Abstract
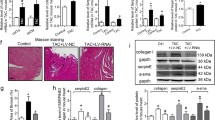
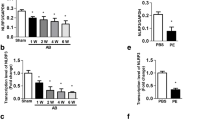
Organ fibrosis has been viewed as a major medical problem that leads to progressive dysfunction of the organ and eventually the death of patients. Stress-related hormone norepinephrine (NE) has been reported to exert fibrogenic actions in the injured organ. Nix plays a critical role in pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling and heart failure through mediating cardiomyocyte apoptosis. However, cardiac remodeling also includes fibrosis. Whether Nix is involved in stress-induced fibrosis remains unclear. The present study was designed to determine the role of Nix in NE-induced NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. The results showed that Nix was upregulated and closely associated with cell proliferation, collagen and fibronectin expression in NIH/3T3 fibroblasts following NE treatment. Overexpression of Nix promoted collagen and fibronectin expression, whereas the suppression of Nix resulted in a strong reduction in collagen and fibronectin expression. Moreover, the increases in collagen and fibronectin expression induced by NE were successively increased when Nix was overexpressed and reduced when Nix was inhibited. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the PKC activation is responsible for the upregulation of Nix induced by NE. Inhibition of Nix expression with α-adrenoceptor antagonist, β-adrenoceptor antagonist or PKC inhibitor attenuated NE-induced collagen and fibronectin expression. Our data revealed that Nix is a novel mediator of NE-induced fibrosis. Thus, it would provide a new insight into the development of effective preventative measures and therapies of tissue fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Ahmad R (2012) Understanding the mechanism of hepatic fibrosis and potential therapeutic approaches. Saudi J Gastroenterol Off J Saudi Gastroenterol Assoc 18(3):155–167. doi:10.4103/1319-3767.96445
Akiyama-Uchida Y, Ashizawa N, Ohtsuru A, Seto S, Tsukazaki T, Kikuchi H, Yamashita S, Yano K (2002) Norepinephrine enhances fibrosis mediated by TGF-beta in cardiac fibroblasts. Hypertension 40(2):148–154
Bassi G, Radermacher P, Calzia E (2006) Catecholamines and vasopressin during critical illness. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35(4):839–857. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2006.09.012, x
Bentmann A, Kawelke N, Moss D, Zentgraf H, Bala Y, Berger I, Gasser JA, Nakchbandi IA (2010) Circulating fibronectin affects bone matrix, whereas osteoblast fibronectin modulates osteoblast function. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 25(4):706–715. doi:10.1359/jbmr.091011
Bernini G, Galetta F, Franzoni F, Bardini M, Taurino C, Moretti A, Bernini M, Berti P, Miccoli P, Salvetti A (2008) Normalization of catecholamine production following resection of phaeochromocytoma positively influences carotid vascular remodelling. Eur J Endocrinol Eur Fed Endocr Soc 159(2):137–143. doi:10.1530/EJE-08-0126
Chou SF, Chen HL, Lu SC (2003) Sp1 and Sp3 are involved in up-regulation of human deoxyribonuclease II transcription during differentiation of HL-60 cells. Eur J Biochem FEBS 270(8):1855–1862
Delcayre C, Swynghedauw B (2002) Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. The role of aldosterone. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34(12):1577–1584
Diwan A, Wansapura J, Syed FM, Matkovich SJ, Lorenz JN, Dorn GW 2nd (2008) Nix-mediated apoptosis links myocardial fibrosis, cardiac remodeling, and hypertrophy decompensation. Circulation 117(3):396–404. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.727073
Diwan A, Matkovich SJ, Yuan Q, Zhao W, Yatani A, Brown JH, Molkentin JD, Kranias EG, Dorn GW 2nd (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria crosstalk in NIX-mediated murine cell death. J Clin Invest 119(1):203–212. doi:10.1172/JCI36445
Dorn GW 2nd (2005) Physiologic growth and pathologic genes in cardiac development and cardiomyopathy. Trends Cardiovasc Med 15(5):185–189. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2005.05.009
Dorn GW 2nd, Kirshenbaum LA (2008) Cardiac reanimation: targeting cardiomyocyte death by BNIP3 and NIX/BNIP3L. Oncogene 27(Suppl 1):S158–S167. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.53
Edgley AJ, Krum H, Kelly DJ (2012) Targeting fibrosis for the treatment of heart failure: a role for transforming growth factor-beta. Cardiovasc Ther 30(1):e30–e40. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00228.x
Flint MS, Baum A, Episcopo B, Knickelbein KZ, Liegey Dougall AJ, Chambers WH, Jenkins FJ (2013) Chronic exposure to stress hormones promotes transformation and tumorigenicity of 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Stress 16(1):114–121. doi:10.3109/10253890.2012.686075
Galvez AS, Brunskill EW, Marreez Y, Benner BJ, Regula KM, Kirschenbaum LA, Dorn GW 2nd (2006) Distinct pathways regulate proapoptotic Nix and BNip3 in cardiac stress. J Biol Chem 281(3):1442–1448. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509056200
Goldstein DS (2003) Catecholamines and stress. Endocr Regul 37(2):69–80
Greenhalgh SN, Iredale JP, Henderson NC (2013) Origins of fibrosis: pericytes take centre stage. F1000 Prime Rep 5:37. doi:10.12703/P5-37
Igreja AC, Mesquita Kde C, Cowper SE, Costa IM (2012) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: concepts and perspectives. An Bras Dermatol 87(4):597–607
Kehat I, Molkentin JD (2010) Molecular pathways underlying cardiac remodeling during pathophysiological stimulation. Circulation 122(25):2727–2735. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.942268
Kim J, Padanilam BJ (2013) Renal nerves drive interstitial fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 24(2):229–242. doi:10.1681/ASN.2012070678
Kim E, Muga SJ, Fischer SM (2004) Identification and characterization of a phorbol ester-responsive element in the murine 8S-lipoxygenase gene. J Biol Chem 279(12):11188–11197. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313291200
Kimura K, Iwano M (2009) Molecular mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. Nihon Rinsho Men’eki Gakkai Kaishi Jpn J Clin Immunol 32(3):160–167
Kohli S, Chhabra A, Jaiswal A, Rustagi Y, Sharma M, Rani V (2013) Curcumin suppresses gelatinase B mediated norepinephrine induced stress in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. PLoS One 8(10):e76519. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076519
Lewis D, Scullion J (2012) Palliative and end-of-life care for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: challenges and dilemmas. Int J Palliat Nurs 18(7):331–337
Liu Y (2011) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol 7(12):684–696. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2011.149
Noble PW, Barkauskas CE, Jiang D (2012) Pulmonary fibrosis: patterns and perpetrators. J Clin Investig 122(8):2756–2762. doi:10.1172/JCI60323
Oben JA, Yang S, Lin H, Ono M, Diehl AM (2003) Norepinephrine and neuropeptide Y promote proliferation and collagen gene expression of hepatic myofibroblastic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302(4):685–690
Oben JA, Roskams T, Yang S, Lin H, Sinelli N, Torbenson M, Smedh U, Moran TH, Li Z, Huang J, Thomas SA, Diehl AM (2004) Hepatic fibrogenesis requires sympathetic neurotransmitters. Gut 53(3):438–445
Oberbeck R (2006) Catecholamines: physiological immunomodulators during health and illness. Curr Med Chem 13(17):1979–1989
Oka T, Komuro I (2012) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of organ fibrosis. Nihon Rinsho Jpn J Clin Med 70(9):1510–1516
Okuneva V, Zhvania M, Japaridze N, Gelazonia L, Lordkipanidze T (2009) Stress-system: corticotropin-releasing hormone and catecholamines (review). Georgian Med News 172–173:65–69
Polyakova V, Loeffler I, Hein S, Miyagawa S, Piotrowska I, Dammer S, Risteli J, Schaper J, Kostin S (2011) Fibrosis in endstage human heart failure: severe changes in collagen metabolism and MMP/TIMP profiles. Int J Cardiol 151(1):18–33. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.04.053
Rassler B, Marx G, Schierle K, Zimmer HG (2012) Catecholamines can induce pulmonary remodeling in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 30(5):1134–1147. doi:10.1159/000343304
Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, Scaringe S, Marshall WS, Khvorova A (2004) Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 22(3):326–330. doi:10.1038/nbt936
Sakamoto S, Taniguchi T (2001) Identification of a phorbol ester-responsive element in the interferon-gamma receptor 1 chain gene. J Biol Chem 276(40):37237–37241. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105543200
Shao Y, Redfors B, Stahlman M, Tang MS, Miljanovic A, Mollmann H, Troidl C, Szardien S, Hamm C, Nef H, Boren J, Omerovic E (2013) A mouse model reveals an important role for catecholamine-induced lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of stress-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail 15(1):9–22. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfs161
Sottile J, Hocking DC (2002) Fibronectin polymerization regulates the composition and stability of extracellular matrix fibrils and cell-matrix adhesions. Mol Biol Cell 13(10):3546–3559. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-01-0048
Tanaka T, Kurabayashi M, Aihara Y, Ohyama Y, Nagai R (2000) Inducible expression of manganese superoxide dismutase by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate is mediated by Sp1 in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(2):392–401
Taylor M, Barr M, Stevens G, Bryson-Taylor D, Agho K, Jacobs J, Raphael B (2010) Psychosocial stress and strategies for managing adversity: measuring population resilience in New South Wales, Australia. Popul Health Metrics 8:28. doi:10.1186/1478-7954-8-28
Velling T, Risteli J, Wennerberg K, Mosher DF, Johansson S (2002) Polymerization of type I and III collagens is dependent on fibronectin and enhanced by integrins alpha 11beta 1 and alpha 2beta 1. J Biol Chem 277(40):37377–37381. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206286200
Yang Q, Zhang YW, Liu HY, Song YH, Tang WX (2008) Effects of norepinephrine on the proliferation and activation of rat hepatic stellate cells. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi Chin J Hepatol 16(11):844–848
Yussman MG, Toyokawa T, Odley A, Lynch RA, Wu G, Colbert MC, Aronow BJ, Lorenz JN, Dorn GW 2nd (2002) Mitochondrial death protein Nix is induced in cardiac hypertrophy and triggers apoptotic cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 8(7):725–730. doi:10.1038/nm719
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank professors Gerald W. Dorn II for providing the Nix plasmid. This work was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31071022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Wang, X., Gong, J. et al. The stress-related hormone norepinephrine induced upregulation of Nix, contributing to ECM protein expression. Cell Stress and Chaperones 19, 903–912 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0515-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0515-6