Abstract
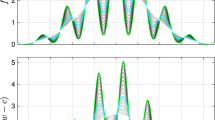
In this paper after analyzing the adaptation process of the proportionate normalized least mean square (PNLMS) algorithm, a statistical model is obtained to describe the convergence process of each adaptive filter coefficient. Inspired by this result, a modified PNLMS algorithm based on precise magnitude estimate is proposed. The simulation results indicate that in contrast to the traditional PNLMS algorithm, the proposed algorithm achieves faster convergence speed in the initial convergence state and lower misalignment in the stead stage with much less computational complexity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benesty J, Gänsler T, Morgan D R, et al. Advances in network and acoustic echo cancellation: Digital signal processing [M]. New York: Springer, 2001.
ITU-T Recommendation G.168, Digital network echo cancellers [S].
Gong Yan-wei, Ji Xiao-jun, Huang Feng-yi, et al. Fast affine projections algorithm for adaptive noise canceling and its application on the fetal electroncardiogram extraction [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Science), 2009, 14(6): 690–694.
Bershad N J, Bist A. Fast coupled adaptation for sparse impulse responses using a partial Haar transform [J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Procesing, 2005, 53(3): 966–976.
Duttweiler D L. Subsampling to estimate delay with application to echo cancelling [J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, 1983, 31(5): 1090–1099.
Ho K C, Blunt S D. Adaptive sparse system identification using wavelets [J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems — II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 2002, 49(10): 656–667.
Ho K C, Blunt S D. Rapid Identification of a sparse impulse response using an adaptive algorithm in the Haar domain [J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Procesing, 2003, 51(3): 628–638.
Duttweiler D L. Proportionate normalized least mean squares adaptation in echo cancelers [J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 2000, 8(5): 508–518.
Gay S L, Lucent B L. An efficient, fast converging adaptive filter for network echo cancellation [C]//Conference Record of the Thirty-Second Asilomar Conference on Signals, System and Computers. Pacific Grove, CA, USA: IEEE, 1998: 394–398.
Nekuii M, Atarodi M. A fast converging algorithm for network echo cancellation [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(4): 427–430.
Deng H, Doroslovacki M. Improving convergence of the PNLMS algorithm for sparse impulse response identification [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2005, 12(3): 181–184.
Deng H, Doroslovacki M. Proportionate adaptive algorithms for network echo cancellation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(5): 1794–1804.
Paleologu H C, Ciochiná S, Benesty J. Variable step-size NLMS algorithm for under-modeling acoustic echo cancellation [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2008, 15(1): 5–8.
Paleologu H C, Benesty J, Gaensler T, et al. Class of double-talk detectors based on the holder inequality [C]//IEEE Internaltional Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing. Prague, The Czech Republic: IEEE, 2011: 425–428.
Gunther J. Learning echo paths during continuous double-talk using semi-blind source separation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 2012, 20(2): 646–660.
Haykin S O. Adaptive filter theory [M]. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, USA: Prentice-Hall, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, Hx., Lai, Xh., Chen, Ld. et al. An improved proportionate normalized least mean square algorithm for sparse impulse response identification. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 18, 742–748 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-013-1460-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-013-1460-8
Key words
- adaptive algorithm
- echo cancellation (EC)
- proportionate normalized least mean square (PNLMS) algorithm
- proportionate step-size
- sparse impulse response