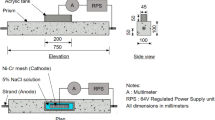
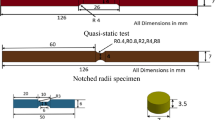
Abstract
A new prestressing strand was recently developed. The objective of this study is to investigate and provide the mechanical properties of the new strand, as these properties are essential in the design and construction of prestressed concrete structures. The experimental program includes a tensile test, a fatigue test, a relaxation test, and a stress corrosion test. In the tensile test, an optimal gripping method was initially determined and the measured ultimate strength was found to be higher the nominal strength of the new strand. The new strand does not exhibit any degradation in its mechanical performance after fatigue loading. Compared to the existing strand with the strength of 1,860 MPa, the new strand also showed equal or enhanced performance in the stress relaxation and the stress corrosion tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM A416 (2012). Standard specification for steel strand, Uncoated Seven-Wire for Prestressed Concrete, USA.
Fib (2005). Acceptance of stay cable systems using prestressing steels, International Federation for Structural Concrete fib, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Godfrey, H. J. (1956). “The physical properties and methods of testing prestressed concrete wire strand.” PCI Journal, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 38–47.
Hill, A. T. Jr. (2006). Material properties of grade 300 and grade 270 prestressing strands and their impact on the design of bridges, MSc Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, April 2006.
ISO 15630-3 (2010). Steel for the reinforcement and prestressing of concrete — Test methods — Part 3: Prestressing steel, The International Organization for Standardization, Switzerland.
JIS G3536 (1999). Japanese industrial standard, Uncoated stress-relieved steel wires and strands for prestressed concrete, Japan.
Kim, J. K., Lee, P. G., and Lee, M. S. (2010). “Development of 2,160 MPa strand and application technology.” KCI Journal, pp. 68–70. (in Korean)
KS B 0802 (2003). Method of tensile test for metallic materials, Korean Standards Association.
KS D 7002 (2011). Uncoated stress-relieved steel wires and strands for prestressed concrete, Korean Standards Association.
Podolney, W. Jr. (1967). “Understanding the steel in prestressing.” PCI Journal, Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 54–64.
EN 10138-3 (2009). Prestressing steels — Part 3: Strand, European Standard, European Committee for Standardization (CEN), Brussels.
Preston, H. K. (1985). “Testing 7-wire strand for prestressed concrete — The state of the art.” PCI Journal, Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 134–155.
Preston, H. K. (1990). “Handling prestressed concrete strand.” PCI Journal, Vol. 35, No. 6, pp. 68–71.
Walsh, K. Q. and Kurama, Y. C. (2010) “Behavior of unbonded posttensioning monostrand anchorage systems under monotonic tensile loading.” PCI Journal, Winter 2010, pp. 97–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.K., Kim, JS. & Kwon, S.H. Mechanical properties of a new prestressing strand with ultimate strength of 2160 MPa. KSCE J Civ Eng 18, 607–615 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-0065-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-0065-6