Abstract
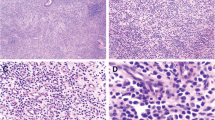
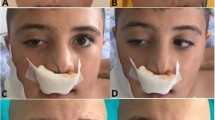
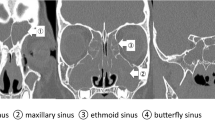
A 44-year-old Japanese man presented with fever and sore throat. He had a history of refractory chronic sinusitis that did not respond to several years of pharmacotherapy, and underwent endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) 5 months prior to his presentation, but his symptoms persisted. A biopsy specimen was taken from the right nasal cavity, and extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) was diagnosed. Two years after complete remission was achieved by chemoradiation therapy, he developed hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) without recurrence of ENKTL. Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-DNA copy number was relatively high and EBV-infected lymphocytes (CD8 + T cells) were detected in the peripheral blood. Pathological review of the biopsy specimens taken during ESS showed that CD8 + T cells with slightly atypia infiltrating the stroma were EBV positive. These findings suggested that the patient had underlying chronic active EBV infection (CAEBV) that caused the refractory chronic sinusitis, eventually developed into ENKTL, and also caused HLH. Clinicians should consider adult-onset CAEBV in the differential diagnosis of patients with refractory chronic sinusitis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimura H, Ito Y, Kawabe S, Gotoh K, Takahashi Y, Kojima S, et al. EBV-associated T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases in nonimmunocompromised hosts: prospective analysis of 108 cases. Blood. 2012;119:673–86.
Cohen JI, Jaffe ES, Dale JK, Pittaluga S, Heslop HE, Rooney CM, et al. Characterization and treatment of chronic active Epstein–Barr virus disease: a 28-year experience in the United States. Blood. 2011;117:5835–49.
Arai A, Imadome KI, Watanabe Y, Yoshimori M, Koyama T, Kawaguchi T, et al. Clinical features of adult-onset chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection: a retrospective analysis. Int J Hematol. 2011;93:602–9.
Kawamoto K, Miyoshi H, Suzuki T, Kozai Y, Kato K, Miyahara M, et al. A distinct subtype of Epstein–Barr virus-positive t/nk-cell lymphoproliferative disorder: Adult patients with chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection-like features. Haematologica. 2018;103:1018–28.
Yonese I, Sakashita C, Imadome KI, Kobayashi T, Yamamoto M, Sawada A, et al. Nationwide survey of systemic chronic active EBV infection in Japan in accordance with the new WHO classification. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2918–26.
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3059–67.
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H, et al. A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:389–400.
Yamaguchi M, Suzuki R, Oguchi M, Asano N, Amaki J, Akiba T, et al. Treatments and outcomes of patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma diagnosed between 2000 and 2013: a cooperative study in Japan. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:32–9.
Kasahara YYA, Takei K, Kanegane C, Okada K, Ohta K, Seki H, Igarashi N, Maruhashi K, Katayama K, Katoh E, Terao G, Sakiyama Y, Koizumi S. Differential cellular targets of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection between acute EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and chronic active EBV infection. Blood. 2001;98:1882–8.
Trempat P, Tabiasco J, Andre P, Faumont N, Meggetto F, Delsol G, et al. Evidence for early infection of nonneoplastic natural killer cells by Epstein–Barr virus. J Virol. 2002;76:11139–42.
Kimura H. Pathogenesis of chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection: is this an infectious disease, lymphoproliferative disorder, or immunodeficiency? Rev Med Virol. 2006;16:251–61.
Kimura H, Cohen JI. Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus disease. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1–6.
Shimomura M, Morishita H, Meguro T, Seto S, Kimura M, Hamazaki M. Chronic active EBV infection with features of granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Pediatr Int. 2016;58:639–42.
Sedaghat AR. Chronic rhinosinusitis. Infect Ears Nose Throat Sinuses. 2018;96:155–68.
Ueno M, Nakano K, Miyagawa I, Tanaka Y. Five cases of IgG4-related disease with nasal mucosa and sinus involvement. Intern Med. 2020;59:1905–11.
Liu W, Ren J, Shu Q. Aggressive sinonasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma mimicking refractory sinusitis in a 4-year-old boy. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2012;31:288–94.
Takahashi E, Ohshima K, Kimura H, Hara K, Suzuki R, Kawa K, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of the age-related differences in patients with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-associated extranasal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma with reference to the relationship with aggressive NK cell leukaemia and chronic active EBV infection-associated lymphoproliferative disorders. Histopathology. 2011;59:660–71.
Acknowledgements
The manuscript was edited and proofread by Editage (www.editage.jp).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kitamura, W., Fujiwara, H., Matsumura, A. et al. Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection presenting as refractory chronic sinusitis. Int J Hematol 116, 139–145 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03306-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03306-y