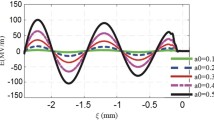
Abstract
The past two decades have seen an exponential growth of interest in one of the least explored region of the electromagnetic spectrum, the terahertz (THz) frequency band, ranging from to 0.1 to 10 THz. Once only the realm of astrophysicists studying the background radiation of the universe, THz waves have become little by little relevant in the most diverse fields, such as medical imaging, industrial inspection, remote sensing, fundamental science, and so on. Remarkably, THz wave radiation can be generated and detected by using ambient air as the source and the sensor. This is accomplished by creating plasma under the illumination of intense femtosecond laser fields. The integration of such a plasma source and sensor in THz time-domain techniques allows spectral measurements covering the whole THz gap (0.1 to 10 THz), further increasing the impact of this scientific tool in the study of the four states of matter.
In this review, the authors introduce a new paradigm for implementing THz plasma techniques. Specifically, we replaced the use of elongated plasmas, ranging from few mm to several cm, with sub-mm plasmas, which will be referred to as microplasmas, obtained by focusing ultrafast laser pulses with high numerical aperture optics (NA from 0.1 to 0.9).
The experimental study of the THz emission and detection from laser-induced plasmas of submillimeter size are presented. Regarding the microplasma source, one of the interesting phenomena is that the main direction of THz wave emission is almost orthogonal to the laser propagation direction, unlike that of elongated plasmas. Perhaps the most important achievement is the demonstration that laser pulse energies lower than 1 mJ are sufficient to generate measurable THz pulses from ambient air, thus reducing the required laser energy requirement of two orders of magnitude compared to the state of art. This significant decrease in the required laser energy will make plasma-based THz techniques more accessible to the scientific community, as well as opening new potential industrial applications.
Finally, experimental observations of THz radiation detection with microplasmas are also presented. As fully coherent detection was not achieved in this work, the results presented herein are to be considered a first step to understand the peculiarities involved in using the microplasma as a THz sensor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nuss M C, Auston D H, Capasso F. Direct subpicosecond measurement of carrier mobility of photoexcited electrons in gallium arsenide. Physical Review Letters, 1987, 58(22): 2355–2358
Exter M, Fattinger C, Grischkowsky D. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of water vapor. Optics Letters, 1989, 14(20): 1128–1130
Kolner B H, Buckles R A, Conklin P M, Scott R P. Plasma characterization with terahertz pulses. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2008, 14(2): 505–512
Jepsen P U, Cooke D G, Koch M. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging-modern techniques and applications. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2011, 5(1): 124–166
Ulbricht R, Hendry E, Shan J, Heinz T F, Bonn M. Carrier dynamics in semiconductors studied with time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2011, 83(2): 543–586
McIntosh A I, Yang B, Goldup S M, Watkinson M, Donnan R S. Terahertz spectroscopy: a powerful new tool for the chemical sciences? Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(6): 2072–2082
Kübler C, Ehrke H, Huber R, Lopez R, Halabica A, Haglund R F Jr, Leitenstorfer A. Coherent structural dynamics and electronic correlations during an ultrafast insulator-to-metal phase transition in VO2. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(11): 116401
Leahy-Hoppa M R, Fitch M J, Zheng X, Hayden L M, Osiander R. Wideband terahertz spectroscopy of explosives. Chemical Physics Letters, 2007, 434(4-6): 227–230
Davies A G, Burnett A D, Fan W, Linfield E H, Cunningham J E. Terahertz spectroscopy of explosives and drugs. Materials Today, 2008, 11(3): 18–26
Dai J, Xie X, Zhang X C. Detection of broadband terahertz waves with a laser-induced plasma in gases. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(10): 103903
Karpowicz N, Dai J, Lu X, Chen Y, Yamaguchi M, Zhao H, Zhang X C, Zhang L, Zhang C, Price-Gallagher M, Fletcher C, Mamer O, Lesimple A, Johnson K. Coherent heterodyne time-domain spectrometry covering the entire ‘terahertz gap’. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(1): 011131
Liu J, Zhang X C. Birefringence and absorption coefficients of alpha barium borate in terahertz range. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106(2): 023107
Zalkovskij M, Zoffmann Bisgaard C, Novitsky A, Malureanu R, Savastru D, Popescu A, Uhd Jepsen P, Lavrinenko A V. Ultrabroadband terahertz spectroscopy of chalcogenide glasses. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(3): 031901
D’Angelo F, Mics Z, Bonn M, Turchinovich D. Ultra-broadband THz time-domain spectroscopy of common polymers using THz air photonics. Optics Express, 2014, 22(10): 12475–12485
McLaughlin C V, Hayden L M, Polishak B, Huang S, Luo J, Kim T D, Jen A K Y. Wideband 15 THz response using organic electrooptic polymer emitter-sensor pairs at telecommunication wavelengths. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(15): 151107
Seifert T, Jaiswal S, Martens U, Hannegan J, Braun L, Maldonado P, Freimuth F, Kronenberg A, Henrizi J, Radu I, Beaurepaire E, Mokrousov Y, Oppeneer P M, Jourdan M, Jakob G, Turchinovich D, Hayden L M, Wolf M, Münzenberg M, Kläui M, Kampfrath T. Efficient metallic spintronic emitters of ultrabroadband terahertz radiation. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(7): 483–488
Clough B, Dai J, Zhang X C. Laser air photonics: beyond the terahertz gap. Materials Today, 2012, 15(1-2): 50–58
Chen Y, Yamaguchi M, Wang M, Zhang X C. Terahertz pulse generation from noble gases. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91 (25): 251116
Lu X, Karpowicz N, Chen Y, Zhang X C. Systematic study of broadband terahertz gas sensor. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93 (26): 261106
Kress M, Löffler T, Eden S, Thomson M, Roskos H G. Terahertzpulse generation by photoionization of air with laser pulses composed of both fundamental and second-harmonic waves. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(10): 1120–1122
Xie X, Dai J, Zhang X C. Coherent control of THz wave generation in ambient air. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(7): 075005
Leisawitz D T, Danchi W C, DiPirro M J, Feinberg L D, Gezari D Y, Hagopian M, Langer W D, Mather J C, Moseley S H, Shao M, Silverberg R F, Staguhn J G, Swain M R, Yorke H W, Zhang X L. Scientific motivation and technology requirements for the SPIRIT and SPECS far-infrared/submillimeter space interferometers. In: Proceedings of SPIE 4013, UV, Optical, and IR Space Telescopes and Instruments. Munich, Germany: SPIE, 2000, 36–46
Ferguson B, Zhang X C. Materials for terahertz science and technology. Nature Materials, 2002, 1(1): 26–33
Siegel P H. Terahertz technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(3): 910–928
Tonouchi M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(2): 97–105
Kimmitt M F. Restrahlen to T-rays -100 years of terahertz radiation. Journal of Biological Physics, 2003, 29(2–3): 77–85
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: David H. Auston. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 6–8
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Maurice F. Kimmitt ‘A Person Who Makes ThingsWork’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(1): 6–9
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Thomas G. Phillips ‘The Sky Above, the Mountain Below’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(5): 478–484
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Frank C. De Lucia ‘The Numbers Count’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(6): 578–583
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Richard J. Saykally -water, water everywhere..... IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(3): 266–270
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: RobertW.Wilson the foundations of THz radio science. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(2): 162–166
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Daniel R. Grischkowsky ‘We Search for Truth and Beauty’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(4): 378–382
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneers: Manfred Winnewisser and Brenda PrudenWinnewisser: ‘Equating Hamiltonians to nature’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(3): 229–236
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Sir John B. Pendry ‘Theoretical Physics for a Practical World’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(6): 693–701
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Philippe Goy “If You Agree with the Majority, You Might be Wrong”. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(4): 348–353
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Federico Capasso “Physics by Design: Engineering Our Way Out of the THz Gap”. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(1): 6–13
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Fritz Keilmann-‘RF Biophysics: From strong field to near field’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(5): 506–514
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Koji Mizuno ‘50 Years in Submillimeter-Waves: From Otaku to Sensei’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(2): 130–133
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Erik L. Kollberg ‘Instrument Maker to the Stars’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(5): 538–544
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Michael Bass ‘The THz Light at the End of the Tunnel’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(4): 410–417
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Shenggang Liu ‘China’s Father of Vacuum and Microwave Electronics’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(1): 6–11
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Mattheus (Thijs) de Graauw ‘Intention, Attention, Execution’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(2): 138–146
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Robert J. Mattauch “Two Terminals Will Suffice”. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(6): 646–652
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Tatsuo Itoh ‘Transmission Lines and Antennas: Left and Right’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(3): 298–306
Siegel P H. Terahertz pioneer: Xi-Cheng Zhang ‘The Face of THz’. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2015, 5 (5): 706–714
Phillips T G, Keene J. Submillimeter astronomy (heterodyne spectroscopy). Proceedings of the IEEE, 1992, 80(11): 1662–1678
Siegel P H, Pikov V. Impact of low intensity millimetre waves on cell functions. Electronics Letters, 2010, 46(26): S70
Alexandrov B S, Gelev V, Bishop A R, Usheva A, Rasmussen K O. DNA breathing dynamics in the presence of a terahertz field. Physics Letters A, 2010, 374(10): 1214–1217
Yang Y, Mandehgar M, Grischkowsky D R. Broadband THz pulse transmission through the atmosphere. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 264–273
Svelto O, Hanna D C. Principles of Lasers. Boston, MA: Springer, 2009
Wu Z, Fisher A S, Goodfellow J, Fuchs M, Daranciang D, Hogan M, Loos H, Lindenberg A. Intense terahertz pulses from SLAC electron beams using coherent transition radiation. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84(2): 022701
Elias L R, Hu J, Ramian G. The UCSB electrostatic accelerator free electron laser: first operation. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research. Section A, Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1985, 237(1-2): 203–206
Reimann K. Table-top sources of ultrashort THz pulses. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2007, 70(10): 1597–1632
Kitaeva G K. Terahertz generation by means of optical lasers. Laser Physics Letters, 2008, 5(8): 559–576
Hebling J, Yeh K L, Hoffmann M C, Bartal B, Nelson K A. Generation of high-power terahertz pulses by tilted-pulse-front excitation and their application possibilities. Journal of the Optical Society of America. B, Optical Physics, 2008, 25(7): B6
Rice A, Jin Y, Ma X F, Zhang X C, Bliss D, Larkin J, Alexander M. Terahertz optical rectification from <110>zinc-blende crystals. Applied Physics Letters, 1994, 64(11): 1324–1326
Fülöp J A, Pálfalvi L, Klingebiel S, Almási G, Krausz F, Karsch S, Hebling J. Generation of sub-mJ terahertz pulses by optical rectification. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(4): 557–559
Shalaby M, Hauri C P. Demonstration of a low-frequency threedimensional terahertz bullet with extreme brightness. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 5976
Hirori H, Doi A, Blanchard F, Tanaka K. Single-cycle terahertz pulses with amplitudes exceeding 1 MV/cm generated by optical rectification in LiNbO3. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(9): 091106
Auston D H. Picosecond optoelectronic switching and gating in silicon. Applied Physics Letters, 1975, 26(3): 101–103
Mourou G, Stancampiano C V, Antonetti A, Orszag A. Picosecond microwave pulses generated with a subpicosecond laser-driven semiconductor switch. Applied Physics Letters, 1981, 39(4): 295–296
Budiarto E, Margolies J, Jeong S, Son J, Bokor J. High-intensity terahertz pulses at 1-kHz repetition rate. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1996, 32(10): 1839–1846
Look D C. Molecular beam epitaxial GaAs grown at low temperatures. Thin Solid Films, 1993, 231(1-2): 61–73
Beard M C, Turner G M, Schmuttenmaer C A. Subpicosecond carrier dynamics in low-temperature grown GaAs as measured by time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 90(12): 5915–5923
Richards P L. Bolometers for infrared and millimeter waves. Journal of Applied Physics, 1994, 76(1): 1–24
Mauskopf P D, Bock J J, Del Castillo H, Holzapfel W L, Lange A E. Composite infrared bolometers with Si3N4 micromesh absorbers. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(4): 765–771
Nahum M, Martinis J M. Ultrasensitive-hot-electron microbolometer. Applied Physics Letters, 1993, 63(22): 3075–3077
Golay M J E. A pneumatic infra-red detector. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1947, 18(5): 357–362
Gautschi G. Piezoelectric Sensorics: Force, Strain, Pressure, Acceleration and Acoustic Emission Sensors, Materials and Amplifiers. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2002
Komiyama S, Astafiev O, Antonov V, Kutsuwa T, Hirai H. A single-photon detector in the far-infrared range. Nature, 2000, 403 (6768): 405–407
Kim K T, Zhang C, Shiner A D, Schmidt B E, Légaré F, Villeneuve D M, Corkum P B. Petahertz optical oscilloscope. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(12): 958–962
Teo S M, Ofori-Okai B K, Werley C A, Nelson K A. Single-shot THz detection techniques optimized for multidimensional THz spectroscopy. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2015, 86(5): 051301
Wu Q, Zhang X C. Free-space electro-optic sampling of terahertz beams. Applied Physics Letters, 1995, 67(24): 3523–3525
Leitenstorfer A, Hunsche S, Shah J, Nuss M C, Knox W H. Detectors and sources for ultrabroadband electro-optic sampling: experiment and theory. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 74(11): 1516–1518
Auston D H, Smith P R. Generation and detection of millimeter waves by picosecond photoconductivity. Applied Physics Letters, 1983, 43(7): 631–633
Grischkowsky D, Keiding S, van Exter M, Fattinger C. Farinfrared time-domain spectroscopy with terahertz beams of dielectrics and semiconductors. Journal of the Optical Society of America. B, Optical Physics, 1990, 7(10): 2006
Wu Q, Hewitt T D, Zhang X C. Two-dimensional electro-optic imaging of THz beams. Applied Physics Letters, 1996, 69(8): 1026–1028
Mittleman D M, Jacobsen R H, Nuss M C. T-ray imaging. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 1996, 2(3): 679–692
Mittleman D M, Hunsche S, Boivin L, Nuss M C. T-ray tomography. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(12): 904–906
Woodward R M, Cole B E, Wallace V P, Pye R J, Arnone D D, Linfield E H, Pepper M. Terahertz pulse imaging in reflection geometry of human skin cancer and skin tissue. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2002, 47(21): 3853–3863
Seco-Martorell C, López-Domínguez V, Arauz-Garofalo G, Redo-Sanchez A, Palacios J, Tejada J. Goya’s artwork imaging with Terahertz waves. Optics Express, 2013, 21(15): 17800–17805
Zhong H, Xu J Z, Xie X, Yuan T, Reightler R, Madaras E, Zhang X C. Nondestructive defect identification with terahertz time-of-flight tomography. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2005, 5(2): 203–208
Beard M C, Turner G M, Schmuttenmaer C A. Terahertz Spectroscopy. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(29): 7146–7159
Sell A, Leitenstorfer A, Huber R. Phase-locked generation and field-resolved detection of widely tunable terahertz pulses with amplitudes exceeding 100 MV/cm. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(23): 2767–2769
Kampfrath T, Tanaka K, Nelson K A. Resonant and nonresonant control over matter and light by intense terahertz transients. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(9): 680–690
Schubert O, Hohenleutner M, Langer F, Urbanek B, Lange C, Huttner U, Golde D, Meier T, Kira M, Koch S W, Huber R. Subcycle control of terahertz high-harmonic generation by dynamical Bloch oscillations. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(2): 119–123
Hamster H, Sullivan A, Gordon S, White W, Falcone R W. Subpicosecond, electromagnetic pulses from intense laser-plasma interaction. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 71(17): 2725–2728
Löffler T, Jacob F, Roskos H G. Generation of terahertz pulses by photoionization of electrically biased air. Applied Physics Letters, 2000, 77(3): 453–455
Cook D J, Hochstrasser RM. Intense terahertz pulses by four-wave rectification in air. Optics Letters, 2000, 25(16): 1210–1212
Liu J, Zhang X C. Terahertz-radiation-enhanced emission of fluorescence from gas plasma. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103 (23): 235002
Clough B, Liu J, Zhang X C. Laser-induced photoacoustics influenced by single-cycle terahertz radiation. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(21): 3544–3546
Hamster H, Sullivan A, Gordon S, Falcone R W. Short-pulse terahertz radiation from high-intensity-laser-produced plasmas. Physical Review E: Statistical Physics, Plasmas, Fluids, and Related Interdisciplinary Topics, 1994, 49(1): 671–677
Durand M, Houard A, Prade B, Mysyrowicz A, Durécu A, Moreau B, Fleury D, Vasseur O, Borchert H, Diener K, Schmitt R, Théberge F, Chateauneuf M, Daigle J F, Dubois J. Kilometer range filamentation. Optics Express, 2013, 21(22): 26836–26845
D’Amico C, Houard A, Franco M, Prade B, Mysyrowicz A, Couairon A, Tikhonchuk V T. Conical forward THz emission from femtosecond-laser-beam filamentation in air. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(23): 235002
Houard A, Liu Y, Prade B, Tikhonchuk V T, Mysyrowicz A. Strong enhancement of terahertz radiation from laser filaments in air by a static electric field. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100 (25): 255006
Liu Y, Houard A, Prade B, Mysyrowicz A, Diaw A, Tikhonchuk V T. Amplification of transition-Cherenkov terahertz radiation of femtosecond filament in air. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(5): 051108
Mitryukovskiy S I, Liu Y, Prade B, Houard A, Mysyrowicz A. Coherent synthesis of terahertz radiation from femtosecond laser filaments in air. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(22): 221107
Kim K Y, Glownia J H, Taylor A J, Rodriguez G. Terahertz emission from ultrafast ionizing air in symmetry-broken laser fields. Optics Express, 2007, 15(8): 4577–4584
Karpowicz N, Zhang X C. Coherent terahertz echo of tunnel ionization in gases. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(9): 093001
Bergé L, Skupin S, Köhler C, Babushkin I, Herrmann J. 3D numerical simulations of THz generation by two-color laser filaments. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110(7): 073901
Clerici M, Peccianti M, Schmidt B E, Caspani L, Shalaby M, Giguère M, Lotti A, Couairon A, Légaré F, Ozaki T, Faccio D, Morandotti R. Wavelength scaling of terahertz generation by gas ionization. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110(25): 253901
Oh T I, Yoo Y J, You Y S, Kim K Y. Generation of strong terahertz fields exceeding 8 MV/cm at 1 kHz and real-time beam profiling. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(4): 041103
Thomson M D, Blank V, Roskos H G. Terahertz white-light pulses from an air plasma photo-induced by incommensurate two-color optical fields. Optics Express, 2010, 18(22): 23173–23182
Dai J, Zhang X C. Terahertz wave generation from gas plasma using a phase compensator with attosecond phase-control accuracy. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(2): 021117
Wen H, Lindenberg A M. Coherent terahertz polarization control through manipulation of electron trajectories. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(2): 023902
Dai J, Karpowicz N, Zhang X C. Coherent polarization control of terahertz waves generated from two-color laser-induced gas plasma. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(2): 023001
Zhong H, Karpowicz N, Zhang X C. Terahertz emission profile from laser-induced air plasma. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88 (26): 261103
Klarskov P, Strikwerda A C, Iwaszczuk K, Jepsen P U. Experimental three-dimensional beam profiling and modeling of a terahertz beam generated from a two-color air plasma. New Journal of Physics, 2013, 15(7): 075012
Blank V, Thomson M D, Roskos H G. Spatio-spectral characteristics of ultra-broadband THz emission from two-colourphotoexcited gas plasmas and their impact for nonlinear spectroscopy. New Journal of Physics, 2013, 15(7): 075023
You Y S, Oh T I, Kim K Y. Off-axis phase-matched terahertz emission from two-color laser-induced plasma filaments. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(18): 183902
Gorodetsky A, Koulouklidis A D, Massaouti M, Tzortzakis S. Physics of the conical broadband terahertz emission from twocolor laser-induced plasma filaments. Physical Review A., 2014, 89(3): 033838
Wang T J, Yuan S, Chen Y, Daigle J F, Marceau C, Théberge F, Châteauneuf M, Dubois J, Chin S L. Toward remote high energy terahertz generation. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(11): 111108
Wang T J, Daigle J F, Yuan S, Théberge F, Châteauneuf M, Dubois J, Roy G, Zeng H, Chin S L. Remote generation of high-energy terahertz pulses from two-color femtosecond laser filamentation in air. Physical Review A., 2011, 83(5): 053801
Nahata A, Heinz T F. Detection of freely propagating terahertz radiation by use of optical second-harmonic generation. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(1): 67–69
Liu J, Zhang X C. Enhancement of laser-induced fluorescence by intense terahertz pulses in gases. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2011, 17(1): 229–236
Liu J, Dai J, Zhang X C. Ultrafast broadband terahertz waveform measurement utilizing ultraviolet plasma photoemission. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, Optical Physics, 2011, 28(4): 796
Liu J, Dai J, Chin S L, Zhang X C. Broadband terahertz wave remote sensing using coherent manipulation of fluorescence from asymmetrically ionized gases. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(9): 627–631
Clough B, Liu J, Zhang X C. “All air-plasma” terahertz spectroscopy. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(13): 2399–2401
Maker P D, Terhune R W, Savage C M. Optical third harmonic generation. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress, Quantum Electron. Paris: Dunod Éditeur, 1964, 1559
Talebpour A, Yang J, Chin S L. Semi-empirical model for the rate of tunnel ionization of N2 and O2 molecule in an intense Ti: sapphire laser pulse. Optics Communications, 1999, 163(1-3): 29–32
Couairon A, Mysyrowicz A. Femtosecond filamentation in transparent media. Physics Reports, 2007, 441(2-4): 47–189
Chin S L. Femtosecond Laser Filamentation. New York: Springer, 2010
Abdollahpour D, Suntsov S, Papazoglou D G, Tzortzakis S. Measuring easily electron plasma densities in gases produced by ultrashort lasers and filaments. Optics Express, 2011, 19(18): 16866–16871
Arévalo E, Becker A. Theoretical analysis of fluorescence signals in filamentation of femtosecond laser pulses in nitrogen molecular gas. Physical Review A., 2005, 72(4): 043807
Talebpour A, Petit S, Chin S. Re-focusing during the propagation of a focused femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser pulse in air. Optics Communications, 1999, 171(4-6): 285–290
Bukin V V, Vorob’ev N S, Garnov S V, Konov V I, Lozovoi V I, Malyutin A A, Shchelev M Y, Yatskovskii I S. Formation and development dynamics of femtosecond laser microplasma in gases. Quantum Electronics, 2006, 36(7): 638–645
Martin F, Mawassi R, Vidal F, Gallimberti I, Comtois D, Pépin H, Kieffer J C, Mercure H P. Spectroscopic study of ultrashort pulse laser-breakdown plasmas in air. Applied Spectroscopy, 2002, 56 (11): 1444–1452
Herzberg G. Molecular Spectra and Molecular Structure. Malabar, FL: R.E. Krieger Pub. Co, 1989
Becker A, Bandrauk A D, Chin S L. S-matrix analysis of nonresonant multiphoton ionisation of inner-valence electrons of the nitrogen molecule. Chemical Physics Letters, 2001, 343(3-4): 345–350
Xu H L, Azarm A, Bernhardt J, Kamali Y, Chin S L. The mechanism of nitrogen fluorescence inside a femtosecond laser filament in air. Chemical Physics, 2009, 360(1-3): 171–175
Vidal F, Comtois D, Chien C Y, Desparois A, La Fontaine B, Johnston T W, Kieffer J C, Mercure H P, Pepin H, Rizk F A. Modeling the triggering of streamers in air by ultrashort laser pulses. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2000, 28(2): 418–433
Sato M, Higuchi T, Kanda N, Konishi K, Yoshioka K, Suzuki T, Misawa K, Kuwata-Gonokami M. Terahertz polarization pulse shaping with arbitrary field control. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(9): 724–731
Amico C D, Houard A, Akturk S, Liu Y, Le Bloas J, Franco M, Prade B, Couairon A, Tikhonchuk V T, Mysyrowicz A. Forward THz radiation emission by femtosecond filamentation in gases: theory and experiment. New Journal of Physics, 2008, 10(1): 013015
Acknowledgements
This research was sponsored by the National Science Foundation (ECCS-1229968) and the Army Research Office under Grants No. US ARMY W911NF-14-1-0343 and W911NF-17-1-0428. Part of the research in Zhejiang University (ZJU) was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61473255).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Invited Paper
Fabrizio Buccheri graduated from University of Palermo with a Bachelor of Engineering and a Master of Engineering in Electronics Engineering in November 2007 and November 2010 respectively, both with full marks and honor. His undergraduate thesis project with the title “Optical Biosensor based on Surface Plasmon Resonance for Wine Quality Control” won the first prize as best undergraduate project at the regional level. In 2010, Fabrizio was awarded a research internship from the Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique in Varennes, Canada, under the supervision of Prof. R. Morandotti. In Canada, Fabrizio developed his experimental master thesis project with the title “Terahertz Time Domain Spectroscopy with Subwavelength Spatial Resolution.” In 2011, Fabrizio is awarded a Fulbright scholarship to support the pursuit of his PhD degree in the United States. He joined Prof. X.-C. Zhang’s research group in Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and then followed him to University of Rochester, The Institute of Optics. In 2016, he was awarded the Best Graduate Student Project from The Institute of Optics by Rochester Precision Optics. Fabrizio is an active member of the professional associations OSA and SPIE.
Fabrizio currently works for Prysmian Group designing the next generation monitoring systems for the energy industry.
Pingjie Huang is an associate professor in the State Key Laboratory of Industrial Control Technology, College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University (ZJU). He received his Ph.D. degree in mechanical engineering, with specialty in information sensing and instrumentation from Zhejiang University in 2004 and obtained his B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees from Huazhong Agricultural University in 1996 and Xi’an University of Technology in 1999, respectively. His research interests mainly focus on advanced transducer and measurement, process and environmental information processing and event detection, and computer control system design and development, etc. He is a key member of the research group in Zhejiang University for early warning techniques and systems for urban water quality assurance, NDT&E of conductive structures, food products, water samples, and bio-tissue etc. base on THz-TDS, UV-Vis, and ECT methods. In these five years, he has authored/co-authored more than 40 peer-reviewed papers and conference papers.
Supported by the CSC and starting from September 2017 for a period of one year, Pingjie Huang is a visiting scholar in Prof. Xi- Cheng Zhang’s research group in The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester working on terahertz science and technology.
Xi-Cheng Zhang, Parker Givens Chair of Optics, was Director of The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester (UR), NY, a foremost institution in optics and optical physics research and education (Jan. 2012–Jun. 2017). Prior to joining UR, he pioneered world-leading research in the field of ultrafast laser-based terahertz technology and optical physics at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI), Troy NY (‘92-‘12). At RPI, he is the Eric Jonsson Professor of Science; Acting Head at the Department of Physics, Applied Physics & Astronomy; Professor of Electrical, Computer & System; and Founding Director of the Center for THz Research. He is co-founder of Zomega Terahertz Corp. With a B.S. degree (‘82) from Peking University, he earned the M.S. (‘83) and Ph.D. (‘86) degrees in Physics from Brown University, RI.
Dr. Zhang served as Editor-in-Chief of Optics Letters, OSA (‘14- ‘19). He is a Fellow of AAAS, APS, IEEE, OSA, and SPIE. Previous positions included visiting scientist at MIT (‘85), Physical Tech. Division of Amoco Research Center (‘87), EE Dept. at Columbia University (‘87-‘91); Distinguished Visiting Scientist at Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Caltech (2006). He holds 29 US patents, and is a prolific author and speaker.
His honors and awards include: Humboldt Prize ‘18); Australian Academy of Science Selby Fellow (‘17); IRMMW-THz Kenneth Button Prize (‘14); OSA William F. Meggers Award (‘12); IEEE Photonics Society William Streifer Scientific Achievement Award (‘11); RensselaerWilliam H.Wiley 1866 Award (‘09); Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Fellowship & NRC-CIAR Distinguished Visiting Scientist, Canada (‘04); First Heinrich Rudolf Hertz Lecturer, RWTH, Aachen, Germany (‘03). He also served two years as a Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE/LEOS. He received Rensselaer Early Career Award (‘96), Research Corporation Cottrell Scholar Award (‘95), NSF Early Career Award (‘95), K.C. Wong Prize, K.C. Wong Foundation, Hong Kong (‘95), NSF Research Initiation Award (‘92). In ‘93-‘94, he was an AFOSR-SRPF Fellow at Hanscom Air Force Base.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buccheri, F., Huang, P. & Zhang, XC. Generation and detection of pulsed terahertz waves in gas: from elongated plasmas to microplasmas. Front. Optoelectron. 11, 209–244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-018-0819-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-018-0819-8