Abstract
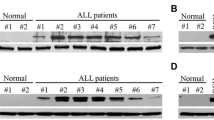
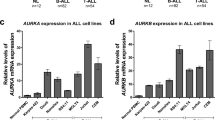
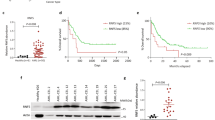
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of rapamycin and its underlying mechanisms on acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells. We found that the p14, p15, and p57 genes were not expressed in ALL cell lines (Molt-4 and Nalm-6) and adult ALL patients, whereas mTOR, 4E-BP1, and p70S6K were highly expressed. In Molt-4 and Nalm-6 cells exposed to rapamycin, cell viability decreased and the cell cycle was arrested at the G1/S phase. Rapamycin restored p14, p15, and p57 gene expression through demethylation of the promoters of these genes. As expected, rapamycin also increased p14 and p15 protein expression in both Molt-4 and Nalm-6 cells, as well as p57 protein expression in Nalm-6 cells. Rapamycin additionally decreased mTOR and p70S6K mRNA levels, as well as p70S6K and p-p70S6K protein levels. However, depletion of mTOR by siRNA did not alter the expression and promoter methylation states of p14, p15, and p57. These results indicate that the inhibitory effect of rapamycin may be due mainly to increased p14, p15, and p57 expression via promoter demethylation and decreased mTOR and p70S6K expression in ALL cell lines. These results suggest a potential role for rapamycin in the treatment of adult ALL.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kantarjian H, Thomas D, O’Brien S, Cortes J, Giles F, Jeha S, et al. Long-term follow-up results of hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone (Hyper-CVAD), a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 2004;101:2788–801.
Garcia-Manero G, Thomas DA. Salvage therapy for refractory or relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2001;15:163–205.
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 2006;124:471–84.
Li X, Yang Q, Yu H, Wu L, Zhao Y, Zhang C, et al. LIF promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer through the AKT-mTOR pathway. Oncotarget. 2014;5:788–801.
Kelly KR, Rowe JH, Padmanabhan S, Nawrocki ST, Carew JS. Mammalian target of rapamycin as a target in hematological malignancies. Target Oncol. 2011;6:53–61.
Hay N, Sonenberg N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1926–45.
Herbert TP, Tee AR, Proud CG. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway regulates the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 at multiple sites. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:11591–6.
Bahrami BF, Ataie-Kachoie P, Pourgholami MH, Morris DL. p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (Rps6kb1): an update. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:1019–25.
Porta C, Paglino C, Mosca A. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front Oncol. 2014;4:64.
García-Morales P, Hernando E, Carrasco-García E, Menéndez-Gutierrez MP, Saceda M, Martínez-Lacaci I. Cyclin D3 is down-regulated by rapamycin in HER-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:2172–81.
Decker T, Hipp S, Ringshausen I, Bogner C, Oelsner M, Schneller F, et al. Rapamycin-induced G1 arrest in cycling B-CLL cells is associated with reduced expression of cyclin D3, cyclin E, cyclin A, and survivin. Blood. 2003;101:278–85.
Williams RT, Sherr CJ. The INK4-ARF (CDKN2A/B) locus in hematopoiesis and bcr-abl-induced leukemias. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:461–7.
Stott FJ, Bates S, James MC, McConnell BB, Starborg M, Brookes S, et al. The alternative product from the human CDKN2A locus, p14(ARF), participates in a regulatory feedback loop with p53 and MDM2. EMBO J. 1998;17:5001–14.
Wolff L, Bies J. p15Ink4b functions in determining hematopoietic cell fates: implications for its role as a tumor suppressor. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2013;50:227–31.
Borriello A, Caldarelli I, Bencivenga D, Criscuolo M, Cucciolla V, Tramontano A, et al. p57(Kip2) and cancer: time for a critical appraisal. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9:1269–84.
Paul E, Paul E, Uggla B, Deneberg S, Bengtzen S, Hermansson M, et al. Low p14ARF expression in de novo acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype is associated with poor survival. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50:1512–8.
Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Castillejo JA, Agirre X, Barrios M, Navarro G, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of cancer-related genes: a strong independent prognostic factor in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2004;104:2492–8.
Bueso-Ramos C, Xu Y, McDonnell TJ, Brisbay S, Pierce S, Kantarjian H, et al. Protein expression of a triad of frequently methylated genes, p73, p57Kip2, and p15, has prognostic value in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia independently of its methylation status. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3932–9.
Wong IH, Ng MH, Huang DP, Lee JC. Aberrant p15 promoter methylation in adult and childhood acute leukemias of nearly all morphologic subtypes: potential prognostic implications. Blood. 2000;95:1942–9.
Li Y, Nagai H, Ohno T, Yuge M, Hatano S, Ito E, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of p57(KIP2) gene in the promoter region in lymphoid malignancies of B-cell phenotype. Blood. 2002;100:2572–7.
Kohno T, Yamada Y, Tawara M, Takasaki Y, Kamihira S, Tomonaga M, et al. Inactivation of p14ARF as a key event for the progression of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2007;31:1625–32.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–51.
Menon S, Manning BD. Common corruption of the mTOR signaling network in human tumors. Oncogene. 2008;27(Suppl 2):S43–51.
Petroulakis E, Parsyan A, Dowling RJ, LeBacquer O, Martineau Y, Bidinosti M, et al. p53-dependent translational control of senescence and transformation via 4E-BPs. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:439–46.
Kwon HK, Bae GU, Yoon JW, Kim YK, Lee HY, Lee HW, et al. Constitutive activation of p70S6K in cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res. 2002;25:685–90.
Vispé S, Deroide A, Davoine E, Desjobert C, Lestienne F, Fournier L, et al. Consequences of combining siRNA-mediated DNA methyltransferase 1 depletion with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in human leukemic KG1 cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:15265–82.
Tasian SK, Teachey DT, Rheingold SR. Targeting the PI3K/mTOR pathway in pediatric hematologic malignancies. Front Oncol. 2014;4:108.
Márk Á, Hajdu M, Váradi Z, Sticz TB, Nagy N, Csomor J, et al. Characteristic mTOR activity in Hodgkin-lymphomas offers a potential therapeutic target in high risk disease–—a combined tissue microarray, in vitro and in vivo study. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:250.
Tian F, Dong L, Zhou Y, Shao Y, Li W, Zhang H, et al. Rapamycin-induced apoptosis in HGF-stimulated lens epithelial cells by AKT/mTOR, ERK and JAK2/STAT3 pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:13833–48.
Li J, Xue L, Hao H, Li R, Luo J. Rapamycin combined with celecoxib enhanced antitumor effects of mono treatment on chronic myelogenous leukemia cells through downregulating mTOR pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:6467–74.
Herman JG, Civin CI, Issa JP, Collector MI, Sharkis SJ, Baylin SB. Distinct patterns of inactivation of p15INK4B and p16INK4A characterize the major types of hematological malignancies. Cancer Res. 1997;57:837–41.
Shen L, Toyota M, Kondo Y, Obata T, Daniel S, Pierce S, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of p57KIP2 identifies a cell-cycle regulatory pathway with prognostic impact in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:4131–6.
Garcia-Manero G, Bueso-Ramos C, Daniel J, Williamson J, Kantarjian HM, Issa JP. DNA methylation patterns at relapse in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1897–903.
Hagiwara K, Li Y, Kinoshita T, Kunishma S, Ohashi H, Hotta T, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of the p57KIP2 gene is a sensitive biomarker for detecting minimal residual disease in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2010;34:50–4.
Yang H, Kadia T, Xiao L, Bueso-Ramos CE, Hoshino K, Thomas DA, et al. Residual DNA methylation at remission is prognostic in adult Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2009;113:1892–8.
Bhatla T, Wang J, Morrison DJ, Raetz EA, Burke MJ, Brown P, et al. Epigenetic reprogramming reverses the relapse-specific gene expression signature and restores chemosensitivity in childhood B-lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2012;119:5201–10.
Burke MJ, Lamba JK, Pounds S, Cao X, Ghodke-Puranik Y, Lindgren BR, et al. A therapeutic trial of decitabine and vorinostat in combination with chemotherapy for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2014;89:889–95.
Tomasoni R, Basso V, Pilipow K, Sitia G, Saccani S, Agresti A, et al. Rapamycin-sensitive signals control TCR/CD28-driven Ifng, Il4 and Foxp3 transcription and promoter region methylation. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:2086–96.
Sun D, Toan X, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Lu R, Wang X, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway inhibition enhances the effects of 5-aza-dC on suppressing cell proliferation in human gastric cancer cell lines. Sci China C Life Sci. 2008;51:640–7.
Zheng J, Hudder A, Zukowski K, Novak RF. Rapamycin sensitizes Akt inhibition in malignant human breast epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2010;296:74–87.
Daniel C, Wennhold K, Kim HJ, von Boehmer H. Enhancement of antigen-specific Treg vaccination in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:16246–51.
Cheng ZY, Guo XL, Yang XY, Niu ZY, Li SH, Wang SY, et al. PTEN and rapamycin inhibiting the growth of K562 cells through regulating mTOR signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2008;27:87.
Chiarini F, Falà F, Tazzari PL, Ricci F, Astolfi A, Pession A, et al. Dual inhibition of class IA phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin as a new therapeutic option for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3520–8.
Vega F, Medeiros LJ, Leventaki V, Atwell C, Cho-Vega JH, Tian L, et al. Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway contributes to tumor cell survival in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6589–97.
Peponi E, Drakos E, Reyes G, Leventaki V, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ. Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling promotes cell cycle progression and protects cells from apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol. 2006;169:2171–80.
Gu L, Zhou C, Liu H, Gao J, Li Q, Mu D, et al. Rapamycin sensitizes T-ALL cells to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:150.
Brown VI, Fang J, Alcorn K, Barr R, Kim JM, Wasserman R, et al. Rapamycin is active against B-precursor leukemia in vitro and in vivo, an effect that is modulated by IL-7-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:15113–8.
Wang Z, Xu F, Yuan N, Niu Y, Lin W, Cao Y, et al. Rapamycin inhibits pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by downregulating DNA and RNA polymerases. Leuk Res. 2014;38:940–7.
Mayerhofer M, Aichberger KJ, Florian S, Krauth MT, Hauswirth AW, Derdak S, et al. Identification of mTOR as a novel bifunctional target in chronic myeloid leukemia: dissection of growth-inhibitory and VEGF-suppressive effects of rapamycin in leukemic cells. FASEB J. 2005;19:960–2.
Yang X, He G, Gong Y, Zheng B, Shi F, Shi R, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor rapamycin enhances anti-leukemia effect of imatinib on Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Eur J Haematol. 2014;92:111–20.
Altman JK, Platanias LC. Exploiting the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in hematologic malignancies. Curr Opin Hematol. 2008;15:88–94.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Fenglin Cao from the Institute of Hematology and Oncology (Heilongjiang Province) for providing technical assistance. We also thank Dr. Yinchang Mi from the Institute of Hematology and Blood Disease Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College for providing the Molt-4 and Nalm-6 cell lines. This research was supported by the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (20132307110022), the Science and Technology project of Heilongjiang Province (GC12C303-4), the Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars of Heilongjiang Province (LCO7C22), the Application Technology Research and Development Project of the Harbin Science and Technology Bureau (2014RFQGJ145), and the Science Foundation of the First Affiliated Hospital at Harbin Medical University (2013B14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Kong, X., Cui, G. et al. Rapamycin restores p14, p15 and p57 expression and inhibits the mTOR/p70S6K pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Int J Hematol 102, 558–568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1858-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1858-1