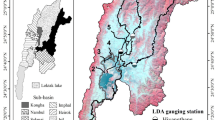
The object of this research is to analyze the water quality improvement of Lake Paldang by implementing Integrated Lake Basin Management (ILBM). To establish ILBM, the basin environment database was built as well as water environment management support system for monitoring present conditions, and predicting changes in basin environment. The major contaminants in Lake Paldang Basin are from domestic pollution, agricultural land, and livestock. Scenarios for reducing contaminants were targeting the increase percentage of sewered population, agricultural and livestock contaminants reduction to analyze the water quality improvement effects. This study applied the SWAT model to Lake Paldang Basin using the basin environment database to improve the water quality of Lake Paldang in Korea. The results of calibration and validation of flow rate, Suspended Solids (SS), Total Nitrogen (TN) and Total Phosphorus (TP) showed that the measurement values and simulation values turned out to be similar, and that it is possible to apply the SWAT model to Lake Paldang Basin. The reduction efficiency of SS by scenario was 11-45%, TN 8-37%, and TP 7-35% and this shows that water quality was significantly improved prior to application. Therefore, to improve the water quality of Lake Paldang, it is recommended to implement the ILBM which is considered to play an important role in making water quality management policy in Korea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, J., Hong, Y., Kang, H., Kim, H., Han, D., Jang, J., Seo, D., and Park, Y. (2010). “Water quality management strategy in the context of climate change I.” Korea Environment Institute, Republic of Korea, pp. 112–116.
Arnold, J. G., Williams, J. R., Nicks, A. D., and Sammons, N. B. (1990). “SWRRB: A basin scale simulation model for soil and water resources management.” Texas A&M Univ. Press, College Station, TX.
ASCE (1993). “ASCE Task committee on definition of criteria for evaluation of watershed models of the watershed management committee.” Irrigation Drainage Engineering, Vol. 119, No. 3, pp. 429-44
Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research-Consortium for Spatial Information (CGIAR-CSI), https://doi.org/www.cgiar-csi.org.
Donigian, A. S. Jr. (2000). HSPF Training Workshop Handbook and CD. Lecture #19, Calibration and Verification Issues, Slide #L19-22, EPA Headquarters, Washington Information Center, 10–14 January, 2000, Presented and prepared for U.S. EPA, Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology, Washington, D.C.
Eckhardta, K. and Arnold, J. G. (2001). “Automatic calibration of a distributed catchment model.” Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 251, Nos. 1–2, pp. 103–109, DOI: 10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00429-2.
Environmental Geographic Information System (EGIS), https://doi.org/egis.me.go.kr.
Global Water Partnership Technical Advisory Committee (GWP-TAC). (2000). Integrated Water Resources Management, TAC Background Papers, 4.
Hwang, J., Kim, Y., Kwon, J., Park, J., Noh, J., and Yi, Y. (2014), “Hydrodynamic and water quality modeling for gate operation: A case study for the Seonakdong River basin in Korea” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, KSCE, Vol. 18, No. 1, pp. 73–80, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-013-0025-6.
International Lake Environment Committee (ILEC) Foundation (2005). Managing Lakes and their Basins for Sustainable Use.
International Lake Environment Committee (ILEC) Foundation (2007). Global Environment Facility-Lake Basin Management Initiative Project.
Jang, J., Jung, K., and Yoon, C. (2012). “Modification of SWAT model for simulation of organic matter in Korean watersheds.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 66, No. 11, pp. 2355–2362, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2012.465.
Kang, B., Kim, Y., Lee, J., and Kim, S. (2015). “Hydro-environmental runoff projection under GCM scenario downscaled by Artificial Neural Network in the Namgang Dam watershed, Korea.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, KSCE, Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 434–445, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-015-0580-0.
Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA), https://doi.org/web.kma.go.kr.
Lee, D., Kim, J., Mendoza, J., Lee, C., and Kang, J. (2017). “Potential use of ionic species for identifying source land-uses of stormwater runoff.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 75, No. 4, pp. 978–986, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2016.575.
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA). (2005). Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis.
Ministry of Environment (ME) (2008a). Investigation of Pollution loading amount, Republic of Korea.
Ministry of Environment (ME) (2008b). Improvement Plan of Sewage, Republic of Korea.
Ministry of Science and Technology (MST) (2006). Sustainable Water Resources Research Program, Republic of Korea.
Nash, J. E. and Sutcliffe, J. V. (1970). “River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I-A discussion of principles.” Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 10, No. 3, pp. 282–290, DOI: 10.1016/0022-1694 (70)90255-6.
National Geographic Information Institute (NGII), https://doi.org/www.ngii.go.kr.
Paldang Water Quality Improvement Center (PWQIC). (2011). A white book of Paldang, Republic of Korea.
Park, M., Ha, R., Kim, N., Lim, K., and Kim, S. (2014). “Assessment of future climate and vegetation canopy change impacts on hydrological behavior of Chungju dam watershed using SWAT model.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, KSCE, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 1185–1196, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-013-0176-5.
Statistics Korea, https://doi.org/sgis.kostat.go.kr. U.S. Geological Survey Global Land Cover Characterization (USGSGLCC), https://doi.org/edc2.usgs.gov/glcc/glcc.php.
Waterbase, https://doi.org/www.waterbase.org.
Water Resources Management Information System (WAMIS), https://doi.org/www.wamis.go.kr.
Water Management Information System, https://doi.org/water.nier.go.kr.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, HC., Shimizu, Y. & Kim, SK. Effect Analysis Regarding Different Scenarios to Improve Water Quality of the Lake Paldang Basin in Korea. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 3246–3253 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1305-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1305-3