Abstract
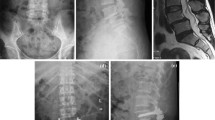
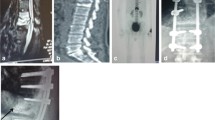
To evaluate the clinical outcome, effectiveness and safety of the surgical management of traumatic lumbar spondylolisthesis with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) with short segmental instrumentation fixation. A retrospective review of a consecutive series of 24 patients with traumatic lumbar spondylolisthesis treated with TLIF procedure was carried out. Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring was used to confirm the peripheral neural function intact during the reduction of the spondylolisthesis. Preoperative clinical and radiographic evaluation of all cases were originally collected prospectively. Data regarding blood loss, operative time, duration of hospital stay, radiographic fusion, instrumentation failure and clinical result were collected and observed at regular follow-up periods. All patients were engaged in high-energy accidents in the lower back and 16 patients had concomitant injuries. The mean operative time was 124 min, mean blood loss was 350 mL, and mean hospital stay was 6.5 days. There were no complications such as incision infection, cerebrospinal fluide (CSF) leakage and nerve root injury and so on. All patients demonstrated a solid lumbar interbody fusion within 4 months, and no evidence of spondylolisthesis correction loss, instrumentation failure and loosing. They all were completely asymptomatic, with normal neurologic findings, and had resumed their previous level of physical activities on the final follow-up. Meticulous clinical examination and careful imaging assessment could assist an early diagonosis in cases of traumatic lumbar spondylolisthesis. Performing open reduction and the TLIF procedure as soon as possible could restore segmental stability and painless function. The TLIF procedure was a safe, effective technique to treat traumatic lumbar spondylolisthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilchinscky M E. Traumatic lumbosacral dislocation: A case report and review of the literature [J]. Orthopedics, 1987, 10(9): 1271–1274.
Davis A A, Carragee E J. Bilateral facet dislocation at the lumbosacral joint: A report of a case and review of literature [J]. Spine, 1993, 18(16): 2540–2544.
Beguiristain J, Schweitzer D, Mora G, et al. Traumatic lumbosacral dislocation in a 5-year-old boy with eight years follow-up [J]. Spine, 1995, 20(3): 362–366.
Denis F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries [J]. Spine, 1983, 8(8): 817–831.
Denis F. Spinal stability as defined by the threecolumn spine concept in acute spinal trauma [J]. Clin Orthop, 1984, 189: 65–76.
Aihara T, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, et al. Fracture-dislocation of the fifth lumbar vertebra: A new classification [J]. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 1998, 80(5): 840–845.
Veras del Monte, Luis M, Bago J. Traumatic lumbosacral dislocation [J]. Spine, 2000, 25(6): 756–759.
Verlaan J J, Oner F C, Dhert W J A, et al. Traumatic lumbosacral dislocation: Case report [J]. Spine, 2001, 26(17): 1942–1944.
Barsa P, Buchvald P, Suchomel P, et al. Traumatic spondylolisthesis of L5-S1 [J]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech, 2003, 70(2): 121–125.
DiPaola C P, Molinari R W. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2008, 16(3): 130–139.
Ekman P, Möller H, Tullberg T, et al. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis [J]. Spine, 2007, 32(20): 2178–2183.
Skowronski J, Wojnar J, Bielecki M. Interbody fusion and transpedicular fixation in the treatment of spondylolisthesis [J]. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil, 2007, 9(2): 149–155.
Jacobs W C, Vreeling A, de Kleuver M. Fusion for low-grade adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: A systematic review of the literature [J]. European Spine Journal, 2006, 15(4): 391–402.
Roaf R. A study of the mechanics of spinal injuries [J]. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 1960, 42(4): 810–823.
Steinitz D K, Alexander D I, Leighton R K, et al. Late displacement of a fracture and dislocation at the lumbosacral junction: A case study [J]. Spine, 1997, 22(9): 1024–1027.
Herrin L D, Williams R C. Fracture dislocation of the lumbosacral spine: Report of a case and review of the literature [J]. Clin Orthop, 1984, 186: 205–211.
Das de S, McCreath S W. Lumbosacral fracturedislocations: A report of four cases [J]. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 1981, 63(1): 58–60.
Sears W. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lytic spondylolisthesis: Restoration of sagittal balance using insert-and-rotate interbody spacers [J]. Spine Journal, 2005, 5(2): 161–169.
Molinari R W, Sloboda J F, Arrington E C. Low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis treated with instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion in U.S. servicemen [J]. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques, 2005, 18(Sup): S24–S29.
Muggleton J M, Kondracki A R. Spinal fusion for lumbar instability: Does it have a scientific basis? [J]. Journal of Spinal Disorders, 2000, 13(3): 200–204.
La Rosa G, Conti A, Cacciola F, et al. Pedicle screw fixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis: Does posterior lumbar interbody fusion improve outcome over posterolateral fusion? [J]. Journal of Neurosurg, 2003, 99(Sup): 143–150.
Hosono N, Namekata M, Makino T, et al. Perioperative complications of primary posterior lumbar interbody fusion for nonisthmic spondylolisthesis: Analysis of risk factors [J]. Journal of Neurosurg: Spine, 2008, 9(5): 403–407.
Hackenberg L, Halm H, Bullmann V, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: A safe technique with satisfactory three to five year results [J]. European Spine Journal, 2005, 14(6): 551–558.
Yan D L, Pei F X, Li J, et al. Comparative study of PILF and TLIF treatment in adult degenerative spondylolisthesis [J]. European Spine Journal, 2008, 17(10): 1311–1316.
el-Masry M A, Khayal H, Salah H. Unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) using a single cage for treatment of low grade lytic spondylolisthesis [J]. Acta Orthop Belg, 2008, 74(5): 667–671.
Dhall S S, Wang M Y, Mummaneni P V. Clinical and radiographic comparison of mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in 42 patients with long-term follow-up [J]. Journal of Neurosurg: Spine, 2008, 9(6): 560–565.
Lee D Y, Jung T G, Lee S H. Single-level instrumented mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in elderly patients [J]. Journal of Neurosurg: Spine, 2008, 9(2): 137–144.
Rodriguez-Olaverri J C, Zimick N C, Merola A, et al. Comparing the clinical and radiological outcomes of pedicular transvertebral screw fixation of the lumbosacral spine in spondylolisthesis versus unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) with posterior fixation using anterior cages [J]. Spine, 2008, 33(18): 1977–1981.
Lauber S, Schulte T L, Liljenqvist U, et al. Clinical and radiologic 2–4-year results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2 [J]. Spine, 2006, 31(15): 1693–1698.
Ebraheim N A, Savolaine E R, Shapiro P, et al. Unilateral lumbosacral facet joint dislocation associated with vertical shear sacral fracture [J]. Journal of Orthopqedic Trauma, 1991, 5(4): 498–503.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Jg., Zeng, Bf., Kong, Wq. et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for traumatic lumbar spondylolisthesis. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 15, 626–631 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-010-1059-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-010-1059-2