Abstract
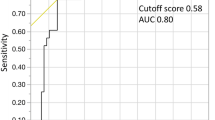
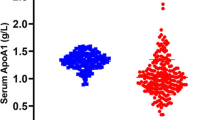
Various systems for predicting the prognosis of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) have been developed. However, associations between performance status (PS) and prognosis of MDS require further investigation. To objectively assess the impact of PS on survival, we examined laboratory findings associated with PS, including serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), albumin (ALB), and total cholesterol (CHOL). Patients (n = 123; male 86, female 37; median age 74 yrs.) diagnosed with MDS or myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms at Kanazawa Medical University Hospital between 2010 and 2020 were enrolled and grouped by cutoff values determined by receiver operating characteristic analysis: 0.44 mg/dL for CRP, 4.0 g/dL for ALB, and 120 mg/dL for CHOL. The median follow-up period was 17.6 months. Kaplan–Meier analysis revealed that overall survival (OS) in the high CRP, low ALB, and low CHOL groups was significantly shorter than in the low CRP, high ALB, and high CHOL groups, respectively. Multivariable analysis revealed that elevated serum CRP was an independent prognostic risk factor independent of gender, bone marrow blast percentage, and cytogenetics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang YH. Myelodysplastic syndromes and overlap syndromes. Blood Res. 2021;56:S51-s64.
Garcia-Manero G, Chien KS, Montalban-Bravo G. Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2021 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2020;95:1399–420.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89:2079–88.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Sole F, et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2012;120:2454–65.
Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G, et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2496–506.
Bejar R, Stevenson KE, Caughey BA, Abdel-Wahab O, Steensma DP, Galili N, et al. Validation of a prognostic model and the impact of mutations in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:3376–82.
Sotirova T, Stojanovic A, Genadieva-Stavric S, Krstevska S, Spasovski D, Balkanov T. Influence of prognostic factors on overall survival in myelodysplastic syndromes. Mater Sociomed. 2014;26:292–6.
Kawabata H, Usuki K, Shindo-Ueda M, Kanda J, Tohyama K, Matsuda A, et al. Serum ferritin levels at diagnosis predict prognosis in patients with low blast count myelodysplastic syndromes. Int J Hematol. 2019;110:533–42.
Tennant GB, Al-Sabah AI, Burnett AK. Prognosis of myelodysplasic patients: non-parametric multiple regression analysis of populations stratified by mean corpuscular volume and marrow myeloblast number. Br J Haematol. 2002;119:87–96.
Wang H, Wang X, Xu X, Lin G. Mean corpuscular volume predicts prognosis in MDS patients with abnormal karyotypes. Ann Hematol. 2010;89:671–9.
Baba Y, Saito B, Shimada S, Sasaki Y, Murai S, Abe M, et al. Association of red cell distribution width with clinical outcomes in myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2018;67:56–9.
Bejar R. Clinical and genetic predictors of prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica. 2014;99:956–64.
Papageorgiou SG, Kotsianidis I, Bouchla A, Symeonidis A, Galanopoulos A, Viniou NA, et al. Serum ferritin and ECOG performance status predict the response and improve the prognostic value of IPSS or IPSS-R in patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia treated with 5-azacytidine: a retrospective analysis of the Hellenic national registry of myelodysplastic and hypoplastic syndromes. Ther Adv Hematol. 2020;11:2040620720966121.
Nazha A, Hu ZH, Wang T, Lindsley RC, Abdel-Azim H, Aljurf M, et al. A personalized prediction model for outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26:2139–46.
McMillan DC. The systemic inflammation-based Glasgow Prognostic Score: a decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39:534–40.
Dolan RD, Laird BJA, Klepstad P, Kaasa S, Horgan PG, Paulsen Ø, et al. An exploratory study examining the relationship between performance status and systemic inflammation frameworks and cytokine profiles in patients with advanced cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98: e17019.
Chidambaram V, Zhou L, Ruelas Castillo J, Kumar A, Ayeh SK, Gupte A, et al. Higher serum cholesterol levels are associated with reduced systemic inflammation and mortality during tuberculosis treatment independent of body mass index. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:696517.
Liu Y, Coresh J, Eustace JA, Longenecker JC, Jaar B, Fink NE, et al. Association between cholesterol level and mortality in dialysis patients: role of inflammation and malnutrition. JAMA. 2004;291:451–9.
Shibata H. Nutritional factors on longevity and quality of life in Japan. J Nutr Health Aging. 2001;5:97–102.
WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, France, 2017.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982;51:189–99.
Schanz J, Tuchler H, Sole F, Mallo M, Luno E, Cervera J, et al. New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia after MDS derived from an international database merge. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:820–9.
Akobeng AK. Understanding diagnostic tests 3: Receiver operating characteristic curves. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96:644–7.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:452–8.
Ganter U, Arcone R, Toniatti C, Morrone G, Ciliberto G. Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Embo j. 1989;8:3773–9.
Andus T, Geiger T, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Tran-Thi TA, Decker K, et al. Regulation of synthesis and secretion of major rat acute-phase proteins by recombinant human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IL-6) in hepatocyte primary cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1988;173:287–93.
Komrokji RS, Corrales-Yepez M, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Al Ali NH, Padron E, Rollison DE, et al. Hypoalbuminemia is an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Hematol. 2012;87:1006–9.
Ohno Y, Nakashima J, Nakagami Y, Gondo T, Ohori M, Hatano T, et al. Clinical implications of preoperative serum total cholesterol in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2014;83:154–8.
Gao R, Liang JH, Wang L, Zhu HY, Wu W, Cao L, et al. Low serum cholesterol levels predict inferior prognosis and improve NCCN-IPI scoring in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 2018;143:1884–95.
Tang J, Yin H, Wu JZ, Xia Y, Liang JH, Chen RZ, et al. Low serum cholesterol levels predict inferior prognosis and improve prognostic index scoring for peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Leuk Res. 2021;103:106534.
Artz AS, Logan B, Zhu X, Akpek G, Bufarull RM, Gupta V, et al. The prognostic value of serum C-reactive protein, ferritin, and albumin prior to allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica. 2016;101:1426–33.
Sakamoto S, Kawabata H, Kanda J, Uchiyama T, Mizumoto C, Kondo T, et al. Differing impacts of pretransplant serum ferritin and C-reactive protein levels on the incidence of chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2013;97:109–16.
Baba Y, Saito B, Shimada S, Sasaki Y, Fujiwara S, Arai N, et al. Increased serum C-reactive protein is an adverse prognostic factor in low-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Int J Hematol. 2021;114:441–8.
Arinobu Y, Kashiwado Y, Miyawaki K, Ayano M, Kimoto Y, Mitoma H, et al. Autoimmune manifestations associated with myelodysplastic syndrome predict a poor prognosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e25406.
Komrokji RS, Kulasekararaj A, Al Ali NH, Kordasti S, Bart-Smith E, Craig BM, et al. Autoimmune diseases and myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:E280–3.
Zhang Q, Zhao K, Shen Q, Han Y, Gu Y, Li X, et al. Tet2 is required to resolve inflammation by recruiting Hdac2 to specifically repress IL-6. Nature. 2015;525:389–93.
Busque L, Sun M, Buscarlet M, Ayachi S, Feroz Zada Y, Provost S, et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is associated with clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2430–8.
Jaiswal S, Natarajan P, Silver AJ, Gibson CJ, Bick AG, Shvartz E, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis and risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:111–21.
Asada S, Kitamura T. Clonal hematopoiesis and associated diseases: a review of recent findings. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:3962–71.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (17591060 to Y. Masaki), Kanazawa Medical University Research Foundation (S2004-16, S2007-5 to Y. Masaki). Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, H29 Nanchi, Yasufumi Masaki, etc. (Nan)-General-019, Yasufumi Masaki, H27-28 Nanchi, Yasufumi Masaki, etc. (Nan)-General-002, Yasufumi Masaki,-008, Yasufumi Masaki, the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Grant No.17591060, Yasufumi Masaki, 15K09510, Yasufumi Masaki, Kanazawa Medical University, Grant Nos. S2004-16, Yasufumi Masaki, S2007-5, Yasufumi Masaki, Grant No. K2011-7, Yasufumi Masaki, Grant No. H2011-11, Yasufumi Masaki, AR2012-06, Yasufumi Masaki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict-of-interest
YM received research grants from Kyowa Kirin Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Eisai Pharma, Ono Pharma, Pfizer Pharma, Asahi Kasei Pharma, MSD Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo Pharma, Taisho Pharma, Taiho Pharma, Takeda Pharma, Chugai Pharma, Teijin Pharma, Nippon Kayaku, and Mochida Pharma, outside the submitted work. All other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Yanagisawa, H., Kawabata, H., Ueda, Y. et al. Prognostic impacts of serum levels of C-reactive protein, albumin, and total cholesterol in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Int J Hematol 116, 81–88 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03321-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03321-z