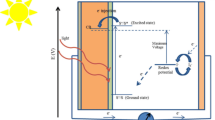
Abstract
Investigation on the mechanism and kinetics of charge transfer at semiconductor/electrolyte interface is significant for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency and developing novel and high-efficiency photovoltaic devices. Scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM), as a powerful analytical technique, has a potential advantage of high spatial and temporal resolution. It has been expanded into a broad range of research fields since the first inception of SECM in 1989 by Bard groups, which includes biological, enzymes, corrosion, energy conversion and storage (such as solar cells, hydrogen and battery). Herein, we review the basic principles and the development of SECM, and chiefly introduce the recent advances of SECM investigation in photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells including solar cells and PEC water splitting. These advances include rapid screening of photocatalysts/photoelectrodes, interfacial reaction kinetics and quantitation of reaction intermediates, which is significant for evaluating the performance, choosing catalysts and developing novel composite photoanodes and high efficiency devices. Finally, we briefly describe the development trends of SECM in energy research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holdren J P. Energy and sustainability. Science, 2007, 315(5813): 737
Lianos P. Review of recent trends in photoelectrocatalytic conversion of solar energy to electricity and hydrogen. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 210: 235–254
Li D, Shi J, Li C. Transition-metal-based electrocatalysts as cocatalysts for photoelectrochemical water splitting: a mini review. Small, 2018, 14(23): 1704179
Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37–38
Klotz D, Grave D A, Dotan H, Rothschild A. Empirical analysis of the photoelectrochemical impedance response of hematite photoanodes for water photo-oxidation. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2018, 9(6): 1466–1472
Wang M, Chen P, Humphry-Baker R, Zakeeruddin S M, Grätzel M. The influence of charge transport and recombination on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. ChemPhysChem, 2009, 10(1): 290–299
Klotz D, Ellis D S, Dotan H, Rothschild A. Empirical in operando analysis of the charge carrier dynamics in hematite photoanodes by PEIS, IMPS and IMVS. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(34): 23438–23457
Tsyganok A, Klotz D, Malviya K D, Rothschild A, Grave D A. Different roles of Fe1–xNixOOH co-catalyst on hematite (a-Fe2O3) photoanodes with different dopants. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(4): 2754–2759
Berera R, van Grondelle R, Kennis J T. Ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy: principles and application to photosynthetic systems. Photosynthesis Research, 2009, 101(2-3): 105–118
Pei G X, Wijten J H J, Weckhuysen B M. Probing the dynamics of photogenerated holes in doped hematite photoanodes for solar water splitting using transient absorption spectroscopy. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(15): 9806–9811
Wang M, Alemu G, Shen Y. Scanning probe microscopy investigation of metal oxides nanocrystalline. In: Current Microscopy Contributions to Advances in Science and Technology, Chapter 3, 2012, 1377–1386
Esposito D V, Baxter J B, John J, Lewis N S, Moffat T P, Ogitsu T, O’Neil G D, Pham T A, Talin A A, Velazquez J M, Wood B C. Methods of photoelectrode characterization with high spatial and temporal resolution. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(10): 2863–2885
Cen J, Wu Q, Liu M, Orlov A. Developing new understanding of photoelectrochemical water splitting via in-situ techniques: a review on recent progress. Green Energy & Environment, 2017, 2(2): 100–111
Miki T, Yanagi H. Scanning probe microscopic characterization of surface-modified n-TiO2 single-crystal electrodes. Langmuir, 1998, 14(12): 3405–3410
Wierzbinski E, Szklarczyk M. Photoelectrochemical and in situ atomic force microscopy studies of films derived from o-methoxyaniline solution on gallium arsenide (100) photoelectrode. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 424(2): 191–200
Toma F M, Cooper J K, Kunzelmann V, McDowell M T, Yu J, Larson D M, Borys N J, Abelyan C, Beeman J W, Yu K M, Yang J, Chen L, Shaner M R, Spurgeon J, Houle F A, Persson K A, Sharp I D. Mechanistic insights into chemical and photochemical transformations of bismuth vanadate photoanodes. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12012
Economou N J, Mubeen S, Buratto S K, McFarland E W. Investigation of arrays of photosynthetically active heterostructures using conductive probe atomic force microscopy. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(6): 3328–3334
Nakamura R, Nakato Y. Primary intermediates of oxygen photoevolution reaction on TiO2 (Rutile) particles, revealed by in situ FTIR absorption and photoluminescence measurements. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(4): 1290–1298
Zandi O, Hamann T W. Determination of photoelectrochemical water oxidation intermediates on haematite electrode surfaces using operando infrared spectroscopy. Nature Chemistry, 2016, 8(8): 778–783
McKelvey K, Nadappuram B P, Actis P, Takahashi Y, Korchev Y E, Matsue T, Robinson C, Unwin P R. Fabrication, characterization, and functionalization of dual carbon electrodes as probes for scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM). Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(15): 7519–7526
Zampardi G, Klink S, Kuznetsov V, Erichsen T, Maljusch A, La Mantia F, Schuhmann W, Ventosa E. Combined AFM/SECM investigation of the solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries. Chemelectrochem, 2015, 2(10): 1607–1611
Takahashi Y, Shevchuk A I, Novak P, Murakami Y, Shiku H, Korchev Y E, Matsue T. Simultaneous noncontact topography and electrochemical imaging by SECM/SICM featuring ion current feedback regulation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(29): 10118–10126
Baranski A, Diakowski P. Application of AC impedance techniques to scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2004, 8(10): 683–692
Mirkin M, Fan F, Bard A. Scanning electrochemical microscopy part 13. Evaluation of the tip shapes of nanometer size microelectrodes. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1992, 328(1-2): 47–62
Bard A, Fan F, Kwak J, Lev O. Scanning electrochemical microscopy: introduction and principles. Analytical Chemistry, 1989, 61(3): 132–138
Engstrom R, Pharr C. Scanning electrochemical microscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 1989, 61(19): 1099A–1104A
Polcari D, Dauphin-Ducharme P, Mauzeroll J. Scanning electrochemical microscopy: a comprehensive review of experimental parameters from 1989 to 2015. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(22): 13234–13278
Rodriguez-López J, Alpuche-Aviles M A, Bard A J. Selective insulation with poly(tetrafluoroethylene) of substrate electrodes for electrochemical background reduction in scanning electrochemical microscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(5): 1813–1818
Rodríguez-López J. Surface interrogation mode of scanning electrochemical microscopy (SI-SECM): an approach to the study of adsorption and (electro)catalysis at electrodes. Electroanalytical Chemistry: A Series of Advances, 2012, 24: 287–341
Zhang B, Xu X, Zhang X, Huang D, Li S, Zhang Y, Zhan F, Deng M, He Y, Chen W, Shen Y, Wang M. Investigation of dye regeneration kinetics in sensitized solar cells by scanning electrochemical microscopy. ChemPhysChem, 2014, 15(6): 1182–1189
Weng Y, Hsiao K. Composition optimization of ZnO-based photocatalyst arrays by scanning electrochemical microscopy and the characterization of efficient photocatalysts. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(8): 3238–3248
Li F, Ciani I, Bertoncello P, Unwin P R, Zhao J J, Bradbury C R, Fermin D J. Scanning electrochemical microscopy of redoxmediated hydrogen evolution catalyzed by two-dimensional assemblies of palladium nanoparticles. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(26): 9686–9694
Zhang B, Yuan H, Zhang X, Huang D, Li S, Wang M, Shen Y. Investigation of regeneration kinetics in quantum-dots-sensitized solar cells with scanning electrochemical microscopy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(23): 20913–20918
Alemu G, Zhang B, Li J, Xu X, Cui J, Shen Y, Wang M. Investigation of dye-regeneration kinetics at dye-sensitized p-type CuCrO2 film/electrolytes interface with scanning electrochemical microscopy. Nano, 2014, 9(5): 1440008
Martin C, Bozic-Weber B, Constable E, Glatzel T, Housecroft C, Wright I. Development of scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) techniques for the optimization of dye sensitized solar cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 119: 86–91
Schmidt I, Plettenberg I, Kimmich D, Ellis H, Witt J, Dosche C, Wittstock G. Spatially resolved analysis of screen printed photoanodes of dye-sensitized solar cells by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 222: 735–746
Shen Y, Träuble M, Wittstock G. Detection of hydrogen peroxide produced during electrochemical oxygen reduction using scanning electrochemical microscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(3): 750–759
Li H, Du M, Mleczko M J, Koh A L, Nishi Y, Pop E, Bard A J, Zheng X. Kinetic study of hydrogen evolution reaction over strained MoS2 with sulfur vacancies using scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138 (15): 5123–5129
Jung C, Sánchez-Sánchez CM, Lin C L, Rodríguez-López J, Bard A J. Electrocatalytic activity of Pd-Co bimetallic mixtures for formic acid oxidation studied by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(16): 7003–7008
Sánchez-Sánchez C M, Rodríguez-López J, Bard A J. Scanning electrochemical microscopy. 60. Quantitative calibration of the SECM substrate generation/tip collection mode and its use for the study of the oxygen reduction mechanism. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(9): 3254–3260
Ventosa E, Schuhmann W. Scanning electrochemical microscopy of Li-ion batteries. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17 (43): 28441–28450
Xu F, Beak B, Jung C. In situ electrochemical studies for Li + ions dissociation from the LiCoO2 electrode by the substrate-generation/tip-collection mode in SECM. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16(1): 305–311
Bülter H, Peters F, Schwenzel J, Wittstock G. Spatiotemporal changes of the solid electrolyte interphase in lithium-ion batteries detected by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Angewandte Chemie, 2014, 53(39): 10531–10535
Sumboja A, Tefashe U, Wittstock G, Lee P S. Investigation of charge transfer kinetics of polyaniline supercapacitor electrodes by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2015, 2(1): 1400154
Zhang Q, Ye Z, Zhu Z, Liu X, Zhang J, Cao F. Separation and kinetic study of iron corrosion in acidic solution via a modified tip generation/substrate collection mode by SECM. Corrosion Science, 2018, 139: 403–409
Lee J, Ye H, Pan S, Bard A J. Screening of photocatalysts by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(19): 7445–7450
Sreekanth N, Phani K L. Selective reduction of CO2 to formate through bicarbonate reduction on metal electrodes: new insights gained from SG/TC mode of SECM. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2014, 50(76): 11143–11146
Rodríguez-López J, Bard A J. Scanning electrochemical microscopy: surface interrogation of adsorbed hydrogen and the open circuit catalytic decomposition of formic acid at platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(14): 5121–5129
Fernández J L, White JM, Sun Y, Tang W, Henkelman G, Bard A J. Characterization and theory of electrocatalysts based on scanning electrochemical microscopy screening methods. Langmuir, 2006, 22 (25): 10426–10431
Jantz D, Leonard K. Characterizing electrocatalysts with scanning electrochemical microscopy. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(22): 7431–7440
Li Y, Ning X, Ma Q, Qin D, Lu X. Recent advances in electrochemistry by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 80: 242–254
Rincón M E, Trujillo M E, Ávalos J, Casillas N. Photoelectrochemical processes at interfaces of nanostructured TiO2/carbon black composites studied by scanning photoelectrochemical microscopy. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2007, 11(9): 1287–1294
Bozic B, Figgemeier E. Scanning electrochemical microscopy under illumination: an elegant tool to directly determine the mobility of charge carriers within dye-sensitized nanostructured semiconductors. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2006, 21 (21): 2268–2270
Tefashe U M, Loewenstein T, Miura H, Schlettwein D, Wittstock G. Scanning electrochemical microscope studies of dye regeneration in indoline (D149)-sensitized ZnO photoelectrochemical cells. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2010, 650(1): 24–30
Tefashe U M, Rudolph M, Miura H, Schlettwein D, Wittstock G. Photovoltaic characteristics and dye regeneration kinetics in D149-sensitized ZnO with varied dye loading and film thickness. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2012, 14(20): 7533–7542
Tefashe U M, Nonomura K, Vlachopoulos N, Hagfeldt A, Wittstock G. Effect of cationon dye regeneration kinetics of N719-sensitized TiO2 films in acetonitrile-based and ionic-liquid-based electrolytes investigated by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(6): 4316–4323
Shen Y, Nonomura K, Schlettwein D, Zhao C, Wittstock G. Photoelectrochemical kinetics of eosin y-sensitized zinc oxide films investigated by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2006, 12(22): 5832–5839
Shen Y, Tefashe U M, Nonomura K, Loewenstein T, Schlettwein D, Wittstock G. Photoelectrochemical kinetics of Eosin Y-sensitized zinc oxide films investigated by scanning electrochemical microscopy under illumination with different LED. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 55(2): 458–464
Xu X, Zhang B, Cui J, Xiong D, Shen Y, Chen W, Sun L, Cheng Y, Wang M. Efficient p-type dye-sensitized solar cells based on disulfide/thiolate electrolytes. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(17): 7963–7969
Kojima A, Teshima K, Shirai Y, Miyasaka T. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(17): 6050–6051
Hsu H, Ji L, Du M, Zhao J, Yu E, Bard A. Optimization of PbI2/MAPbI3 perovskite composites by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(35): 19890–19895
Alemu G, Li J, Cui J, Xu X, Zhang B, Cao K, Shen Y, Cheng Y, Wang M. Investigation on regeneration kinetics at perovskite/oxide interface with scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2015, 3(17): 9216–9222
Jang J, Lee J, Ye H, Fan F, Bard A. Rapid screening of effective dopants for Fe2O3 photocatalysts with scanning electrochemical microscopy and investigation of their photoelectrochemical properties. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(16): 6719–6724
Currao A. Photoelectrochemical water splitting. Chimia, 2007, 61 (12): 815–819
Acar C, Dincer I, Zamfirescu C. A review on selected heterogeneous photocatalysts for hydrogen production. International Journal of Energy Research, 2014, 38(15): 1903–1920
Acar C, Dincer I. A review and evaluation of photoelectrode coating materials and methods for photoelectrochemical hydrogen production. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(19): 7950–7959
Shi Q, Murcia-López S, Tang P, Flox C, Morante J, Bian Z, Wang H, Andreu T. Role of tungsten doping on the surface states in BiVO4 photoanodes for water oxidation: tuning the electron trapping process. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(4): 3331–3342
Yang Y, Niu S, Han D, Liu T, Wang G, Li Y. Progress in developing metal oxide nanomaterials for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(19): 1700555
Zhang X, Zhang B, Zuo Z, Wang M, Shen Y. N/Si co-doped oriented single crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorods for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2015, 3(18): 10020–10025
Zhang X, Yang H, Zhang B, Shen Y, Wang M. BiOI-TiO2 nanocomposites for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2016, 3(1): 1500273
Harrison S, Hayne M. Photoelectrolysis using type-II semiconductor heterojunctions. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 11638
Wang H, Zhang L, Chen Z, Hu J, Li S, Wang Z, Liu J, Wang X. Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(15): 5234–5244
Yang J, Wang D, Han H, Li C. Roles of cocatalysts in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(8): 1900–1909
Zhang X, Zhang B, Liu S, Kang H, Kong W, Zhang S, Shen Y, Yang B. RGO modified Ni doped FeOOH for enhanced electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 436: 974–980
Zhang X, Zhang B, Luo Y, Lv X, Shen Y. Phosphate modified N/Si co-doped rutile TiO2 nanorods for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 391: 288–294
Zhang X, Zhang B, Huang D, Yuan H, Wang M, Shen Y. TiO2 nanotubes modified with electrochemically reduced graphene oxide for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Carbon, 2014, 80: 591–598
Shi W, Zhang X, Brillet J, Huang D, Li M, Wang M, Shen Y. Significant enhancement of the photoelectrochemical activity of WO3 nanoflakes by carbon quantum dots decoration. Carbon, 2016, 105: 387–393
Shi W, Zhang X, Li S, Zhang B, Wang M, Shen Y. Carbon coated Cu2O nanowires for photoelectrochemical water splitting with enhanced activity. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 358: 404–411
Zhang X, Zhang B, Cao K, Brillet J, Chen J, Wang M, Shen Y. A perovskite solar cell-TiO2@BiVO4 photoelectrochemical system for direct solar water splitting. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2015, 3(43): 21630–21636
Chen Y S, Manser J S, Kamat P V. All solution-processed lead halide perovskite-BiVO4 tandem assembly for photolytic solar fuels production. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137 (2): 974–981
Brillet J, Yum J, Cornuz M, Hisatomi T, Solarska R, Augustynski J, Grätzel M, Sivula K. Highly efficient water splitting by a dualabsorber tandem cell. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(12): 824–828
Park H, Kweon K, Ye H, Paek E, Hwang G, Bard A. Factors in the metal doping of BiVO4 for improved photoelectrocatalytic activity as studied by scanning electrochemical microscopy and firstprinciples density-functional calculation. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(36): 17870–17879
Leonard K, Nam K, Lee H, Kang S, Park H, Bard A. ZnWO4/WO3 composite for improving photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(31): 15901–15910
Ye H, Park H, Bard A. Screening of electrocatalysts for photoelectrochemical water oxidation on W-doped BiVO4 photocatalysts by scanning electrochemic al microscopy. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(25): 12464–12470
Ye H, Lee J, Jang J, Bard A. Rapid screening of BiVO4-based photocatalysts by scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) and studies of their photoelectrochemical properties. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(31): 13322–13328
Lu X, Hu Y, He H. Electron transfer kinetics at interfaces using secm (scanning electrochemical microscopy). In: Sur U K, ed. Recent Trend in Electrochemical Science and Technology. Rijeka: In Tech, 2012, 127–156
Ahn H S, Bard A J. Surface interrogation scanning electrochemical microscopy of Ni1–xFexOOH (0<x<0.27) oxygen evolving catalyst: kinetics of the “fast” iron sites. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(1): 313–318
Zhang B, Zhang X, Xiao X, Shen Y. Photoelectrochemical water splitting system–a study of interfacial charge transfer with scanning electrochemical microscopy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(3): 1606–1614
Rastgar S, Wittstock G. Characterization of photoactivity of nanostructured BiVO4 at polarized liquid-liquid interfaces by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(46): 25941–25948
Ahn H S, Bard A J. Surface interrogation of CoPi water oxidation catalyst by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(2): 612–615
Zigah D, Rodríguez-López J, Bard A J. Quantification of photoelectrogenerated hydroxyl radical on TiO2 by surface interrogation scanning electrochemical microscopy. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2012, 14(37): 12764–12772
Park H, Leonard K, Bard A. Surface interrogation scanning electrochemical microscopy (SI-SECM) of photoelectrochemistry at a W/Mo-BiVO4 semiconductor electrode: quantification of hydroxyl radicals during water oxidation. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(23): 12093–12102
Cho S, Park H, Lee H, Nam K, Bard A. Metal doping of BiVO4 by composite electrodeposition with improved photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(44): 23048–23056
Krumov M R, Simpson B H, Counihan M J, Rodríguez-López J. In situ quantification of surface intermediates and correlation to discharge products on hematite photoanodes using a combined scanning electrochemical microscopy approach. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(5): 3050–3057
Kim J Y, Ahn H S, Bard A J. Surface interrogation scanning electrochemical microscopy for a photoelectrochemical reaction: water oxidation on a hematite surface. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(5): 3045–3049
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51602120), Natural Science Foundation of Education Department of Henan Province (No. 17A430023), and the opening project of Henan Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanocomposites and Applications (No. hkd20170106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaofan Zhang received her Ph.D. degree in Photoelectric Information Engineering from Huazhong University of Science and Technology in 2015. She joined Henan Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanocomposite and Applications and Institute of Nanostructured Functional Materials at Huanghe Science and Technology College in 2015. Now she is a lecturer, working in School of Environment and Civil Engineering of Dongguan University of Technology from 2018. Her research interests are related to energy conversion, and focus on solar water splitting, dynamics investigation of photoelectrochemical interfacial reaction and electrocatalysis.
Man Liu received her M.Sc degree from the College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering at Zhengzhou University in 2013. Currently, she works on Henan Provincial Key Laboratory of Nano-composite and Applications of Huanghe Science and Technology College. Her research interests mainly focus on analysis of materials by means of NMR spectrometer, mass spectrograph, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy(SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Weiqian Kong obtained her M.Sc degree from Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM) in Soochow University in 2015. Then she works as a teaching assistant until now in Henan Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanocomposite and Applications, Institute of Nanostructured Functional Materials of Huanghe Science and Technology College. Her research interests focus on carbon nanomaterials and their applications in detection and catalysis, photoelectrochemical water splitting, energy and environmental applications.
Hongbo Fan received his B.Sc. degree from Henan Normal University in 1983, his M.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees from Huazhong University of Science and Technology in 1996 and 2003, respectively. He worked as a postdoctoral research fellow at South China University of Technology from 2003 to 2005. Prof. Fan joined Dongguan University of Technology in 2005. Currently, he is the dean of School of Environment and Civil Engineering and the director of Dongguan Clean Production Technology Center. His research interests are related to energy storage materials, intelligence materials, as well as energy efficiency and environmental protection, and so on.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liu, M., Kong, W. et al. Recent advances in solar cells and photo-electrochemical water splitting by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Front. Optoelectron. 11, 333–347 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-018-0852-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-018-0852-7