Abstract
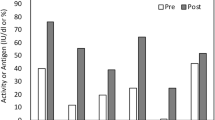
Rivaroxaban, which targets factor Xa and does not reduce proteins C/S, was chosen to treat a 6-year-old girl with homozygous protein S (PS) deficiency who developed skin necrosis while on warfarin. Owing to the lack of experience with rivaroxaban in children, the girl was started with 5 mg once-daily, which was gradually increased to 40 mg daily. The increasing dosage was driven by the need to avoid recurrence of skin necrosis. During dose-escalation, four pharmacokinetics assays were carried out measuring drug plasma concentrations and their effect on hemostatic parameters. We report the laboratory work-up, with special reference to parameters of thrombin-generation. Rivaroxaban concentrations by HPLC were correlated with those by the anti-factor Xa assay (r 2 = 0.92, p < 0.01), but there was an overestimation by HPLC. Thrombin-generation parameters, such as the area under the curve (referred to as ETP), peak-thrombin, and velocity-index, when measured after addition of thrombomodulin, showed unexpected changes: ETP decreased, but peak-thrombin and velocity-index increased. Similar patterns were obtained in a PS-depleted plasma and in plasma from patients with heterozygous PS deficiency, but not in plasma from controls. In conclusion, these preliminary results suggest that PS may be a determinant of velocity and peak-thrombin, but not of the total amount of thrombin generated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
DiScipio RG, Davie EW. Characterization of protein S, a gammacarboxyglutamic acid containing protein from bovine and human plasma. Biochemistry. 1979;18:899–904.
Walker FJ. Regulation of activated protein C by a new protein. A possible function for bovine protein S. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:5521–4.
Koedam JA, Meijers JC, Sixma JJ, et al. Inactivation of human factor VIII by activated protein C. Cofactor activity of protein S and protective effect of von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1988;82:1236–43.
Heeb MJ, Mesters RM, Tans G, et al. Binding of protein S to factor Va associated with inhibition of prothrombinase that is independent of activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:2872–7.
Broekmans AW, Bertina RM, Reinalda-Poot J, et al. Hereditary protein S deficiency and venous thrombo-embolism. A study in three Dutch families. Thromb Haemost. 1985;53:273–7.
Price VE, Ledingham DL, Krümpel A, et al. Diagnosis and management of neonatal purpura fulminans. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;16:318–22.
Martinelli I, Bucciarelli P, Artoni A, et al. Anticoagulant treatment with rivaroxaban in severe protein S deficiency. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e1435–9.
Hemker HC, Giesen P, Al Dieri R, et al. Calibrated automated thrombin generation measurement in clotting plasma. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2003;33:4–15.
Chantarangkul V, Clerici M, Bressi C, et al. Thrombin generation assessed as endogenous thrombin potential in patients with hyper- or hypo-coagulability. Haematologica. 2003;88:547–54.
Dargaud Y, Trzeciak MC, Bordet JC, et al. Use of calibrated automated thrombinography ± thrombomodulin to recognise the prothrombotic phenotype. Thromb Haemost. 2006;96:562–7.
Tripodi A, Primignani M, Chantarangkul V, et al. An imbalance of pro- vs anti-coagulation factors in plasma from patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:2105–11.
Baglin T, Hillarp A, Tripodi A, et al. Measuring oral direct inhibitors (ODIs) of thrombin and factor Xa: a recommendation from the subcommittee on control of anticoagulation of the scientific and standardisation committee of the international society on thrombosis and haemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:756–60.
Samama MM, Contant G, Spiro TE, et al. Rivaroxaban anti-factor Xa chromogenic assay field trial laboratories. Evaluation of the anti-factor Xa chromogenic assay for the measurement of rivaroxaban plasma concentrations using calibrators and controls. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107:379–87.
Tripodi A. Which test to use to measure the anticoagulant effect of rivaroxaban: the prothrombin time test. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:576–8.
Samama MM, Martinoli JL, LeFlem L, et al. Assessment of laboratory assays to measure rivaroxaban–an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103:815–25.
Tripodi A, Chantarangkul V, Guinet C, et al. The INR calibrated for rivaroxaban-(INRrivaroxaban) has the potential to normalize PT results for rivaroxaban-treated patients. Results of an in vitro study. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:226–8.
Kremers RM, Peters TC, Wagenvoord RJ, et al. The balance of pro- and anticoagulant processes underlying thrombin generation. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13:437–47.
Sehgal A, Barros S, Ivanciu L, et al. An RNAi therapeutic targeting antithrombin to rebalance the coagulation system and promote hemostasis in hemophilia. Nat Med. 2015;21:492–7.
Ragni MV. Targeting antithrombin to treat hemophilia. New Engl J Med. 2015;373:389–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Tripodi, A., Martinelli, I., Chantarangkul, V. et al. Thrombin generation and other coagulation parameters in a patient with homozygous congenital protein S deficiency on treatment with rivaroxaban. Int J Hematol 103, 165–172 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1898-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1898-6