Abstract
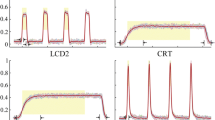
It is known that the performance of liquid-crystal display (LCD) monitors, such as the luminance and contrast ratio, is dependent on the viewing angle. Our purpose in this study was to compare the angular performance and the effect on observer performance of different types of LCD monitors. The luminance performance and contrast ratio as a function of viewing angle (−60° to 60°) in each direction for two types of LCD monitors, namely, a general-purpose LCD monitor and one especially designed for medical use, were measured in this study. Furthermore, the observer performance at various viewing angles in the horizontal direction for a medical-grade LCD monitor was investigated by eight observers based on a contrast-detail diagram. The two types of LCD monitors showed notable variations in luminance and contrast ratio as a function of the viewing angle. Acceptable viewing angles in terms of the contrast ratio were much smaller in each direction than those for nominal viewing angles in the specifications provided by the manufacturers, and those for the medical-grade LCD monitor in the horizontal and vertical directions were broader than those of the general-purpose LCD monitor. There was no significant difference in observer performance between 0° and 40°. On the other hand, our results showed a statistically significant difference in observer performance between 0° and 60°.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashimoto N. Characteristic of general-purpose monitor and medical-grade monitor. Jpn J Rad Tech. 2006;57:28–36. (in Japanese).
Hashimoto N. Image display devices (3) LCD monitor. Jpn J Rad Tech. 2003;59(1):21–8. (in Japanese).
Kimura N, Fujioka K. Fundamentals of liquid crystal displays and their recent technology. Jap J Rad Tech. 2004;60(10):1361–8. (in Japanese).
Saunders RS, Samei E. Resolution and noise measurements of five CRT and LCD medical displays. Med Phys. 2006;33:308–19.
Ichikawa K, Kodera Y, Nishimura A, Hasegawa M, Kimura N, Takemura A, et al. Analysis method of noise power spectrum for medical monochrome liquid crystal displays. Radiol Phys Technol. 2008;2:201–7.
Samei E, Wright LS. Viewing angle performance of medical liquid crystal displays. Med Phys. 2006;33:645–54.
Samei E, Poola A, Ulissey JM, Lewin MJ. Digital mammography: comparative performance of color LCD and monochrome CRT displays. Acad Radiol. 2007;14:539–46.
Electronic Industries Association of Japan. Measuring methods for matrix liquid crystal display modules. Tokyo: Electronic Industries Association of Japan; 1995. p. 14–5.
JESRA X-0093 quality assurance (QA) guideline for medical imaging display systems. Japan Industries Association of Radiological Systems. Tokyo, Japan 2005 http://www.jira-net.or.jp/e/index.htm.
AAPM on-line report no. 03, assessment of display performance for medical imaging systems, http://deckard.mc.duke.edu/~samei/tg18_files/tg18.pdf.
Morishita J, Dogomori K, Hatanaka S, Hiwasa T, Nakamura Y, Hashimoto N, et al. Effect of test patterns on measurement of the luminance of LCD devices by use of a telescopic-type luminance meter. Radiol Phys Technol. 2008;1:95–9.
The Illuminating Engineering Institute of Japan. Luminance measurement. In: Measurement of lighting with extension. Nihon Rikougaku Syupankai. Tokyo, Japan 1987. p 95–100 (in Japanese).
The Illuminating Engineering Institute of Japan. Luminance measurement. In: Manual for luminance measurement. Nihon Rikougaku Syupankai. Tokyo, Japan 2003. p 231–242 (in Japanese).
Mark M, Helena F, Patrick CB. A comparison of low contrast performance for amorphous silicon/caesium iodide direct radiography with a computed radiography: a contrast detail phantom study. Radiography. 2007;13:89–94.
Digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM) part 14: grayscale standard display function PS 3.1-2007 http://www.nema.org/stds/ps3-14.cfm.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Noriyuki Hashimoto, Shigehisa Ogawa (Nanao Corporation, Fukuoka, Japan), Hidetaka Arimura, Ph.D., and Seiji Kumazawa, Ph.D. (Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medical Sciences, KyushuUniversity) for helpful discussions and to former students of Kyushu University (Kei Okamoto, B.Sc., Noriyuki Nagami, B.Sc., Yuji Tsutsui, B.Sc., Hiroshi Hamasaki, B.Sc.) and to graduate students of Kyushu University (Junya Ogushi, B.Sc., Yasuo Kawata, B.Sc., Daisuke Yamamoto, B.Sc.) for participating in this study as observers. The authors thank Eiji Sato, PSP Corp., Tokyo, Japan, for providing image-viewing software. We are grateful to the editorial assistant of this journal for providing initial and final polishing of the submitted manuscript in improving the readability and English expressions, and the editors and reviewers for giving us useful comments and suggestions for improving our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hatanaka, S., Morishita, J., Hiwasa, T. et al. Comparison of viewing angle and observer performances in different types of liquid-crystal display monitors. Radiol Phys Technol 2, 166–174 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-009-0061-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-009-0061-6