Abstract
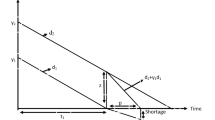
This paper focuses on the last stock problem of substitutive service parts, which is a hot problem in practice. Considering that a firm faces two types of service parts with a certain substitution coefficient, we study the optimization problem of minimizing the total expected cost. Using the non-linear programming theory and method, we find the optimal preserved quantities for the optimization problem. The relation between the product substitution characteristic and the total cost of service parts is analyzed. And an example is given to show the application of our model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teunter R H, Fortuin L. End-of-life service: A case study [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1998, 107(1): 19–34.
Wong H, Cattrysse D, van Oudheusden D. Stocking decisions for repairable spare parts pooling in a multi-hub system [J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2005, 93: 309–317.
Fu Y. Research on service parts logistics operation based on continuous production [J]. Logistics Technology, 2002, 1(22): 28–30.
Kutanoglu E, Lohiya D. Integrated inventory and transportation mode selection: A service parts logistics system [J]. Transportation Research. Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2008, 44(5): 665–683.
Tiemessen H G H, Fleischmann M, van Houtum G J, et al. Dynamic demand fulfillment in spare parts networks with multiple customer classes [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2013, 228(2): 367–380.
Caggiano K E, Jackson P L, Muckstadt J A, et al. Optimizing service parts inventory in a multiechelon, multi-item supply chain with time-based customer service-level agreements [J]. Operations Research, 2007, 55(2): 303–318.
Yang G Y, Dekker R, Gabor A F, et al. Service parts inventory control with lateral transshipment and pipeline stock flexibility [J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2013, 142(2): 278–289.
Caglar D, Li C L, Simchi-Levi D. Two-echelon spare parts inventory system subject to a service constraint [J]. IIE Transactions, 2004, 36(7): 655–666.
Pasternack B A, Drezner Z. Optimal inventory policies for substitutable commodities with stochastic demand [J]. Naval Research Logistics, 1991, 38(2): 221–240.
Stavrulaki E. Inventory decisions for substitutable products with stock-dependent demand [J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2011, 129(1): 65–78.
Rao U S, Swaminathan J M, Zhang J. Multiproduct inventory planning with downward substitution, stochastic demand and setup costs [J]. IIE Transactions, 2004, 36(1): 59–71.
Bassok Y, Anupindi R, Akella R. Single-period multiproduct inventory models with substitution [J]. Operations Research, 1999, 47(4): 632–642.
Frank K C, Zhang R Q, Duenyas I. Optimal policies for inventory systems with priority demand classes [J]. Operations Research, 2003, 51(6): 993–1002.
Xu H, Yao D, Zheng S. Optimal control of replenishment and substitution in an inventory system with non-stationary batch demand [J]. Production and Operations Management, 2011, 20(5), 727–736.
Tan B, Karabati S. Retail inventory management with stock-out based dynamic demand substitution [J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2013, 145(1): 78–87.
Rudi N, Kapur S, Pyke D F. A two-location inventory model with transshipment and local decision making [J]. Management Science, 2001, 47(12): 1668–1680.
Rockafellar R T. Convex analysis [M]. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 1997.
van Slyke R, Wets R. Programming under uncertainty and stochastic optimal control [J]. SIAM Journal on Control, 1966, 4(1): 179–193.
Yang Shi-lin, Peng Liang-xue. Derivative problem on double integral function [J]. Studies in College Mathematics, 2006, 9(2): 40–41 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, L., Li, Qc. Optimal last stock of substitutive service parts. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 20, 752–757 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-015-1686-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-015-1686-8