Abstract
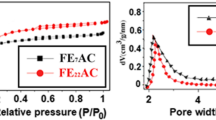
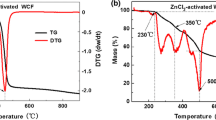
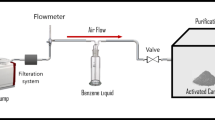
A new type of benzene adsorption material was prepared by using the airtight heat treatment method. This method can directly transform the organic impurities of the activated alumina waste into carbon with adsorption capability. The microstructure and carbon content of materials were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), BET (Brunauer Emmett Teller) surface area analysis and elemental analysis. The influences of heat treatment temperature on the properties of the composite materials were discussed. The benzene adsorption capability of the material was investigated. The experimental results show that the optimal heat treatment process condition is airtight heating at 400°C for 2 h. The resulting sample has carbon mass fraction of 3.57%, specific surface area of 234.70m2/g, pore volume of 0.41m3/g, and average pore size of 6.59 nm. The samples show excellent benzene adsorption capability with an adsorption rate of 21.80%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan Ya-nan, Li Feng, Yi Xiao-dong, et al. A novel method for preparation of activated alumina [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2008, 29(10): 975–978 (in Chinese).
Chen Y Q, Wu R P, Ye X F. Structural characterization and property study on the activated aluminaactivated carbon composite material [J]. Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry, 2012, 31(3): 315–320.
Xu Zhi-bin, Kong Xue-jun, Zhao An-yang. Preliminary studying of recycling aluminum from waste catalyst [J]. Journal of Anqing Teachers College: Natual Science, 2002, 10(1): 8 (in Chinese).
Zheng Yun-hong, Ruan Yu-zhong, Yu Yan, et al. Research of microstructures of actived almina regenerated by hydrogen nitrate dipping method [J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic, 2007, 26(4): 821–825 (in Chinese).
Tchepel O, Penedo A, Gomes M. Assessment of population exposure to air pollution by benzene [J]. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 2007, 210(3): 407–410.
Skov H, Hansen A B, Lorenzen G, et al. Benzene exposure and the effect of traffic pollution in copenhagen, Denmark [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35: 2463–2471.
Lou Shu-li, Zhang Hai-jun. Harm and management of indoor air pollution [J]. Chinese Journal of Radiological Health, 2007, 16(3): 330–331 (in Chinese).
Li Zhi-lin, Ma Xiang. Analysis of the current situation of benzene pollution in interior air and countermeasures [J]. Shanxi Scinece and Technology, 2007(4): 109–110 (in Chinese).
Li Yong-xiang, Liu Tian-sheng, Gao Jian-feng. Influence of baking conditions on preparing γ-Al2O3 [J]. Journal of North China Institute Technology, 2004, 25(4): 277–280 (in Chinese).
Gregg S J, Sing K S W. Adsorption surface area and porosity [M]. Beijing: Beijing Chemical Industry Press, 1989 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the Special Fund for 2010 Petty Invention and Petty Creation of Fujian Provincial Development and Reform Commission (No. MFGT[2010]1093), and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2011J01291)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin-feng, P., Wu, Rp. & Chen, Xj. Preparation of benzene adsorption materials using waste activated alumina. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 17, 373–376 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-012-1290-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-012-1290-0