Abstract
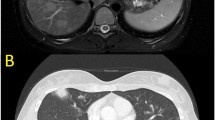
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis (LYG) is a rare Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-driven B-cell lymphoproliferative disease affecting mainly extranodal sites such as the lung, central nervous system (CNS), skin, kidney, and liver. We report a case of low-grade LYG involving the CNS that was successfully treated with interferon alpha (IFNα). A 69-year-old woman developed necrotic erythema of the skin and was initially diagnosed with pyoderma gangrenosum based on skin biopsy. She showed a limited response to prednisolone. Approximately 6 months after the initial onset, low-grade LYG was diagnosed after detection of CNS lesions on brain biopsy. The whole blood EBV-DNA load determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction was slightly elevated. Two months into IFNα therapy, skin and CNS lesions had responded favorably and the EBV-DNA load decreased. IFNα plays an important role in treatment of LYG through its antiproliferative, immunomodulatory, and anti-EBV effects. To our knowledge, this is the first case report of successful treatment with IFNα in Japan. Further investigation is necessary to determine optimal use of IFNα for LYG.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liebow AA, Carrington CR, Friedman PJ. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Hum Pathol. 1972;3:457–558.
Colby TV. Current histological diagnosis of lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(Suppl 1):S39-42.
Melani C, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH. Pathobiology and treatment of lymphomatoid granulomatosis, a rare EBV-driven disorder. Blood. 2020;135:1344–52.
Wilson WH, Kingma DW, Raffeld M, Wittes RE, Jaffe ES. Association of lymphomatoid granulomatosis with Epstein–Barr viral infection of B lymphocytes and response to interferon-alpha 2b. Blood. 1996;87:4531–7.
Dunleavy K, Chattopadhyay P, Kawada J, Calattini S, Gostick E, Price D, et al. Immune characteristics associated with lymphomatoid granulomatosis and outcome following treatment with interferon-alpha. Blood. 2010;116:963.
Melani C, Roschewski M, Pittaluga S, Cohen J, Lucas AN, Steinberg SM, et al. Phase II study of interferon-alpha and DA-EPOCH+/−R in lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Blood. 2018;132:785.
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1244.
Fujimoto A, Ikejiri F, Arakawa F, Ito S, Okada Y, Takahashi F, et al. Simultaneous discordant B-lymphoblastic lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2021;155:308–17.
Kobayashi S, Kikuchi Y, Sato K, Matsukuma S, Matsuki Y, Horikoshi H, et al. Reversible iatrogenic, MTX-associated EBV-driven lymphoproliferation with histopathological features of a lymphomatoid granulomatosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Hematol. 2013;92:1561–4.
Aiko N, Sekine A, Umeda S, Katano T, Matama G, Isomoto K, et al. The spontaneous regression of grade 3 methotrexate-related lymphomatoid granulomatosis: a case report and literature review. Intern Med. 2018;57:3163–7.
Fassas A, Jagannath S, Desikan KR, Shah HR, Shaver R, Waldron J, et al. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis following autologous stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999;23:79–81.
Kwon EJ, Katz KA, Draft KS, Seykora JT, Rook AH, Wasik MA, et al. Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease with features of lymphomatoid granulomatosis in a lung transplant patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:657–63.
Haque AK, Myers JL, Hudnall SD, Gelman BB, Lloyd RV, Payne D, et al. Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: lesions with Epstein–Barr virus infection. Mod Pathol. 1998;11:347–56.
Kano Y, Kodaira M, Ushiki A, Kosaka M, Yamada M, Shingu K, et al. The complete remission of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated isolated central nervous system lymphomatoid granulomatosis: a case report and review of the literature. Intern Med. 2017;56:2497–501.
Song JY, Pittaluga S, Dunleavy K, Grant N, White T, Jiang L, et al. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis—a single institute experience: pathologic findings and clinical correlations. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39:141–56.
Patsalides AD, Atac G, Hedge U, Janik J, Grant N, Jaffe ES, et al. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis: abnormalities of the brain at MR imaging. Radiology. 2005;237:265–73.
Shapiro RS, Chauvenet A, McGuire W, Pearson A, Craft AW, McGlave P, et al. Treatment of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders with interferon alfa and intravenous gamma globulin. N Engl J Med. 1988;318:1334.
Faro A. Interferon-alpha and its effects on post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1998;20:425–36.
Raison CL, Borisov AS, Majer M, Drake DF, Pagnoni G, Woolwine BJ, et al. Activation of central nervous system inflammatory pathways by interferon-alpha: relationship to monoamines and depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:296–303.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to Fumiko Arakawa, Ph.D. of Department of Pathology, Kurume University School of Medicine, for technical support with the PCR experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamasaki, Y., Morishige, S., Komaki, S. et al. A case of lymphomatoid granulomatosis with central nervous system involvement successfully treated with IFNα. Int J Hematol 114, 502–508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-021-03178-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-021-03178-8