Abstract
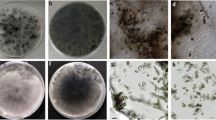
The native pathogens of waterhyacinth in China, were studied and compared on pathogenicity by Koch’s postulate. Nine pathogenic fungi, YBH, YBB, YB, YYX, YY, YBA1, YBA2, YBA3 and YYB12, were isolated from diseased waterhyacinth plants, and collected from Zhejiang province and Shanghai. According to cultural characteristics, the nine isolates were preliminarily identified. Isolates YBH and YBB were Collectotrichum sp.; YB, YYX and YY were placed in fungi imperfecti; the isolates YBA1, YBA2, YBA3 and YYB12 were Alternaria sp. The isolate YBH was the highly virulent with a disease index (DI) of 65.28% after one month inoculation. The isolate YBA3 was equily virulent, with the disease index of 67% after 7 day introduction. These two pathogens appear to have the potential as biocontrol agents and they deserve further study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gopal B. Water hyacinth [M]. New York: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1987: 471.
Center T D. Biological control of weeds: Water hyacinth and water lettuce [C]//Pest Management in the Sub Tropics. Biological Control. Hampshire: [s.n.], 1994: 482–521.
Perkins B D. Potential for waterhyacinth management with biological agents [C]//Proceedings Tall Timbers Conference on Ecological Animal Control by Habitat Management. 1972: 53–64.
Charudattan. R. Integrated control of water hyacinth with pathogen, insects, and herbicide [J]. Weed Science, 1986, 34(sl):26–30.
Cordo H A. Recommendations for finding and prioritizing new agents for biocontrol of water hyacinth [C]//Strategies for Water Hyacinth Control. Florida: Fort Lauderdale, 1995: 181–185.
Martinez Jimenez M, Charudattan R. Survey and evaluation of Mexican native fungi for potential biocontrol of water hyacinth [J]. J Aquat Plant Manage, 1998, 36:145–148.
Wei J C. The manual of fungi identification [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and technology Press, 1982.
Zong Z F, Kang Z S.The theory of plant pathology [M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press of China, 2002.
Chu J J, Ding Y, Zhuang Q J. Invasion and control of water hyacinth (eichhornia crassipes) in China [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 2006, 7(8): 623–626.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863) of China (No. 2006AA10A214)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Zhao, N. & Chu, Jj. Nine pathogenic fungi of waterhyacinth isolated in China. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 13, 617–622 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-008-0617-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-008-0617-3