Abstract
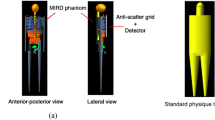
The present study aimed to develop a simple computer simulation method of low-dose radiographs based on a radiograph acquired at a clinical-dose level. A chest phantom was used for the development of this method. In this method, a simulated low-dose image was obtained from a clinical-dose image using an input–output characteristic curve of a flat panel detector and noise metrics of the standard deviation (SD) and noise power spectrum. We applied this method for low-dose images of a chest phantom to evaluate the simulation accuracy. The noise SDs were compared between the simulated and real images corresponding to 1/2, 1/4, and 1/8 of clinical doses. The relative error of noise SDs in the chest phantom images was less than 3%. Therefore, we believe that the proposed simulation method has the potential to be useful for determination of the optimal exposure condition in chest radiography to reduce patients’ exposure dose.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
International commission on radiological protection: radiological protection and safety in medicine. ICRP Publication 73. Ann. ICRP26. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1996. p. 1–47.
Moores DM, Regulla D. A review of the scientific basis for radiation protection of the patient. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2011;147:22–9.
Hendee WR, Edward FM. ARALA and an integrated approach to radiation protection. Semin Nucl Med. 1986;16:142–50.
Uffmann M, Schaefer-Prokop C. Digital radiography: the balance between image quality and required radiation dose. Eur J Radiol. 2009;72:202–8.
Willis CE, Slovis TL. The ALARA concept in pediatric CR and DR: dose reduction in pediatric radiographic exams—a white paper conference executive summary. Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34:162–4.
Sund P, Båth M, Kheddache S, Månsson LG. Comparison of visual grading analysis and determination of detective quantum efficiency for evaluating system performance in digital chest radiography. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:48–58.
Saunders RS, Samei E. A method for modifying the image quality parameters of digital radiographic images. Med Phys. 2003;30:3006–177.
Samei E, Flynn MJ, Eyler WR. Detection of subtle lung nodules: relative influence of quantum and anatomic noise on chest radiographs. Radiology. 1999;213:727–34.
Veldkamp WJH, Kroft LJM, Geleijns J. Dose and perceived image quality in chest radiography. Eur J Radiol. 2009;72:209–17.
Bochud FO, Valley JF, Verdun FR, Hessler C, Schnyder P. Estimation of the noisy component of anatomical backgrounds. Med Phys. 1999;26:1365–70.
Veldkamp WJH, Kroft LJM, Van Delft JPA, Geleijns J. A technique for simulating the effect of dose reduction on image quality in digital chest radiography. J Digit Imaging. 2009;22:114–25.
Tanaka R, Ichikawa K, Matsubara K, Kawashima H. Review of a simple noise simulation technique in digital radiography. Radiol Phys Technol. 2012;5:178–85.
Båth M, Håkansson M, Tingberg A, Månsson LG. Method of simulating dose reduction for digital radiographic systems. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2005;114:253–9.
Saito Y, Kawai A, Fujita N, Yamada M, Kodera Y. Reduction of patient dose in digital mammography: simulation of low-dose image from a routine dose. Lect Notes Comput Sci. 2012;7361:611–8.
Saito Y, Sakai M, Fujita N, Kodera Y. Reduction of patient dose in digital mammography: simulation of low-dose image using computed radiography system and flat panel detector system. Proc of SPIE. 2013;8668:86684K.
Samei E, Peck DJ. Hendee's physics of medical imaging. Hoboken: Wiley; 2019. p. 105–125.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Kenji Tokumori, Dr. Hidemi Kamezawa and Dr. Keiich Shida for their important contributions to the chest phantom experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights statement
This research does not involve human participants and animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, R., Katsuragawa, S. Development of a computer simulation technique for low-dose chest radiographs: a phantom study. Radiol Phys Technol 13, 111–118 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-020-00555-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-020-00555-6