Abstract
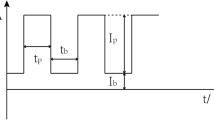
Pulsed tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding is widely used in industry due to its superior properties, so the measurement of arc temperature is important to analyse welding process. Arc image of spectral line in 794.8 nm is captured by high speed camera; both the Abel inversion and the Fowler-Milne method are used to calculate the temperature distribution of the pulsed TIG welding. Characteristic of transient variation in arc intensity and temperature is analyzed. When the change of current happens, intensity and temperature of arc jump as well, it costs several milliseconds. The further the axial position from the tungsten is, the greater the intensity jumps, and the smaller the temperature changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haddad G N, Farmer A J D. Temperature determinations in a free-burning arc. I. Experimental techniques and results in argon [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1984, 17(6): 1189–1196.
Olsen H N. Thermal and electrical properties of an argon plasma [J]. Physics of Fluids, 1959, 2(6): 614–623.
Sawato H, Tashiro S, Nakata K, et al. Measurement of dynamical variation in two-dimensional temperature distribution of TIG pulsed-arcs [J]. Transactions of JWRI, 2010, 39(2): 193–194.
Maouboub E, Coitout H, Parizet M J. Excitation temperature measurements in an argon-CO2 thermal plasma [J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 1999, 27(5): 1469–1475.
Thotnton M F. Spectroscopic determination of temperature distributions for a TIG arc [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1993, 26(9): 1432–1439.
Gu Xiao-yan. Study on arc plasma radiation and its application on welding process inspection [D]. Taiyuan, China: School of Material Science and Engineering, North University of China, 2009 (in Chinese).
Ma S, Gao H, Wu L. Spatial spectroscopic diagnostics of arc plasmas by monochromatic imaging [J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2008, 36(4): 1054–1055.
Ma S, Gao H, Wu L. Modified Fowler-Milne method for the spectroscopic determination of thermal plasma temperature without the measurement of continuum radiation [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2011, 82(1): 013104.
Ma S, Gao H, Wu L. Time resolved characterization of a free-burning argon arc after ignition by optical emission spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 110(2): 026102.
Ma S, Gao H, Zheng S, et al. Spectroscopic measurement of temperatures in pulsed TIG welding arcs [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2011, 44(40): 405202.
Zheng Sen-mu. Spectroscopic diagnosis of pulsed GTAWarc based on image method [D]. Harbin, China: School of Material Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51275299)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Hua, Xm., Xiao, X. et al. Analysis of arc physical property of pulsed tungsten inert gas welding based on Fowler-Milne method. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 18, 343–347 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-013-1404-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-013-1404-3