Abstract
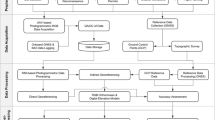
In order to evaluate road safety and manage roads, highway geometric information is necessary. Most highway geometric information is acquired from drawings; however, highway drawings are not always available and even when highway drawings are available, they may not match actual conditions due to subsequent overlay or rehabilitation of the road. To acquire road information for such sections, generally Global Positioning System (GPS) measurement or total station has been used, but this approach is not only highly time-consuming but is also risky, as it involves taking measurements on a road that has moving traffic. Therefore, the Korea Institute of Construction Technology (KICT) developed a survey vehicle, several sensors such as GPS and Inertial Navigation System (INS). The survey vehicle can acquire the positional and attitude data of the vehicle rapidly through the sensors. In this research, a horizontal analysis algorithm, which can analyze highway horizontal geometric information, was developed using the positional and attitude data from the survey vehicle. The algorithm includes the ability to distinguish between tangent and curve sections and can extract highway horizontal geometric information such as transition curve parameters, circular curve radii, center coordinates, and length. The algorithm was applied to the field for verification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AASHTO (2004). A policy on geometric design of highway and streets, 5th Edition, AASHTO, Washington, D.C.
Choi, S. H. (2006). A study on horizontal design criteria using GPS/INS, Master’s Dissertation, Department of Transportation Engineering, University of UST, Korea.
Egbert, D. D. and Fadali, M. S. (1990). Transverse profiler using laserbeam-carried microwave-interferometry, SHRP-IDEA/UFR-90-003.
Hickerson, T. F. (1964). Route location and design, McGraw-Hill, New York, St. Louis, San Francisco, Toronto, London and Sydney.
Ministry of Construction and Transportation. (2000). Standards of the highway structure and facility design, MOCT, Korea.
Sung, J. G., Yun, D. G., and Yoon, C. J. (2003). Development of road safety survey and analysis vehicle: RoSSAV phase 1, Korea Institute of Construction Technology.
Berg, W. D. (1987). Development of a computerized deficiency analysis methodology for the WISDOT highway datalog system, WISDOT, WI.
Yun, D. G. and Sung, J. G. (2007). “Development of cross section data collection and analysis method.” Proc. of the EASTS Vol. 6, Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, pp. 1909–1922.
Yun, D. G. (2008). Development of the highway alignment analysis algorithm using vehicle position and attitude information, PhD Dissertation, Department of Transportation Engineering, Myongji University, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, D.G., Sung, J.G. & Kim, H.S. Development and identification algorithm for horizontal alignment using attitude and positional data of vehicle. KSCE J Civ Eng 17, 797–805 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-013-0279-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-013-0279-z