Abstract
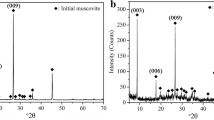
Electrolytic manganese residue (EMR) is generated from electrolytic manganese metal (EMM) industry, and its disposal is currently a serious problem in China. The EMR were calcined in the interval 100–900°C to enhance their pozzolanic activity and characterized by the differential thermal analysis-thermogravimetry (TGDTA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), infra-red (IR) and chemical analysis techniques with the aim to correlate phase transitions and structural features with the pozzolanic activity of calcined EMR. From the phase analysis and compressive strength results, it is found that the EMR calcined within 700–800°C had the best pozzolanic activity due to the decomposition of poorly-crystallized CaSO4 under the reducing ambient created by the decomposition of (NH4)2SO4. The appearance of reactive CaO mainly contributes to the good pozzolanic activity of EMR calcined within 700–800°C. The crystallinity of Mn3O4 increases leading an unfavourable effect on the pozzolanic behaviour of EMR calcined at 900°C. The developed pozzolanic material containing 30% (mass fraction) EMR possesses compressive strength properties at a level similar to 42.5# normal Portland cement, in the range of 41.5–50.5MPa. Besides, leaching results show that EMR blend cement pastes have excellent effect on the solidification of heavy metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan Zhu-zhong, Mei Guang-gui, Li Wei-jian, et al. Metallurgy of manganese [M]. Changsha, China: Press of Central South University of Technology, 2004 (in Chinese).
Liu Ting-jun, Tan Zhong-jian, Liao Sheng-qun. An analysis of trend of EMM industry [J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2007, 24(1): 9–12 (in Chinese).
Zhou Liu-xia. The review and prospects of 50 years in EMM industry of China [J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2010, 28(1): 1–6 (in Chinese).
Duan Ning, Wang Fan, Zhou Chang-bo, et al. Analysis of pollution materials generated from electrolytic manganese industries in China [J]. Resource Conservation Recycling, 2010, 54: 506–511.
Yao Jun, Wu Wen-xue, Yang Xiao-duan, et al. The pollution from the electro-manganese plant in Wan Rong Jiang river [J]. Journal of Jishou University, 1999, 20(3): 74–77 (in Chinese).
Qian Jue-shi, Hou Peng-kun, Wang Zhi, et al. Properties of electrolytic manganese slag used as building materials [J]. Material Review, 2009, 23(5): 59–61 (in Chinese).
Qiao Dun, Qian Jue-shi, Wang Qin-zhen, et al. Utilization of sulfate-rich solid wastes in rural road construction in the three gorges reservoir [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54: 1368–1376.
GB/11906-89, Water quality determination of manganese -- Potassium periodate spectrophotometry method [S] (in Chinese).
GB/T17671-1999, Test method for cements -- Determination of strength [S] (in Chinese).
HJ/557-2010, Test method standard for leaching toxicity of solid wastes -- Horizontal vibration extraction procedure [S] (in Chinese).
Zhang Qiang, Peng Bing, Chai Li-yuan, et al. Study on characteristics of calcium sulfate in electrolytic manganese residue [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2010, 30(5): 70–73 (in Chinese).
Wang Zhi, Sun Jun, Qian Jue-shi, et al. Study on sulfate of electrolytic manganese residue [J]. Material Review, 2010, 24(5): 61–64 (in Chinese).
Division of Inorganic Chemistry of Dalian University of Technology. Inorganic chemistry [M]. Beijing, China: Higher Education Press, 2001 (in Chinese).
Liu Ke-wei, Chen Tian-lang. Studies on the thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate [J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2002, 14(6): 737–738 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51104008 and 51034008), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 20100480202), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20100006120010) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. FRF-TP-12-026A)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Xm., Li, Y., Zhang, Ll. et al. Phase transitions relating to the pozzolanic activity of electrolytic manganese residue during calcination. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 18, 105–110 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-013-1372-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-013-1372-7