Abstract
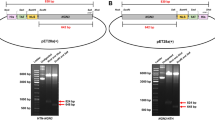
Renalase is a secreted amine oxidase that metabolizes catecholamines. It has been proposed to modulate blood pressure and heart rate and its downregulation might result in hypertension. Despite its potential relevance for human health, the biochemical characterization of renalase is still scarce. The aim of this study is to synthesize the human renalase eukaryotic protein by genetic engineering. The human renalase gene was amplified by polymerase chian reaction (PCR). After digestion by BamH I and Xho I enzymes, the DNA fragments were cloned into the transfer vector, pFastBacHTb-Fc, to generate the pFastBacHTb-renalase expression vector. The ligation products were transformed into E. coli DH10Bac to obtain recombinant transposon rBacmid-renalase. The recombinant transposon was further transferred into insect high-V cells, and the recombinant human renalase eukaryotic protein was expressed successfully.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu J, Li G, Wang P, et al. Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure [J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2005, 115(5): 1275–1280.
Xu J, Desir G V. Renalase, a new renal hormone: Its role in health and disease [J]. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 2007,16(4): 373–378.
Paulis L, Unger T. Novel therapeutic targets for hypertension [J]. Nature Reviews of Cardiology, 2010, 7(18): 431–441
Li G, Xu J, Wang P, et al. Catecholamines regulate the activity, secretion, and synthesis of renalase [J]. Circulation, 2008. 117(10): 1277–1282.
Hennebry S C, Eikelis N, Socratous F, et al. Renalase, a novel soluble FAD-dependent protein, is synthesized in the brain and peripheral nerves [J]. Molecular Psychiatry, 2010, 15(3): 234–236.
Desir G V. Regulation of blood pressure and cardiovascular function by renalase [J]. Kidney International, 2009, 76(4): 366–370.
Desir G V. Renalase deficiency in chronic kidney disease, and its contribution to hypertension and cardiovascular disease [J]. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 2008, 17(2): 181–185.
Wang J, Qi S, Cheng W, et al. Identification, expression and tissue distribution of a renalase homologue from mouse [J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2008, 35(4): 613–620.
Zhao Q, Fan Z, He J, et al. Renalase gene is a novel susceptibility gene for essential hypertension: A two-stage association study in northern Han Chinese population [J]. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2007, 85(8): 877–885.
Go A S, Chertow G M, McCulloch C E, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization [J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2004, 351(13): 1296–1305.
Klein I H, Ligtenberg G, Neumann J, et al. Sympathetic nerve activity is inappropriately increased in chronic renal disease [J]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 2003, 14(12): 3239–3244.
Wang F, Wang N S, Xing T, et al. The cloning and expression of renalase and the preparation of its monoclonal antibody [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Science.), 2009, 14(3): 376–379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the Natural Scientific Research Project of Shanghai (No. 05ZR14086) and the Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (No. 2008Y034)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Wang, Ns. & Xing, T. Construction of eukaryotic recombinant vector of renalase and its expression as a eukaryotic protein. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 15, 637–640 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-010-1061-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-010-1061-8