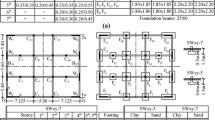
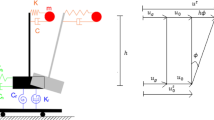
Abstract
Buildings are susceptible to soil structure interaction effects due to the induced changes in the dynamic characteristics of soil during seismic excitation. Because of this detrimental effect, this paper aims at clarifying the soil structure interaction effect on the seismic response of buildings under strong ground motions to provide damage control and enhance the safety level of such buildings. An iterative dynamic analysis was performed using the SAP2000 program to carry out three dimensional time history analysis of nonlinear soil-foundation-building models under a great earthquake ground motion, and the results show that incorporating the soil structure interaction could have a detrimental effect on the building performance and overestimates the top displacements response. On the contrary flexible bases of buildings have a noticeable effect on the structural behavior of buildings by providing pronounced reduction in the internal forces of superstructure response compared to the fixed base buildings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’onofrio, A. and Silvestri, F. (2001). “Influence of microstructure on small strain stiffness and damping of fine graded soils and effects on local site response,” Fourth International Conference on Recent Advances in Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics, San Diego, California.
El Ganainy, H. M., ElNaggar, M. H. (2009). “Efficient 3D non linear Winkler model for shallow foundations.” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, Vol. 29, pp. 1236–1248.
Gazetas, G. and Dobry, R. (1984). “Horizontal response of piles in layered soils.” Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, Vol. 110, No. 1, pp. 20–40.
Kavvadas, M. and Gazetas, G. (1993). “Kinematic seismic response and bending of free-head piles in layered soil.” Geotechnique, Vol. 43, No. 2, pp. 207–222.
Livaoğlu, R. and Doğangün, A. (2006). “Simplified seismic analysis procedures for elevated tanks considering fluid-structure-soil interaction.” Journal of Fluids and Structures, Vol. 22,Issue 3, April, pp. 421–439.
Martin, G. R. and Lam, I. P. (2000). “Earthquake resistant design of foundations: Retrofit of existing foundations proceedings.” GeoEng 2000 Conference, Melbourne, Australia.
Newmark, N. M. and Rosenblueth, E. (1971). “Fundamentals of earthquake engineering.” Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, pp. 93–100.
Ohbta, S. (1982). “Influences of the foundation types and the ground conditions on the natural period of actual buildings.” Transaction of AIJ, pp. 23–31.
SAP2000 (2007). “Nonlinear version11, static and dynamic finite elements analysis of structure.” Computers & Structures, Inc., Berkeley, USA.
Stewart, J. P., Seed, R. B., and Fenves, G. L. (1999). “Seismic soilstructure interaction in buildings. II: Emprical findings.” Journal of Geotechnical and Geo-environmental Engineering, ASCE, Vol. 125, No. 1, pp. 38–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farghaly, A.A., Ahmed, H.H. Contribution of soil-structure interaction to seismic response of buildings. KSCE J Civ Eng 17, 959–971 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-013-0261-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-013-0261-9