Abstract
Background
Many studies have investigated treatment-related sequelae in Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) in high-prevalence areas, but very few have been conducted in low-prevalence areas, including Taiwan and Japan.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed 101 HL patients who had received mediastinal radiotherapy between January 1997 and April 2013.
Results
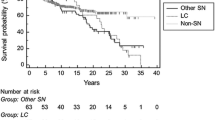
Nine patients had cardiac events and nine patients developed second malignancies. Univariate analysis showed that bulkiness of disease was significantly associated with higher incidence of cardiac events (HR 7.70, 95% CI 1.60–38.00, p = 0.012). Disease stage and cumulative dose of radiotherapy were significantly correlated with incidence of radiation pneumonitis (HR 1.40, 95% CI 1.00–2.10, p = 0.043 and HR 1.10, 95% CI 1.00–1.20, p = 0.009, respectively). All cases of grade III–IV radiation pneumonitis happened in patients receiving a radiation dose higher than 35 Gy and developed within 4 months after radiotherapy.
Conclusions
Despite the similar incidence rates of treatment-related sequelae among HL survivors between areas with high and low prevalence of HL, cardiac events and second malignancies cannot be overlooked in HL survivors in low-prevalence areas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.
Cancer registry annual report in Taiwan area. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Executive Yuan, Republic of China. 2021.
Glaser SL, Hsu JL. Hodgkin’s disease in asians: Incidence patterns and risk factors in population-based data. Leuk Res. 2002;26(3):261–9.
Tarbell NJ, Thompson L, Mauch P. Thoracic irradiation in hodgkin’s disease: disease control and long-term complications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1990;18(2):275–81.
Hodgson DC. Late effects in the era of modern therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma. ASH Educ Progr Book. 2011;2011(1):323–9.
Galper SL, Yu JB, Mauch PM, Strasser JF, Silver B, LaCasce A, et al. Clinically significant cardiac disease in patients with hodgkin lymphoma treated with mediastinal irradiation. Blood. 2011;117(2):412–8.
Swerdlow AJ, Higgins CD, Smith P, Cunningham D, Hancock BW, Horwich A, et al. Second cancer risk after chemotherapy for hodgkin’s lymphoma: A collaborative british cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2011;2011:5.
Schaapveld M, Aleman BMP, Van Eggermond AM, Janus CPM, Krol ADG, Van Der Maazen RWM, et al. Second cancer risk up to 40 years after treatment for hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(26):2499–511.
Fox AM, Dosoretz AP, Mauch PM, Chen Y-H, Fisher DC, LaCasce AS, et al. Predictive factors for radiation pneumonitis in Hodgkin lymphoma patients receiving combined-modality therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83(1):277–83.
Ailawadhi S, Swaika A, Razavi P, Yang D, Chanan-Khan A. Variable risk of second primary malignancy in multiple myeloma patients of different ethnic subgroups. Blood Cancer J. 2014;4(9):e243.
Calip GS, Law EH, Ko NY. Racial and ethnic differences in risk of second primary cancers among breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;151(3):687–96.
Litvak A, Batukbhai B, Russell SD, Tsai HL, Rosner GL, Jeter SC, et al. Racial disparities in the rate of cardiotoxicity of her2-targeted therapies among women with early breast cancer. Cancer. 2018;124(9):1904–11.
Troeschel AN, Liu Y, Collin LJ, Bradshaw PT, Ward KC, Gogineni K, et al. Race differences in cardiovascular disease and breast cancer mortality among us women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(6):1897–905.
Lim YJ, Koh J. Heart-related mortality after postoperative breast irradiation in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ in the contemporary radiotherapy era. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):2790.
Collin LJ, Troeschel AN, Liu Y, Gogineni K, Borger K, Ward KC, et al. A balancing act: racial disparities in cardiovascular disease mortality among women diagnosed with breast cancer. Ann Cancer Epidemiol. 2020;2020:4.
Engert A, Plütschow A, Eich HT, Lohri A, Dörken B, Borchmann P, et al. Reduced treatment intensity in patients with early-stage hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(7):640–52.
Chen J, Li W, Xiang M. Burden of valvular heart disease, 1990–2017: results from the global burden of disease study 2017. J Glob Health. 2020;10:2.
Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, Bennet AM, Blom-Goldman U, Brønnum D, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(11):987–98.
Koh E-S, Sun A, Tran TH, Tsang R, Pintilie M, Hodgson DC, et al. Clinical dose-volume histogram analysis in predicting radiation pneumonitis in hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(1):223–8.
Eich HT, Diehl V, Görgen H, Pabst T, Markova J, Debus J, et al. Intensified chemotherapy and dose-reduced involved-field radiotherapy in patients with early unfavorable hodgkin’s lymphoma: final analysis of the german hodgkin study group hd11 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4199–206.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at Linkou, Taiwan, under grants CMRPG3J0181, CMRPG3G1211, CMRPG3G1212, and CMRPG3G1213. The authors also thank Ms. Hsiao-Jung Tseng for statistical consultation, which was supported by grant for Biostatistical Center from Clinical Research, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CLRPG340599).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, E.YL., Tsan, DL., Chiang, Yy. et al. Treatment-related sequelae in Hodgkin’s lymphoma after mediastinal irradiation. Int J Hematol 115, 363–370 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-021-03264-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-021-03264-x