Abstract
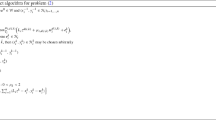
In this paper, we consider additive convex optimization problems in which the objective function is the sum of a large number of convex nondifferentiable cost functions. We assume that each cost function is specifically written as the sum of two convex nondifferentiable functions in which one function is appropriate for the subgradient method, and another one is not. To this end, we propose a distributed optimization algorithm based on the subgradient and proximal methods. The proposed method is also governed by an asynchronous feature that allows time-varying delays when computing the subgradients. We prove the convergences of function values of iterates to the optimal value. To demonstrate the efficiency of the presented theoretical result, we investigate the binary classification problem via support vector machine learning.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets that support the findings of this study are available as follows: (i) The hiseq dataset is available from https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/gene+expression+cancer+RNA-Seq. (ii) The DrivFace dataset is available from https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/DrivFace. (iii) The gisette dataset is available from https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvmtools/datasets/binary.html#gisette.
References
Aybat, N., Wang, Z., Iyengar, G.: An asynchronous distributed proximal gradient method for composite convex optimization. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2454–2462. PMLR (2015)
Aytekin, A.: Asynchronous first-order algorithms for large-scale optimization: analysis and Implementation. PhD thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology (2019)
Bartlett, P.L., Wegkamp, M.H.: Classification with a reject option using a hinge loss. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(8), 1823–1840 (2008)
Bauschke, H.H., Combettes, P.L.: Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces. CMS Books in Mathematics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2017)
Beck, A.: First-Ordered Methods in Optimization. SIAM, Philadelphia (2017)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Incremental proximal methods for large scale convex optimization. Math. Program. 129, 163–195 (2011)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Convex Optimization Algorithms. Athena Scientific, Belmont (2015)
Bertsekas, D.P., Nedić, A., Ozdaglar, A.E.: Convex Analysis and Optimization. Athena Scientific, Belmont (2003)
Blatt, D., Hero, A.O., Gauchman, H.: A convergent incremental gradient method with a constant step size. SIAM J. Optim. 18, 29–51 (2007)
Cegielski, A.: Iterative Methods for Fixed Point Problems in Hilbert Spaces. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 2057. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Ekkarntrong, N., Arunrat, T., Nimana, N.: Convergence of a distributed method for minimizing sum of convex functions with fixed point constraints. J. Inequalities Appl. 197 (2021)
Gurbuzbalaban, M., Ozdaglar, A., Parrilo, P.A.: On the convergence rate of incremental aggregated gradient algorithms. SIAM J. Optim. 27, 1035–1048 (2017)
Hishinuma, K., Iiduka, H.: Incremental and parallel machine learning algorithms with automated learning rate adjustments. Front. Robot. AI 6, 77 (2019)
Iiduka, H.: Fixed point optimization algorithms for distributed optimization in networked systems. SIAM J. Optim. 23(1), 1–26 (2013)
Iiduka, H.: Distributed optimization for network resource allocation with nonsmooth utility functions. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 6(4), 1354–1365 (2019)
Li, Z., Shi, W., Yan, M.: A decentralized proximal-gradient method with network independent step-sizes and separated convergence rates. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67, 4494–4506 (2019)
Li, X., Feng, G., Xie, L.: Distributed proximal algorithms for multi-agent optimization with coupled inequality constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 66(3), 1223–1230 (2021)
Martinet, B.: Determination approchee d’un point fixe d’une application pseudocontractante. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 274A, 163–165 (1972)
Namsak, S., Petrot, N., Nimana, N.: A distributed proximal gradient method with time-varying delays for solving additive convex optimizations. Results Appl. Math. 18, 100370 (2023)
Nedic, A., Olshevsky, A., Ozdaglar, A., Tsitsiklis, J.N.: Distributed subgradient methods and quantization effects. In: 2008 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. https://doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2008.4738860
Nedic, A., Ozdaglar, A.: Distributed subgradient methods for multi-agent optimization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 51(1), 48–61 (2009)
Nedic, A., Ozdaglar, A., Parril, P.A.: Constraint consensus and optimization in multi-agent networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(4), 922–938 (2010)
Niu, Y., Li, H., Wang, Z., Lu, Q., Xia, D., Ji, L.: A distributed stochastic proximal-gradient algorithm for composite optimization. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 8(3), 1383–1393 (2021)
Notarnicola, I., Notarstefano, G.: Asynchronous distributed optimization via a randomized dual proximal gradient. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62, 2095–2106 (2017)
Petrot, N., Nimana, N.: Incremental proximal gradient scheme with penalization for constrained composite convex optimization problems. Optimization 70(5–6), 1307–1336 (2021)
Ram, S.S., Nedic, A., Veeravall, V.V.: Distributed stochastic subgradient projection algorithms for convex optimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 147(3), 516–545 (2010)
Tsianos, K.I., Rabbat, M.G.: Distributed dual averaging for convex optimization under communication delays. In: Proc. Amer. Control Conf., pp. 1067–1072 (2012)
Tsitsiklis, J., Bertsekas, D., Athans, M.: Distributed asynchronous deterministic and stochastic gradient optimization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 31, 803–812 (1986)
Vanli, N.D., Gurbuzbalaban, M., Ozdaglar, A.: Global convergence rate of proximal incremental aggregated gradient methods. SIAM J. Optim. 28, 1282–1300 (2018)
Wang, H., Liao, X., Huang, T., Li, C.: Cooperative distributed optimization in multiagent networks with delays. IEEE Trans. SMC 45(2), 363–369 (2015)
Wu, T., Yuan, K., Ling, Q., Yin, W., Sayed, A.H.: Decentralized consensus optimization with asynchrony and delays. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Netw. 4(2), 293–307 (2018)
Yang, T., Mahdavi, M., Jin, R., Zhu, S.: An efficient primal-dual prox method for non-smooth optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 98(3), 369–406 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Editor and two anonymous referees for comments and remarks which improved the quality and presentation of the paper. T. Arunrat was supported by the Development and Promotion of Science and Technology Talents Project (DPST).
Funding
This work has received funding support from the NSRF via the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research and Innovation [Grant No. B05F650018].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arunrat, T., Namsak, S. & Nimana, N. An asynchronous subgradient-proximal method for solving additive convex optimization problems. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 69, 3911–3936 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-023-01908-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-023-01908-1