Abstract
Introduction
Several functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) have been associated with the degradation or remodeling of the network of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC). Introducing fractal analysis to the field of gastroenterology as a promising data analytics approach to extract key structural characteristics that may provide insightful features for machine learning applications in disease diagnostics. Fractal geometry has advantages over several physically based parameters (or classical metrics) for analysis of intricate and complex microstructures that could be applied to ICC networks.
Methods
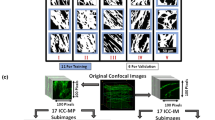
In this study, three fractal structural parameters: Fractal Dimension, Lacunarity, and Succolarity were employed to characterize scale-invariant complexity, heterogeneity, and anisotropy; respectively of three types of gastric ICC network structures from a flat-mount transgenic mouse stomach.
Results
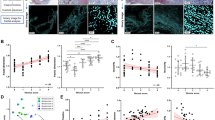
The Fractal Dimension of ICC in the longitudinal muscle layer was found to be significantly lower than ICC in the myenteric plexus and circumferential muscle in the proximal, and distal antrum, respectively (both p < 0.0001). Conversely, the Lacunarity parameters for ICC-LM and ICC-CM were found to be significantly higher than ICC-MP in the proximal and in the distal antrum, respectively (both p < 0.0001). The Succolarity measures of ICC-LM network in the aboral direction were found to be consistently higher in the proximal than in the distal antrum (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The fractal parameters presented here could go beyond the limitation of classical metrics to provide better understanding of the structural-functional relationship between ICC networks and the conduction of gastric bioelectrical slow waves.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdelsalam, M. M., and M. A. Zahran. A novel approach of diabetic retinopathy early detection based on multifractal geometry analysis for OCTA macular images using support vector machine. IEEE Access. 9:22844–22858, 2021.
An, W., C. Wang, H. Zhang, and Z. Bi. Measuring the formal complexity of architectural curved surfaces based on 3D box-counting dimension. Nexus Netw. J. 24:753–766, 2022.
Angeli, T. R., L. K. Cheng, P. Du, T.H.-H. Wang, C. E. Bernard, M.-G. Vannucchi, M. S. Faussone-Pellegrini, C. Lahr, R. Vather, J. A. Windsor, G. Farrugia, T. L. Abell, and G. O’Grady. Loss of interstitial cells of cajal and patterns of gastric dysrhythmia in patients with chronic unexplained nausea and vomiting. Gastroenterology. 149:56-66.e5, 2015.
Berry, R., T. Miyagawa, N. Paskaranandavadivel, P. Du, T. R. Angeli, M. L. Trew, J. A. Windsor, Y. Imai, G. O’Grady, and L. K. Cheng. Functional physiology of the human terminal antrum defined by highresolution electrical mapping and computational modeling. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 311:G895–G902, 2016.
Bunde, A., and S. Havlin. Fractals in Science. Berlin: Springer, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-77953-4.
De Melo, R. H. C., and A. Conci. How succolarity could be used as another fractal measure in image analysis. Telecommun. Syst. 52:1643–1655, 2013.
DePetrillo, P. B., D. Speers, and U. E. Ruttimann. Determining the Hurst exponent of fractal time series and its application to electrocardiographic analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 29:393–406, 1999.
Du, P., G. O’Grady, S. J. Gibbons, R. Yassi, R. Lees-Green, G. Farrugia, L. K. Cheng, and A. J. Pullan. Tissue-specific mathematical models of slow wave entrainment in wild-type and 5-HT(2B) knockout mice with altered interstitial cells of Cajal networks. Biophys. J. 98:1772–1781, 2010.
Gao, J., P. Du, G. O’Grady, R. Archer, G. Farrugia, S. J. Gibbons, and L. K. Cheng. Numerical metrics for automated quantification of interstitial cell of Cajal network structural properties. J. R. Soc. Interface. 10:20130421, 2013.
Gao, J., P. Du, G. O’Grady, R. Archer, S. J. Gibbons, G. Farrugia, and L. K. Cheng. Cellular automaton model for simulating tissue-specific intestinal electrophysiological activity. Conf. Proc. ... Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Annu. Conf. 5537–5540, 2013.
Gkontra, P., K. A. Norton, M. M. Zak, C. Clemente, J. Agüero, B. Ibáñez, A. Santos, A. S. Popel, and A. G. Arroyo. Deciphering microvascular changes after myocardial infarction through 3D fully automated image analysis. Sci. Rep. 81(8):1–19, 2018.
Glenny, R. W., H. T. Robertson, S. Yamashiro, and J. B. Bassingthwaighte. Applications of fractal analysis to physiology. J. Appl. Physiol. 70:2351–2367, 1991.
Goldberger, A. L. Fractal variability versus pathologic periodicity: Complexity loss and stereotypy in disease. Perspect. Biol. Med. 40:543–561, 1997.
Gould, D. J., T. J. Vadakkan, R. A. Poché, and M. E. Dickinson. Multifractal and lacunarity analysis of microvascular morphology and remodeling. Microcirculation. 18:136–151, 2011.
Grover, M., G. Farrugia, M. S. Lurken, C. E. Bernard, M. S. Faussone-Pellegrini, T. C. Smyrk, H. P. Parkman, T. L. Abell, W. J. Snape, W. L. Hasler, A. Ünalp-Arida, L. Nguyen, K. L. Koch, J. Calles, L. Lee, J. Tonascia, F. A. Hamilton, and P. J. Pasricha. Cellular changes in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 140:1575–1585, 2011.
He, C. L., L. Burgart, L. Wang, J. Pemberton, T. Young-Fadok, J. Szurszewski, and G. Farrugia. Decreased interstitial cell of cajal volume in patients with slow-transit constipation. Gastroenterology. 118:14–21, 2000.
Horsfield, K. Morphometry of the small pulmonary arteries in man. Circ. Res. 42:593–597, 1978.
Hughes, A. D., E. Martinez-Perez, A.-S. Jabbar, A. Hassan, N. W. Witt, P. D. Mistry, N. Chapman, A. V. Stanton, G. Beevers, R. Pedrinelli, K. H. Parker, and S. A. M. M. Thom. Quantification of topological changes in retinal vascular architecture in essential and malignant hypertension. J. Hypertens. 24:889–894, 2006.
Huizinga, J. D., N. Zarate, and G. Farrugia. Physiology, injury, and recovery of interstitial cells of Cajal: basic and clinical science. Gastroenterology. 137:1548–1556, 2009.
Isozaki, K., S. Hirota, J. Miyagawa, M. Taniguchi, Y. Shinomura, and Y. Matsuzawa. Deficiency of c-kit+ cells in patients with a myopathic form of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 92:332–334, 1997.
Julián, M., R. Alcaraz, and J. J. Rieta. Application of Hurst exponents to assess atrial reverse remodeling in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Physiol. Meas. 36:2231, 2015.
Klein, S., B. Seidler, A. Kettenberger, A. Sibaev, M. Rohn, R. Feil, H.-D. Allescher, J.-M. Vanderwinden, F. Hofmann, M. Schemann, R. Rad, M. A. Storr, R. M. Schmid, G. Schneider, and D. Saur. Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave activity. Nat. Commun. 4:1630, 2013.
Krohn, S., M. Froeling, A. Leemans, D. Ostwald, P. Villoslada, C. Finke, and F. J. Esteban. Evaluation of the 3D fractal dimension as a marker of structural brain complexity in multiple-acquisition MRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 40:3299–3320, 2019.
Lee, J., II., H. Park, M. A. Kamm, and I. C. Talbot. Decreased density of interstitial cells of Cajal and neuronal cells in patients with slow-transit constipation and acquired megacolon. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 20:1292–8, 2005.
Mah, S. A., R. Avci, L. K. Cheng, and P. Du. Current applications of mathematical models of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the gastrointestinal tract. WIREs Mech. Dis.13:e1507, 2021.
Mah, S. A., R. Avci, P. Du, J.-M. Vanderwinden, and L. K. Cheng. Antral variation of murine gastric pacemaker cells informed by confocal imaging and machine learning methods. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Annu. Int. Conf. 2021:3105–3108, 2021.
Mah, S. A., R. Avci, P. Du, J. M. Vanderwinden, and L. K. Cheng. Deciphering stomach myoelectrical slow wave conduction patterns via confocal imaging of gastric pacemaker cells and fractal geometry. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Annu. Int. Conf. 2022:3514–3517, 2022.
Mah, S. A., P. Du, R. Avci, J.-M. Vanderwinden, and L. K. Cheng. Analysis of regional variations of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the Murine distal stomach informed by confocal imaging and machine learning methods. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 15:193–205, 2022.
Mandelbrot, B. B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman and Company, pp. 394–397, 1982.
Masters, B. R. Fractal analysis of the vascular tree in the human retina. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 6:427–452, 2004.
Murueta-Goyena, A., M. Barrenechea, A. Erramuzpe, S. Teijeira-Portas, M. Pengo, U. Ayala, D. Romero-Bascones, M. Acera, R. Del Pino, J. C. Gómez-Esteban, and I. Gabilondo. Foveal remodeling of retinal microvasculature in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 15:837, 2021.
Nelson, T. R., and D. K. Manchester. Modeling of lung morphogenesis using fractal geometries. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 7:321–327, 1988.
O’Grady, G., P. Du, L. K. Cheng, J. U. Egbuji, W. J. E. P. Lammers, J. A. Windsor, and A. J. Pullan. Origin and propagation of human gastric slow-wave activity defined by high-resolution mapping. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 299:G585–G592, 2010.
Popovic, N., M. Radunovic, J. Badnjar, and T. Popovic. Fractal dimension and lacunarity analysis of retinal microvascular morphology in hypertension and diabetes. Microvasc. Res. 118:36–43, 2018.
Rolle, U., A. P. Piotrowska, L. Nemeth, and P. Puri. Altered distribution of interstitial cells of Cajal in Hirschsprung disease. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 126:928–933, 2002.
Smith, T. G., W. B. Marks, G. D. Lange, W. H. Sheriff, and E. A. Neale. A fractal analysis of cell images. J. Neurosci. Methods. 27:173–180, 1989.
Souza França, L. G., J. G. Vivas Miranda, M. Leite, N. K. Sharma, M. C. Walker, L. Lemieux, and Y. Wang. Fractal and multifractal properties of electrographic recordings of human brain activity: toward its use as a signal feature for machine learning in clinical applications. Front. Physiol. 9:1767, 2018.
Stošić, T., and B. D. Stošić. Multifractal analysis of human retinal vessels. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 25:1101–1107, 2006.
Tolle, C. R., T. R. McJunkin, and D. J. Gorsich. An efficient implementation of the gliding box lacunarity algorithm. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 237:306–315, 2008.
Vanderwinden, J.-M., and J. J. Rumessen. Interstitial cells of Cajal in human gut and gastrointestinal disease. Microsc. Res. Tech. 47:344–360, 1999.
West, B. J. Fractal physiology and the fractional calculus: a perspective. Front. Physiol. 1:12, 2010.
Wu, J., X. Jin, S. Mi, and J. Tang. An effective method to compute the box-counting dimension based on the mathematical definition and intervals. Results Eng.6:100106, 2020.
Xia, Y., J. Cai, E. Perfect, W. Wei, Q. Zhang, and Q. Meng. Fractal dimension, lacunarity and succolarity analyses on CT images of reservoir rocks for permeability prediction. J. Hydrol.579:124198, 2019.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Perrine Hagué, Faculté de Médecine, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium for technical assistance in mice breeding and tissue clearing, and Prof. Dieter Saur, School of Medicine, Technische Universität München, Germany for providing the KitCreERT2, R26mT-mG mice colony founders.
Funding
This work was supported, in part, by grants from the Marsden Fund Council and Rutherford Foundation managed by The Royal Society Te Apārangi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author SM conducted the conception of the study, technical analysis & statistic, and wrote the manuscript. JM provided the microscopic imaging data. RA and PD supervised the project. All authors took part in reviewing and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Associate Editor Jennifer Linderman oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mah, S.A., Avci, R., Vanderwinden, JM. et al. Three-Dimensional Fractal Analysis of the Interstitial Cells of Cajal Networks of Gastrointestinal Tissue Specimens. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 17, 67–81 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-023-00789-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-023-00789-5