Abstract
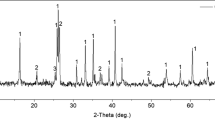
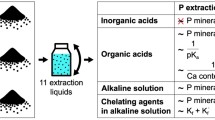
The purpose of this study is to find the optimum conditions, including the type and concentration of solvent, and the solid/liquid ratio, for the extraction of calcium from Paper Sludge Ash (PSA). Solvents with different properties are divided into the following three groups to conduct the calcium extraction experiments: acid (acetic acid and hydrochloric acid), ammonium salt (ammonium chloride and ammonium acetate), and other (sodium citrate and water). The maximum efficiency of calcium extraction using acid is 54% at a concentration of 0.7 M and solid/liquid ratio of 1:25, while ammonium salt and sodium citrate extract calcium up to 30% and 28%, respectively, at a concentration of 0.3 M and solid/liquid ratio of 1:50.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Azdarpour, A., Asadullah, M., Mohammadian, E., Hamidi, H., Junin, R., and Karaei, M. A. (2015). “A review on carbon dioxide mineral carbonation through pH-swing process.” Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 279, pp. 615–630, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.064.
Bobicki, E. R., Liu, Q., Xu, Z., and Zeng, H. (2012). “Carbon capture and storage using alkaline industrial wastes.” Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, Vol. 38, No. 2, pp. 302–320, DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2011.11.002.
Eloneva, S., Teir, S., Salminen, J., Fogelholm, C. J., and Zevenhoven, R. (2008). “Fixation of CO2 by carbonating calcium derived from blast furnace slag.” Energy, Vol. 33, pp. 1461–1467, DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2008.05.003.
Gunning, P. J., Hills, C. D., and Carey, P. J. (2010). “Accelerated carbonation treatment of industrial wastes.” Waste Management, Vol. 30, pp. 1081–1090, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.01.005.
Haynes, W. M. and Lide, D. R. (2010). CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. (91th ed.), CRC Press, USA.
Hu, J., Liu, W., Wang, L., Liu, Q., Chen, F., Yue, H., Liang, B., Lu, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, G., and Li, C. (2017). “Indirect mineral carbonation of blast furnace slag with (NH4)2SO4 as a recyclable extractant.” Journal of Energy Chemistry, In Press, DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2017.06.009.
Jo, H. J., Park, S. H., Jang, Y. N., Chae, S. C., Lee, P. K., and Jo, H. Y. (2014). “Metal extraction and indirect mineral carbonation of waste cement material using ammonium salt solutions.” Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 254, pp. 313–323, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.129.
Kim, M. J., Pak, S. Y., Kim, D., and Jung, S. (2017). “Optimum conditions for extracting Ca from CKD to store CO2 through indirect mineral carbonation.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 629–635, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-016-0913-7.
Kodama, S., Nishimoto, T., Yamamoto, N., Yogo, K., and Yamada, K. (2008). “Development of a new pH-swing CO2 mineralization process with a recyclable reaction solution.” Energy, Vol. 33, No. 5, pp. 776–784, DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2008.01.005.
Kunzler, C., Alves, N., Pereira, E., Nienczewski, J., Ligabye, R., Einloft, S., and Dullius, J. (2011). “CO2 storage with indirect carbonation using industrial waste.” Energy Procedia, Vol. 4, pp. 1010–1017, DOI: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.01.149.
Meyer, N. A., Vogell, J. U., Becker, M., Broadhurst, J. L., Reid, D. L., and Franzidis, J. P. (2014). “Mineral carbonation of PGM mine tailings for CO2 storage in South Africa: A case study.” Mineral Engineering, Vol. 59, pp. 45–51, DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.10.014.
Morel, F. M. M. and Hering, J. G. (1993). Principles and Applications of Aquatic Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., USA.
Olajire, A. A. (2013). “A review of mineral carbonation technology in sequestration of CO2.” Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, Vol. 109, pp. 364–392, DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2013.03.013.
Said, A., Mattila, H. P., Jarvinen, M., and Zevenhoven, R. (2013). “Production of Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC) from steelmaking slag for fixation of CO2.” Applied Energy, Vol. 112, pp. 765–771, DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.12.042.
Sanna, A., Uibu, M., Caramanna, G., Kuusik, R., and Maroto-Valer, M. M. (2014). “A review of mineral carbonation technologies to sequester CO2.” Chemical Society Reviews, Vol. 43, pp. 8049–8080, DOI: 10.1039/C4CS00035H.
Santos, R. M., Chiang, Y. W., Elsen, J., and Van Gerven, T. (2014). “Distinguishing between carbonate and non-carbonate precipitates from the carbonation of calcium-containing organic acid leachates.” Hydrometallurgy, Vol. 147–148, pp. 90–94, DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.05.001.
Sun, Y., Yao, M.S., Zhang, J. P., and Yang, G. (2011). “Indirect CO2 mineral sequestration by steelmaking slag with NH4Cl as leaching solution.” Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 173, No. 2, pp. 437–445, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Kim, MJ. Calcium Extraction from Paper Sludge Ash using Various Solvents to Store Carbon Dioxide. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 4799–4805 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0819-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0819-z