Abstract
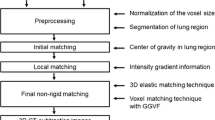
Misregistration errors occur at the periphery of the hepatic region due to respiratory- and interval-related changes in hepatic shape. To reduce these misregistration errors, we developed a temporal and dynamic subtraction technique to enhance small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by using a 3D nonlinear image-warping technique. The study population consisted of 21 patients with HCC. We registered the present and previous arterial-phase CT images or the present nonenhanced and arterial-phase CT images obtained in the same position by 3D global-matching plus 3D nonlinear image-warping. Temporal subtraction images were obtained by subtraction of the previous arterial-phase CT image from the warped present arterial-phase CT image. Dynamic subtraction images were obtained by subtraction of the present nonenhanced CT image from the warped present arterial-phase CT image. When we used this new technique, the number of good or excellent cases increased from 14.2% (3/21 cases) to 71.4% (15/21 cases) on temporal subtraction images. With this technique, subjective rating scores for image quality improved in 57.1% of cases (12/21 cases) on temporal subtraction images and 81.0% of cases (17/21 cases) on dynamic subtraction images. The results indicated that the new subtraction images were greatly improved by use of the 3D nonlinear image-warping technique.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brancatelli G, Baron RL, Peterson MS, Marsh W. Helical CT screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: frequency and causes of false-positive interpretation. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(4):1007–14.
el-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5:87–107.
Schafer DF, Sorrell MF. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1999;353:1253–7.
Baron RL, Peterson MS. Screening the cirrhotic liver for hepatocellular carcinoma with CT and MRI imaging. Radiographics. 2001;21:117–32.
Peterson MS, Baron RL, Marsh JW, Oliver JH, Confer SR, Hunt LE. Pretransplantation surveillance for possible hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: epidemiology and CT-based tumor detection rate in 430 cases with surgical pathologic correlation. Radiology. 2000;217:743–9.
Krinsky GA, Lee VS, Theise ND, Weinreb JC, Rofsky NM, Diflo T, Teperman LW. Hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules in patients with cirrhosis: prospective diagnosis with MR imaging and explantation correlation. Radiology. 2001;219:445–54.
Marin D, Di Martino M, Guerrisi A, De Filippis G, Rossi M, Ginanni Corradini S, Masciangelo R, Catalano C, Passariello R. Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: qualitative comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging and multiphasic 64-section CT. Radiology. 2009;251:85–95.
Okumura E, Sanada S, Suzuki M, Matsui O. Computer-aided temporal and dynamic subtraction technique of the liver for detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma on abdominal CT images. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(19):4759–71.
Okumura E, Sanada S, Suzuki M, Takemura A, Matsui O. Improvement of temporal and dynamic subtraction images on abdominal CT using 3D global image matching and nonlinear warping technique. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52(21):6461–74.
Rohlfing T, Maurer CR Jr, O’Dell WG, Zhong J. Modeling liver motion and deformation during the respiratory cycle using intensity-based nonrigid registration of gated MR images. Med Phys. 2004;31(3):427–32.
Stancanello J, Berna E, Cavedon C, Francescon P, Loeckx D, Cerveri P, Ferrigno G, Baselli G. Preliminary study on the use of nonrigid registration for thoraco-abdominal radiosurgery. Med Phys. 2005;32(12):3777–85.
Christina Lee WC, Tublin ME, Chapman BE. Registration of MR and CT images of the liver: comparison of voxel similarity and surface based registration algorithms. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2005;78(2):101–14.
Brock KM, Balter JM, Dawson LA, Kessler ML, Meyer CR. Automated generation of a four-dimensional model of the liver using warping and mutual information. Med Phys. 2003;30(6):1128–33.
Pevsner A, Davis B, Joshi S, Hertanto A, Mechalakos J, Yorke E, Rosenzweig K, Nehmeh S, Erdi YE, Humm JL, Larson S, Ling CC, Mageras GS. Evaluation of an automated deformable image matching method for quantifying lung motion in respiration-correlated CT images. Med Phys. 2006;33(2):369–76.
Coselmon MM, Balter JM, McShan DL, Kessler ML. Mutual information based CT registration of the lung at exhale and inhale breathing states using thin-plate splines. Med Phys. 2004;31(11):2942–8.
Söhn M, Birkner M, Chi Y, Wang J, Di Y, Berger B, Alber M. Model-independent, multimodality deformable image registration by local matching of anatomical features and minimization of elastic energy. Med Phys. 2008;35(3):866–78.
Sarrut DZ. Deformable registration for image-guided radiation therapy. Med Phys. 2006;16(4):285–97.
McInerney T, Terzopoulos D. Deformable models in medical image analysis: a survey. Med Image Anal. 1996;1(2):91–108.
Hutton BF, Braun M, Thurfjell L, Lau DY. Image registration: an essential tool for nuclear medicine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29(4):559–77.
Kano A, Doi K, MacMahon H, Hassell DD, Giger ML. Digital image subtraction of temporally sequential chest images for detection of interval change. Med Phys. 1994;21(3):453–61.
Ishida T, Katsuragawa S, Nakamura K, MacMahon H, Doi K. Iterative image warping technique for temporal subtraction of sequential chest radiographs to detect interval change. Med Phys. 1999;26(7):1320–9.
Li Q, Katsuragawa S, Ishida T, Yoshida H, Tsukkuda S, MacMahon H, Doi K. Contralateral subtraction: a novel technique for detection of asymmetric abnormalities on digital chest radiography. Med Phys. 2000;27(1):47–55.
Li Q, Katsuragawa S, Doi K. Improved contralateral subtraction images by use of elastic matching technique. Med Phys. 2000;27(6):1934–42.
Abe H, Ishida T, Shiraishi J, Li F, Katsuragawa S, Sone S, MacMahon H, Doi K. Effect of temporal subtraction images on radiologists’ detection of lung cancer on CT: result of the observer performance study with use of file computed tomography images. Acad Radiol. 2004;11:1337–43.
Takao H, Doi I, Watanabe T, Tateno M. Temporal subtraction of thin-section thoracic computed tomography based on a 3-dimensional nonlinear geometric warping technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006;30(2):283–6.
Takao H, Doi I, Takeno M. Evaluation of an automated system for temporal subtraction of thin-section thoracic CT. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(950):85–9.
Oguro S, Tokuda J, Elhawary H, Haker S, Kikinis R, Tempany CM, Hata N. MRI signal intensity based B-spline nonrigid registration for pre- and intraoperative imaging during prostate brachytherapy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(5):1052–8.
Nguyen TN, Moseley JL, Dawson LA, Jaffray DA, Brock KK. Adapting liver motion models using a navigator channel technique. Med Phys. 2009;36(4):1061–73.
Nguyen TN, Moseley JL, Dawson LA, Jaffray DA, Brock KK. Adapting population liver motion models for individualized online image-guided therapy. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008;2008:3945–8.
Brock KK, Hollister SJ, Dawson LA, Balter JM. Creating a four-dimensional model of the liver using finite element analysis. Med Phys. 2002;29(7):1403–5.
Brock KK, Sharpe MB, Dawson LA, Kim SM, Jaffray DA. Accuracy of finite element module-based multi-organ deformable image registration. Med Phys. 2005;32(6):1647–59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Okumura, E., Sanada, S., Suzuki, M. et al. Effectiveness of temporal and dynamic subtraction images of the liver for detection of small HCC on abdominal CT images: comparison of 3D nonlinear image-warping and 3D global-matching techniques. Radiol Phys Technol 4, 109–120 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-010-0110-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-010-0110-1