Abstract
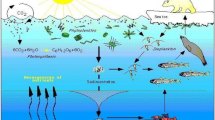
It is well recognized that the greenhouse gas such as Chlorofluoro Carbon (CFC) is responsible for the increase in the average global temperature. The presence of CFC is responsible for the depletion of ozone concentration in the atmosphere due to which the heat accompanied with the sun rays are less absorbed causing increase in the atmospheric temperature of the Earth. The increase in temperature level may directly or indirectly affect the dynamics of interacting species systems. Therefore, in this paper, a mathematical model is proposed and analysed to asses the effects of increasing temperature on the survival or extinction of two competing populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams, P.A.: Describing and quantifying interspecific interactions: a commentary on recent approaches. Oikos 94, 209–218 (2001)
Bertness, M.D., Ewanchuk, P.J.: Latitudinal and climate-driven variation in the strength and nature of biological interactions in New England marshes. Oecologia 132, 392–401 (2002)
Brown, J.H., Valone, T.J., Curtain, C.G.: Reorganization of an arid ecosystem in response to recent climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9729–9733 (1997)
Coulson, T., Catchpole, E.A., Albon, S.D., Morgan, B.J.T., Pemberton, J.M., Clutton-Brock, T.H., Crawley, M.J., Grenfell, B.T.: Age, sex, density, winter weather, and population crashes in soay sheep. Science 292, 1528–1531 (2001)
Davis, A.J., Jenkins, L.S., Lawton, J.H., Shorrocks, B., Wood, S.: Making mistakes when predicting shifts in species range in response to global warming. Nature 391, 783–786 (1998a)
Davis, A.J., Lawton, J.H., Shorrocks, B., Jenkinson, L.S.: Individualistic species responses invalidate simple physiological models of community dynamics under global environmental change. J. Anim. Ecol. 67, 600–612 (1998b)
Edwards, M., Richardson, A.J.: Impact of climate change on marine pelagic phenology and trophic and mismatch. Nature 430, 881–884 (2004)
Fox, J.W., Morin, P.J.: Effects of intra- and interspecific interactions on species responses to environmental change. J. Anim. Ecol. 70, 80–90 (2001)
Hughes, L.: Biological consequences of global warming: is the signal already apparent? Trends Ecol. Evol. 15, 56–61 (2000)
Ives, A.R.: Predicting the response of populations to environmental change. Ecology 76, 926–941 (1995)
Ives, A.R., Gilchrist, G.: Climate change and ecological interactions. In: Kareiva, P.M., Kingsolver, J.G., Huey, R.B. (eds.) Biotic Interactions and Global Change, pp. 120–146. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland (1993)
Jing, L., Morin, P.J.: Temperature-dependent interactions explain unexpected responses to environmental warming in communities of competitors. J. Anim. Ecol. 73, 569–576 (2004)
McCarty, J.P.: Ecological consequences of recent climate change. Conserv. Biol. 15, 320–331 (2001)
Parmesan, C., Yohe, G.: A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 421, 37–42 (2003)
Petchey, O.L., Brose, U., Rall, B.C.: Predicting the effects of temperature on food web connectance. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 365, 2081–2091 (2010)
Root, T.L., Price, J.T., Hall, K.R., Schneider, S.H., Rosenzweig, C., Pounds, J.A.: Fingerprints of global warming on wild animals and plants. Nature 421, 57–60 (2003)
Sanford, E.: Regulation of keystone predation by small changes in ocean temperature. Science 283, 2095–2097 (1999)
Sarmento, H., Montoya, J.M., Vazquez-Dominguez, E., Vaque, D., Gasol, J.M.: Warming effect on marine food web processes: how far can we go when it comes to predictions? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 365, 2137–2149 (2010)
Singer, S.F.: Stratospheric Ozone: Science, Policy, Global Climate Change. Paragon House, New York (1989)
Stenseth, N.C., Mysterud, A., Ottersen, G., Hurrell, J.W., Chan, K.S., Lima, M.: Ecological effects of climate fluctuations. Science 297, 1292–1296 (2002)
Stordal, F., Isaken, I.S.A.: In: USEPA and UNEP, Washington, DC (1986)
Walther, G.R., Post, E., Convey, P., Menzel, A., Parmesan, C., Beebee, T.J.C., Fromentin, J.M., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Bairlein, F.: Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 416, 389–395 (2002)
Wollkind, D.J., Logan, J.A.: Temperature-dependent predator-prey mite ecosystem on apple tree foliage. J. Math. Biol. 6, 265–283 (1978)
Wollkind, D.J., Collings, J.B., Logan, J.A.: Metastability in a temperature-dependent model system for predator-prey mite outbreak interactions on fruit trees. Bull. Math. Biol. 50, 379–409 (1988)
Yvon-Durocher, G., Jones, J.I., Trimmer, M., Woodward, G., Montoya, J.M.: Warming alters the metabolic balance of ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 365, 2117–2126 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misra, O.P., Kalra, P., Rathore, S.K.S. et al. Effect of increasing temperature due to depletion of ozone layer caused by CFC on the dynamics of two competing populations: a model. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 38, 279–293 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-011-0478-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-011-0478-z