Abstract
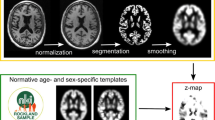
A voxel-based specific regional analysis system for Alzheimer’s disease (VSRAD) was used for quantitative analysis of parahippocampal atropy with 1.5-tesla (T) MRI in a voxel-wise manner. The analysis of images acquired under a different imaging condition provides an error factor that has a calculated value. Clinical application of 3T-MRI is necessary for establishing a normal data base (N-DB) specific for 3T-MRI data, which permits appropriate application of VSRAD. We established an N-DB specific for 3T-MRI for use in VSRAD. The “Z-score of the parahippocampal gyrus” was 0.79 ± 0.32, and the N-DB of each age group did not have a big deflection when we analyzed a group of physically unimpaired persons in an N-DB specific for 3T-MRI. Therefore, we were able to confirm the validity of the customized N-DB. The “Z-score of the parahippocampal gyrus” was 1.62 ± 0.47 for the N-DB of VSRAD. The numerical value was high for the group of physically unimpaired persons.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe O, Yamasue H, Aoki S, Suga M, Yamada H, Kasai K, et al. Aging in the CNS: comparison of gray/white matter volume and diffusion tensor data. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29:102–16.
Miyahira Y, Yu J, Hiramatsu K, Shimazaki Y, Takeda Y. Brain volumetric MRI study in healthy elderly persons using statistical parametric mapping. Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi. 2004;106(2):138–51.
Courchesne E, Chisum HJ, Townsend J, Cowles A, Covington J, Egaas B, et al. Normal brain development and aging: quantitative analysis at in vivo MR imaging in healthy volunteers. Radiology. 2000;216(3):672–82.
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS. A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage. 2001;14(1 Pt 1):21–36.
Taki Y, Goto R, Evans A, Zijdenbos A, Neelin P, Lerch J, et al. Voxel-based morphometry of human brain with age and cerebrovascular risk factors. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25(4):455–63.
Goto M, Aoki S, Abe O, Masumoto T, Watanabe Y, Satake Y, et al. Examination of an imaging method in early Alzheimer disease diagnosis support system (VSRAD). Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2006;62(9):1353–8.
Goto M, Aoki S, Abe O, Masumoto T, Watanabe Y, Satake Y, et al. Utility of axial images in an early Alzheimer disease diagnosis support system (VSRAD). Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2006;62(9):1339–44.
Sasaki M, Inoue T, Tohyama K, Oikawa H, Ehara S, Ogawa A. High-field MRI of the central nervous system: current approaches to clinical and microscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2003;2(3):133–9.
Willinek WA, Born M, Simon B, Tschampa HJ, Krautmacher C, Gieseke J, et al. Time-of-flight MR angiography: comparison of 3.0-T imaging and 1.5-T imaging-initial experience. Radiology. 2003;229(3):913–20.
Cornfeld DM, Weinreb JC. MR imaging of the prostate: 1.5T versus 3T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2007;15(3):433–48.
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189–98.
Fazekas F, hawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA. MR Signal abnormalities at 1.5T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;149(2):351–6.
DeCarli C, Miller BL, Swan GE, Reed T, Wolf PA, Garner J, et al. Predictors of brain morphology for the men of the NHLBI twin study. Stroke. 1999;30(3):529–36.
Salerno JA, Murphy DG, Horwitz B, DeCarli C, Haxby JV, Rapoport SI, et al. Brain atrophy in hypertension. A volumetric magnetic resonance imaging study. Hypertension. 1992;20(3):340–8.
Jernigan TL, Butters N, DiTraglia G, Schafer K, Smith T, Irwin M, et al. Reduced cerebral grey matter observed in alcoholics using magnetic resonance imaging. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991;15(3):418–27.
Pfefferbaum A, Lim KO, Zipursky RB, Mathalon DH, Rosenbloom MJ, Lane B, et al. Brain gray and white matter volume loss accelerates with aging in chronic alcoholics: a quantitative MRI study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992;16(6):1078–89.
Nunnemann S, Wohlschlager AM, Ilg R, Gaser C, Etgen T, Conrad B, et al. Accelerated aging of the putamen in men but not in women. Neurobiol Aging. Jul 2, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Goto, M., Suzuki, Y., Abe, O. et al. Customization of normal data base specific for 3-tesla MRI is mandatory in VSRAD analysis. Radiol Phys Technol 1, 196–200 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-008-0027-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-008-0027-0