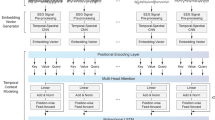
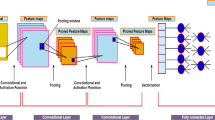
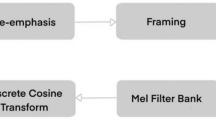
Abstract
Automated sleep stages classification facilitates clinical experts in conducting treatment for sleep disorders, as it is more time-efficient concerning the analysis of whole-night polysomnography (PSG). However, most of the existing research only focused on public databases with channel systems incompatible with the current clinical measurements. To narrow the gap between theoretical models and real clinical practice, we propose a novel deep learning model, by combining the vision transformer with supervised contrastive learning, realizing the efficient sleep stages classification. Experimental results show that the model facilitates an easier classification of multi-channel PSG signals. The mean F1-scores of 79.2% and 76.5% on two public databases outperform the previous studies, showing the model’s great capability, and the performance of the proposed method on the children’s small database also presents a high mean accuracy of 88.6%. Our proposed model is validated not only on the public databases but the provided clinical database to strictly evaluate its clinical usage in practice.
摘要
自动睡眠分期由于其在分析整晚多导睡眠(PSG)信号方面具有高效性, 能够有效支持临床专家对睡眠障碍进行诊疗。然而, 现有的研究主要集中在与实际临床数据不相同的公共数据集上。为了缩小理论模型与实际临床实践之间的差距, 提出了一种新的深度学习模型, 将视觉Transformer与监督对比学习相结合, 实现有效的睡眠阶段分期。实验结果表明, 该模型能够更有效地对多通道PSG信号进行分期。在两个公开的睡眠数据库上该模型平均F1得分分别为79.2%和76.5%, 优于之前的研究, 表明了该模型强大的能力, 在儿童小数据库上的平均准确率也达到了88.6%。提出的模型不仅在公共数据库上进行了验证, 而且在提供的临床数据库上进行了验证, 以严格评估其在临床实践中的使用情况。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
OHAYON M M. Epidemiological overview of sleep disorders in the general population [J]. Sleep Medicine Research, 2011, 2(1): 1–9.
TOBALDINI E, COSTANTINO G, SOLBIATI M, et al. Sleep, sleep deprivation, autonomic nervous system and cardiovascular diseases [J]. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 2017, 74 (Pt B): 321–329.
MAJDE J, KRUEGER J. Links between the innate immune system and sleep [J]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2005, 116(6): 1188–1198.
BARONE D A, CHOKROVERTY S. Neurologic diseases and sleep [J]. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 2017, 12(1): 73–85.
ALI I ABOALAYON K, FAEZIPOUR M, AL-MUHAMMADI W S, et al. Sleep stage classification using EEG signal analysis: A comprehensive survey and new investigation [J]. Entropy, 2016, 18(9): 272.
Berry R, QUAN S, Abreu A, et al. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, Version 2.6 [S]. Darien: American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 2020.
TIAN P, HU J, QI J, et al. A hierarchical classification method for automatic sleep scoring using multi-scale entropy features and proportion information of sleep architecture [J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 37(2): 263–271.
HASSAN A R, BASHAR S K, BHUIYAN M I H. On the classification of sleep states by means of statistical and spectral features from single channel Electroencephalogram [C]//2015 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics. Kochi: IEEE, 2015: 2238–2243.
SEIFPOUR S, NIKNAZAR H, MIKAEILI M, et al. A new automatic sleep staging system based on statistical behavior of local extrema using single channel EEG signal [J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 104: 277–293.
LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning [J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444.
MOUSAVI S, AFGHAH F, ACHARYA U R. SleepEEGNet: Automated sleep stage scoring with sequence to sequence deep learning approach [J]. PloS One, 2019, 14(5): e0216456.
ZHANG H, WANG X, LI H, et al. Auto-annotating sleep stages based on polysomnographic data [J]. Patterns, 2022, 3(1): 100371.
PERSLEV M, JENSEN M H, DARKNER S, et al. U-time: A fully convolutional network for time series segmentation applied to sleep staging [DB/OL]. (2019-10-24) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1910.11162
ZHONG Q H, LEI H B, CHEN Q R, et al. A sleep stage classification algorithm of wearable system based on multiscale residual convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Sensors, 2021, 2021: 8222721.
MICHIELLI N, ACHARYA U R, MOLINARI F. Cascaded LSTM recurrent neural network for automated sleep stage classification using single-channel EEG signals [J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2019, 106: 71–81.
PHAN H, CHEN O Y, TRAN M C, et al. XSleepNet: Multi-view sequential model for automatic sleep staging [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(9): 5903–5915.
JIN H H, YIN H B, HE L N. End-to-end single-channel automatic staging model for sleep EEG signal [J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(3): 242–247 (in Chinese).
JEON Y, KIM S, CHOI H S, et al. Pediatric sleep stage classification using multi-domain hybrid neural networks [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 96495–96505.
SUPRATAK A, DONG H, WU C, et al. DeepSleepNet: A model for automatic sleep stage scoring based on raw single-channel EEG [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2017, 25(11): 1998–2008.
SUPRATAK A, GUO Y K. TinySleepNet: An efficient deep learning model for sleep stage scoring based on raw single-channel EEG [C]//2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society. Montreal: IEEE, 2020: 641–644.
KEMP B, ZWINDERMAN A H, TUK B, et al. Analysis of a sleep-dependent neuronal feedback loop: The slow-wave microcontinuity of the EEG [J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 2000, 47(9): 1185–1194.
GHASSEMI M M, MOODY B E, LEHMAN L W H, et al. You snooze, you win: The PhysioNet/computing in cardiology challenge 2018 [C]//2018 Computing in Cardiology Conference. Maastricht: IEEE, 2018: 1–4.
WOLPERT E A. A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects [J]. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1969, 20(2): 246.
BOLSTAD B M, IRIZARRY R A, ASTRAND M, et al. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias [J]. Bioinformatics, 2003, 19(2): 185–193.
CHEN W X, MCDUFF D. DeepPhys: Video-based physiological measurement using convolutional attention networks [DB/OL]. (2018-05-21) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1805.07888
EOM H, LEE D, HAN S, et al. End-to-end deep learning architecture for continuous blood pressure estimation using attention mechanism [J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(8): 2338.
GUILLOT A, THOREY V. RobustSleepNet: Transfer learning for automated sleep staging at scale [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2021, 29: 1441–1451.
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need [C]//31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. LongBeach: NIPS, 2017: 1–11.
DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale [DB/OL]. (2020-10-22) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition [C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 770–778.
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks [J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90.
KRIZHEVSKY A. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images [D]. Toronto: University of Toronto, 2009.
DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding [DB/OL]. (2018-10-11) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805
BA J L,KIROS J R,HINTON G E. Layer normalization [DB/OL]. (2016-07-21) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450
BHATT D, PATEL C, TALSANIA H, et al. CNN variants for computer vision: History, architecture, application, challenges and future scope [J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(20): 2470.
YIN W P, KANN K, YU M, et al. Comparative study of CNN and RNN for natural language processing [DB/OL]. (2017-02-07) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1702.01923
COHEN M X. Analyzing neural time series data: Theory and practice [M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2014
SAUNSHI N, PLEVRAKIS O, ARORA S, et al. A theoretical analysis of contrastive unsupervised representation learning [C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019: 5628–5637.
KHOSLA P, TETERWAK P, WANG C, et al. Supervised contrastive learning [DB/OL]. (2020-04-23) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2004.11362
SOKOLOVSKY M, GUERRERO F, PAISARNSRISOMSUK S, et al. Deep learning for automated feature discovery and classification of sleep stages [J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2020, 17(6): 1835–1845.
TSINALIS O, MATTHEWS P M, GUO Y K, et al. Automatic sleep stage scoring with single-channel EEG using convolutional neural networks [DB/OL]. (2016-10-05) [2023-05-16]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.01683
PHAN H, ANDREOTTI F, COORAY N, et al. DNN filter bank improves 1-max pooling CNN for single-channel EEG automatic sleep stage classification [C]//2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Honolulu: IEEE, 2018: 453–456.
YOU Y Y, ZHONG X Y, LIU G Z, et al. Automatic sleep stage classification: A light and efficient deep neural network model based on time, frequency and fractional Fourier transform domain features [J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2022, 127: 102279.
FIORILLO L, FAVARO P, FARACI F D. DeepSleepNet-lite: A simplified automatic sleep stage scoring model with uncertainty estimates [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2021, 29: 2076–2085.
KHALILI E, MOHAMMADZADEH ASL B. Automatic sleep stage classification using temporal convolutional neural network and new data augmentation technique from raw single-channel EEG [J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2021, 204: 106063.
BAEK J, LEE C, YU H, et al. Automatic sleep scoring using intrinsic mode based on interpretable deep neural networks [J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 36895–36906.
ZHU T Q, LUO W, YU F. Convolution-and attention-based neural network for automated sleep stage classification [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(11): 4152.
TAUTAN A M, ROSSI A C, DE FRANCISCO R, et al. Automatic Sleep Stage Detection using a Single Channel Frontal EEG [C]//2019 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference. Iasi: IEEE, 2019: 1–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52375254), the Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (No. 21X010301670), the Open Project Program of SJTU-Pinghu Institute of Intelligent Optoelectronics (No. 2022SPIOE104)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Ren, Z., Zhang, T. et al. Transformer-Based Contrastive Learning Method for Automated Sleep Stages Classification. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-024-2734-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-024-2734-z