Abstract
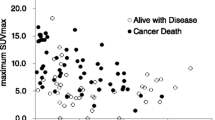
Renal insufficiency (RI) is a frequent manifestation of multiple myeloma (MM) at time of diagnosis but there is no reliable prognostic factor for patients with MM presenting with RI. This study investigated the prognostic impact of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in patients with MM with RI at diagnosis. The records of 209 patients with MM between June 2011 and November 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. PET/CT positivity was defined as the presence of more than three focal lesions or the presence of extramedullary disease. Of 209 patients, 90 (43.1%) had RI and showed similar survival outcomes to patients who had normal renal function. In total, 113 patients (54.0%) were PET/CT-positive, and 46.6% of patients with RI were PET/CT-positive at baseline. In patients with RI, those who were PET/CT-positive showed significantly inferior survival outcomes to those who were PET/CT-negative [progression-free survival (PFS), 12.7 vs. 34.0 months, P < 0.001; overall survival (OS), 42.2 months vs. not reached, P = 0.001]. On multivariate analysis, PET/CT positivity was significantly associated with PFS and OS in patients with RI. In conclusion, PET/CT is a reliable imaging technique for predicting survival outcomes in patients with MM with RI.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30.
Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, et al. Review of 1027 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78:21–33.
Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou V, Bamias A, Gika D, Simeonidis A, Pouli A, Anagnostopoulos A, et al. Renal failure in multiple myeloma: incidence, correlations, and prognostic significance. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:337–41.
Davenport A, Merlini G. Myeloma kidney: advances in molecular mechanisms of acute kidney injury open novel therapeutic opportunities. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:3713–8.
Ho PJ, Moore EM, McQuilten ZK, Wellard C, Bergin K, Augustson B, et al. Renal impairment at diagnosis in myeloma: patient characteristics, treatment, and impact on outcomes. results from the Australia and New Zealand myeloma and related diseases registry. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019;19:e415–24.
Dimopoulos MA, Terpos E, Chanan-Khan A, Leung N, Ludwig H, Jagannath S, et al. Renal impairment in patients with multiple myeloma: a consensus statement on behalf of the International Myeloma Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4976–84.
Torra R, Blade J, Cases A, Lopez-Pedret J, Montserrat E, Rozman C, et al. Patients with multiple myeloma requiring long-term dialysis: presenting features, response to therapy, and outcome in a series of 20 cases. Br J Haematol. 1995;91:854–9.
Augustson BM, Begum G, Dunn JA, Barth NJ, Davies F, Morgan G, et al. Early mortality after diagnosis of multiple myeloma: analysis of patients entered onto the United kingdom Medical Research Council trials between 1980 and 2002—Medical Research Council Adult Leukaemia Working Party. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9219–26.
Dimopoulos MA, Roussou M, Gkotzamanidou M, Nikitas N, Psimenou E, Mparmparoussi D, et al. The role of novel agents on the reversibility of renal impairment in newly diagnosed symptomatic patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2013;27:423–9.
Dimopoulos MA, Delimpasi S, Katodritou E, Vassou A, Kyrtsonis MC, Repousis P, et al. Significant improvement in the survival of patients with multiple myeloma presenting with severe renal impairment after the introduction of novel agents. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:195–200.
Jung SH, Cho MS, Kim HK, Kim SJ, Kim K, Cheong JW, et al. Risk factors associated with early mortality in patients with multiple myeloma who were treated upfront with a novel agents containing regimen. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:613.
Gonsalves WI, Leung N, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, et al. Improvement in renal function and its impact on survival in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2015;5:e296.
Dimopoulos MA, Roussou M, Gavriatopoulou M, Fotiou D, Ziogas DC, Migkou M, et al. Outcomes of newly diagnosed myeloma patients requiring dialysis: renal recovery, importance of rapid response and survival benefit. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7:e571.
Cavo M, Terpos E, Nanni C, Moreau P, Lentzsch S, Zweegman S, et al. Role of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders: a consensus statement by the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:e206–17.
Jung SH, Kwon SY, Min JJ, Bom HS, Ahn SY, Jung SY, et al. (18)F-FDG PET/CT is useful for determining survival outcomes of patients with multiple myeloma classified as stage II and III with the Revised International Staging System. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:107–15.
Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005;67:2089–100.
Zamagni E, Nanni C, Patriarca F, Englaro E, Castellucci P, Geatti O, et al. A prospective comparison of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and whole-body planar radiographs in the assessment of bone disease in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 2007;92:50–5.
Bartel TB, Haessler J, Brown TL, Shaughnessy JD Jr, van Rhee F, Anaissie E, et al. F18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the context of other imaging techniques and prognostic factors in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2009;114:2068–76.
Zamagni E, Patriarca F, Nanni C, Zannetti B, Englaro E, Pezzi A, et al. Prognostic relevance of 18-F FDG PET/CT in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients treated with up-front autologous transplantation. Blood. 2011;118:5989–95.
Minamimoto R, Takahashi N, Inoue T. FDG-PET of patients with suspected renal failure: standardized uptake values in normal tissues. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21:217–22.
Akers SR, Werner TJ, Rubello D, Alavi A, Cheng G. 18F-FDG uptake and clearance in patients with compromised renal function. Nucl Med Commun. 2016;37:825–32.
Kode V, Karsch H, Osman MM, Muzaffar R. Impact of renal failure on F18-FDG PET/CT scans. Front Oncol. 2017;7:155.
Boellaard R, Delgado-Bolton R, Oyen WJ, Giammarile F, Tatsch K, Eschner W, et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: version 2.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:328–54.
Dimopoulos MA, Kastritis E, Michalis E, Tsatalas C, Michael M, Pouli A, et al. The International Scoring System (ISS) for multiple myeloma remains a robust prognostic tool independently of patients’ renal function. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:722–9.
Scheid C, Sonneveld P, Schmidt-Wolf IG, van der Holt B, el Jarari L, Bertsch U, et al. Bortezomib before and after autologous stem cell transplantation overcomes the negative prognostic impact of renal impairment in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a subgroup analysis from the HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 trial. Haematologica. 2014;99:148–54.
Dimopoulos M, Siegel D, White DJ, Boccia R, Iskander KS, Yang Z, et al. Carfilzomib vs bortezomib in patients with multiple myeloma and renal failure: a subgroup analysis of ENDEAVOR. Blood. 2019;133:147–55.
Palumbo A, Avet-Loiseau H, Oliva S, Lokhorst HM, Goldschmidt H, Rosinol L, et al. Revised International Staging System for multiple myeloma: a report from International Myeloma Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:2863–9.
Cho H, Yoon DH, Lee JB, Kim SY, Moon JH, Do YR, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the revised international staging system in multiple myeloma patients treated with novel agents as a primary therapy. Am J Hematol. 2017;92:1280–6.
Kastritis E, Terpos E, Roussou M, Gavriatopoulou M, Migkou M, Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou E, et al. Evaluation of the Revised International Staging System in an independent cohort of unselected patients with multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 2017;102:593–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SHJ and JJL designed the study and HKP and SHJ prepared the manuscript; SRK, JJM, HSB, CMH, SYJ performed the image analysis; JHM, DWB, HJC, SKS, SYA, GYS, DHY, JSA and HJK critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, SY., Park, H.K., Moon, J.H. et al. Prognostic impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with multiple myeloma presenting with renal impairment. Int J Hematol 113, 668–674 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-021-03079-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-021-03079-w