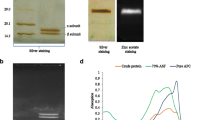
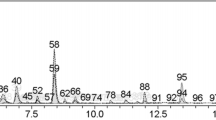
Abstract
Oxidative stress is implicated in numerous diseases, with benzo(α)pyrene (BaP) known for causing substantial oxidative damage. Bifidobacterium longum (B. longum) is recognized as an antioxidant bacterium for certain hosts, yet its influence on oxidative damages instigated by BaP remains undetermined. In our study, we introduced various strains of Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) to BaP to trigger oxidative stress, subsequently treating them with different forms of B. longum to evaluate its protective effects. Additionally, we explored the role of daf-16 in this context. Our findings indicated that in wild-type N2 C. elegans, B. longum—even in the form of inactivated bacteria or bacterial ultrasonic lysates (BULs)—significantly extended lifespan. BaP exposure notably decreased lifespan, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and motility, while simultaneously down-regulating the expression of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-associated genes (sod-3, sek-1, cat-1) and daf-16 downstream genes (sod-3, ctl-2). However, it significantly increased the ROS level, malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and lipofuscin accumulation and up-regulated another daf-16 downstream gene (clk-1) (P <0.05). Interestingly, when further treated with B. longum peptide-1 (BLP-1), opposite effects were observed, and all the aforementioned indices changed significantly. In the case of RNAi (daf-16) C. elegans, BaP exposure significantly shortened the lifespan (P <0.05), which was only slightly prolonged upon further treatment with BLP-1. Furthermore, the expression of daf-16 downstream genes showed minor alterations in RNAi C. elegans upon treatment with either BaP or BLP-1. In conclusion, our findings suggest that B. longum acts as a probiotic for C. elegans. BLP-1 was shown to safeguard C. elegans from numerous oxidative damages induced by BaP, but these protective effects were contingent upon the daf-16 gene.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Abbass M, Chen Y, Arlt VM, Stürzenbaum SR (2021) Benzo[a]pyrene and Caenorhabditis elegans: defining the genotoxic potential in an organism lacking the classical CYP1A1 pathway. Arch Toxicol 95:1055–1069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02968-z
Ajayi BO, Adedara IA, Farombi EO (2016) Benzo(a)pyrene induces oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory cytokines, expression of nuclear factor-kappa B and deregulation of wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colons of BALB/c mice. Food Chem Toxicol 95:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.06.019
Alharthy KM, Albaqami FF, Thornton C, Corrales J, Willett KL (2017) Mechanistic evaluation of benzo[a]pyrene’s developmental toxicities mediated by reduced Cyp19a1b activity. Toxicol Sci 155:135–147. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw182
Alzohairy MA, Khan AA, Alsahli MA, Almatroodi SA, Rahmani AH (2021) Protective effects of thymoquinone, an active compound of nigella sativa, on rats with benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung injury through regulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Molecules 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113218
Atkins SD, Peteira B, Clark IM, Kerry BR, Hirsch PR (2009) Use of real-time quantitative PCR to investigate root and gall colonisation by co-inoculated isolates of the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia. Ann Appl Biol 155:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00333.x
Cong Y, Wang Y, Zhang M, Jin F, Mu J, Li Z, Wang J (2021) Lethal, behavioral, growth and developmental toxicities of alkyl-PAHs and non-alkyl PAHs to early-life stage of brine shrimp, Artemia parthenogenetica. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 220:112302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112302
Espinosa-Diez C, Miguel V, Mennerich D, Kietzmann T, Sánchez-Pérez P, Cadenas S, Lamas S (2015) Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol 6:183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.008
Felkai S, Ewbank JJ, Lemieux J, Labbé JC, Brown GG, Hekimi S (1999) CLK-1 controls respiration, behavior and aging in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J 18:1783–1792. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.7.1783
Ge Y, Chen H, Wang J, Liu G, Cui SW, Kang J, Jiang Y, Wang H (2021) Naringenin prolongs lifespan and delays aging mediated by IIS and MAPK in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct 12:12127–12141. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo02472h
Honda Y, Honda S (2002) Oxidative stress and life span determination in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann N Y Acad Sci 959:466–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02117.x
Hu Q, Liu Z, Guo Y, Lu S, Du H, Cao Y (2021) Antioxidant capacity of flavonoids from Folium Artemisiae argyi and the molecular mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Ethnopharmacol 279:114398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114398
Ilie OD, Ciobica A, Riga S, Dhunna N, McKenna J, Mavroudis I, Doroftei B, Ciobanu AM, Riga D (2020) Mini-review on lipofuscin and aging: focusing on the molecular interface, the biological recycling mechanism, oxidative stress, and the gut-brain axis functionality. Medicina (Kaunas) 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110626
Inupakutika MA, Sengupta S, Devireddy AR, Azad RK, Mittler R (2016) The evolution of reactive oxygen species metabolism. J Exp Bot 67:5933–5943. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw382
Jakubczyk K, Dec K, Kałduńska J, Kawczuga D, Kochman J, Janda K (2020) Reactive oxygen species - sources, functions, oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski 48:124–127
Jelic MD, Mandic AD, Maricic SM, Srdjenovic BU (2021) Oxidative stress and its role in cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 17:22–28. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_862_16
Ji K, Xing C, Jiang F, Wang X, Guo H, Nan J, Qian L, Yang P, Lin J, Li M, Li J, Liao L, Tang J (2013) Benzo[a]pyrene induces oxidative stress and endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction via the activation of the NF-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med 31:922–930. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1288
Khattab SA, Hussien WF, Raafat N, Ahmed Alaa El-Din E (2021) Modulatory effects of catechin hydrate on benzo[a]pyrene-induced nephrotoxicity in adult male albino rats. Toxicol Res (Camb) 10:542–550. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxres/tfab029
Kim KH, Jahan SA, Kabir E, Brown RJ (2013) A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ Int 60:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.07.019
Kim SK, Guevarra RB, Kim YT, Kwon J, Kim H, Cho JH, Kim HB, Lee JH (2019) Role of probiotics in human gut microbiome-associated diseases. J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1335–1340. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1906.06064
Leachi HFL, Marziale MHP, Martins JT, Aroni P, Galdino MJQ, Ribeiro RP (2020) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and development of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in workers. Rev Bras Enferm 73:e20180965. https://doi.org/10.1590/0034-7167-2018-0965
Liu H, Wang Y, Zhang W, Sun W, Ji X, Zhang S, Qiao K (2022) Lentinan extends lifespan and increases oxidative stress resistance through DAF-16 and SKN-1 pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int J Biol Macromol 202:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.071
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J (2016) Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:3221–3247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2223-0
Luo M, Luo D, Liu J, Wang H, Liu X, Yang M, Tian F, Qin S, Li Y (2022) Ameliorative effect of the probiotic peptide against benzo(α)pyrene-induced inflammatory damages in enterocytes. Int Immunopharmacol 112:109255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109255
Martorell P, Alvarez B, Llopis S, Navarro V, Ortiz P, Gonzalez N, Balaguer F, Rojas A, Chenoll E, Ramón D, Tortajada M (2021) Heat-treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT-7347: a whole-cell postbiotic with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and gut-barrier protection properties. Antioxidants (Basel) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040536
Moore MN, Sforzini S, Viarengo A, Barranger A, Aminot Y, Readman JW, Khlobystov AN, Arlt VM, Banni M, Jha AN (2021) Antagonistic cytoprotective effects of C(60) fullerene nanoparticles in simultaneous exposure to benzo[a]pyrene in a molluscan animal model. Sci Total Environ 755:142355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142355
Moreno-Arriola E, Cárdenas-Rodríguez N, Coballase-Urrutia E, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Carmona-Aparicio L, Ortega-Cuellar D (2014) Caenorhabditis elegans: a useful model for studying metabolic disorders in which oxidative stress is a contributing factor. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:705253. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/705253
Murphy CT, Hu PJ (2013) Insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in C. elegans. WormBook, pp 1–43. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.164.1
Murphy CT, McCarroll SA, Bargmann CI, Fraser A, Kamath RS, Ahringer J, Li H, Kenyon C (2003) Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 424:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01789
Nakamura H, Takada K (2021) Reactive oxygen species in cancer: current findings and future directions. Cancer Sci 112:3945–3952. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.15068
Nwaozuzu CC, Partick-Iwuanyanwu KC, Abah SO (2021) Systematic review of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and obstructive lung disease. J Health Pollut 11:210903. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-11.31.210903
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A (2017) Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:8416763. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Prasad KN, Bondy SC (2013) Evaluation of role of oxidative stress on aging in Caenorhabditis elegans: a brief review. Curr Aging Sci 6:215–219. https://doi.org/10.2174/18746098112059990031
Roselli M, Schifano E, Guantario B, Zinno P, Uccelletti D, Devirgiliis C (2019) Caenorhabditis elegans and probiotics interactions from a prolongevity perspective. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205020
Saha S, Mahapatra KK, Mishra SR, Mallick S, Negi VD, Sarangi I, Patil S, Patra SK, Bhutia SK (2020) Bacopa monnieri inhibits apoptosis and senescence through mitophagy in human astrocytes. Food Chem Toxicol 141:111367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111367
Shi H, Liu J, Gao H (2021) Benzo(α)pyrene induces oxidative stress and inflammation in human vascular endothelial cells through AhR and NF-κB pathways. Microvasc Res 137:104179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104179
Slimen IB, Najar T, Ghram A, Dabbebi H, Ben Mrad M, Abdrabbah M (2014) Reactive oxygen species, heat stress and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review. Int J Hyperth 30:513–523. https://doi.org/10.3109/02656736.2014.971446
Sugawara T, Sakamoto K (2018) Killed Bifidobacterium longum enhanced stress tolerance and prolonged life span of Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-16. Br J Nutr 120:872–880. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114518001563
Sweeney MC, Pei D (2003) An improved method for rapid sequencing of support-bound peptides by partial Edman degradation and mass spectrometry. J Comb Chem 5:218–222. https://doi.org/10.1021/cc020113+
Szweda PA, Camouse M, Lundberg KC, Oberley TD, Szweda LI (2003) Aging, lipofuscin formation, and free radical-mediated inhibition of cellular proteolytic systems. Ageing Res Rev 2:383–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1568-1637(03)00028-x
Tejeda-Benitez L, Olivero-Verbel J (2016) Caenorhabditis elegans, a biological model for research in toxicology. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 237:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23573-8_1
Thapliyal S, Babu K (2018) C. elegans locomotion: finding balance in imbalance. Adv Exp Med Biol 1112:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3065-0_14
Vázquez-Gómez G, Rocha-Zavaleta L, Rodríguez-Sosa M, Petrosyan P, Rubio-Lightbourn J (2018) Benzo[a]pyrene activates an AhR/Src/ERK axis that contributes to CYP1A1 induction and stable DNA adducts formation in lung cells. Toxicol Lett 289:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.03.012
Wang Y, Wu Y, Wang Y, Xu H, Mei X, Yu D, Wang Y, Li W (2017) Antioxidant properties of probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050521
Wang H, Liu J, Li T, Liu RH (2018) Blueberry extract promotes longevity and stress tolerance via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct 9:5273–5282. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo01680a
Wang Y, Fang Z, Zhai Q, Cui S, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W, Lu W (2021) Supernatants of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus plantarum strains exhibited antioxidative effects on A7R5 cells. Microorganisms 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020452
Wu H, Huang C, Taki FA, Zhang Y, Dobbins DL, Li L, Yan H, Pan X (2015) Benzo-α-pyrene induced oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans and the potential involvements of microRNA. Chemosphere 139:496–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.031
Yang ZZ, Yu YT, Lin HR, Liao DC, Cui XH, Wang HB (2018) Lonicera japonica extends lifespan and healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Free Radic Biol Med 129:310–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.035
Yu X, Su Q, Shen T, Chen Q, Wang Y, Jia W (2020) Antioxidant peptides from Sepia esculenta hydrolyzate attenuate oxidative stress and fat accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mar Drugs 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100490
Zečić A, Braeckman BP (2020) DAF-16/FoxO in Caenorhabditis elegans and its role in metabolic remodeling. Cells 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010109
Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V, Ye Q, Wu D, Liu Y, Dong W (2016) ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:4350965. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4350965
Zhao L, Zhao Y, Liu R, Zheng X, Zhang M, Guo H, Zhang H, Ren F (2017) The transcription factor DAF-16 is essential for increased longevity in C. elegans exposed to Bifidobacterium longum BB68. Sci Rep 7:7408. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07974-3
Zhou L, Liu J, Bu LL, Liao DF, Cheng SW, Zheng XL (2021) Curcumin acetylsalicylate extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216609
Zia A, Farkhondeh T, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Samarghandian S (2021) The role of curcumin in aging and senescence: molecular mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother 134:111119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111119
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor JiuYao Wang (from the Center for Allergy and Clinical Immunology Research, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, China) for supplying the bacteria and the technical assistance.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1:
Figure S1 (PNG 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ai, L., Luo, D., Wang, H. et al. Ameliorative effects of Bifidobacterium longum peptide-1 on benzo(α)pyrene induced oxidative damages via daf-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Stress and Chaperones 28, 909–920 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-023-01385-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-023-01385-2