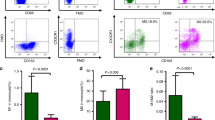
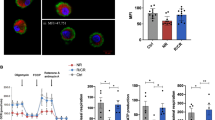
Abstract
Hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) induced by uncontrolled macrophage activation and subsequent graft failure is a frequent and prominent complication after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT), a cause of severe morbidity and death, and a therapeutic challenge. Liposome-incorporated dexamethasone, dexamethasone palmitate (DP), shows greater efficacy against macrophages as compared to dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP). Based on our findings that DP achieves significantly larger decrease than DSP on the viability of primary human macrophages compared in vitro, we tested the effects of DP in patients with HPS. A decrease in number of macrophages in the bone marrow and prevention of engraftment failure were observed in all patients without any severe complications. In conclusion, these data provide a rationale for testing DP as a first-line treatment for patients with HPS after allo-SCT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takagi S, Masuoka K, Uchida N, et al. High incidence of haemophagocytic syndrome following umbilical cord blood transplantation for adults. Br J Haematol. 2009;147:543–53.
Sindrilaru A, Peters T, Wieschalka S, et al. An unrestrained proinflammatory M1 macrophage population induced by iron impairs wound healing in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:985–97.
Imahashi N, Inamoto Y, Ito M, et al. Clinical significance of hemophagocytosis in BM clot sections during the peri-engraftment period following allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011 (in press).
Koyama M, Sawada A, Yasui M, et al. Encouraging results of low-dose etoposide in the treatment of early-onset hemophagocytic syndrome following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2007;86:466–7.
Fukunaga A, Nakamura F, Yoshinaga N, et al. Successful treatment with combined chemotherapy of two adult cases of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in recipients of umbilical cord blood cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2011;93:551–4.
Fauci AS, Dale DC, Balow JE. Glucocorticosteroid therapy: mechanisms of action and clinical considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1976;84:304–15.
Fukuno K, Tsurumi H, Yamada T, et al. Graft failure due to hemophagocytic syndrome after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2001;73:262–5.
Muller M, Renkawitz R. The glucocorticoid receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1088;1991:171–82.
Pak CC, Fidler IJ. Liposomal delivery of biological response modifiers to macrophages. Biotherapy. 1991;3:55–64.
Martinez FO, Gordon S, Locati M, et al. Transcriptional profiling of the human monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization: new molecules and patterns of gene expression. J Immunol. 2006;177:7303–11.
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:677–86.
Sayer HG, Longton G, Bowden R, et al. Increased risk of infection in marrow transplant patients receiving methylprednisolone for graft-versus-host disease prevention. Blood. 1994;84:1328–32.
Inamoto Y, Ito M, Suzuki R, et al. Clinicopathological manifestations and treatment of intestinal transplant-associated microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;44:43–9.
Camps IR. Risk factors for invasive fungal infections in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;32(Suppl 2):S119–23.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to S.N., and in part by a Japanese Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research [(C) 20591118] to T. Nakayama.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiwaki, S., Nakayama, T., Murata, M. et al. Dexamethasone palmitate successfully attenuates hemophagocytic syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: macrophage-targeted steroid therapy. Int J Hematol 95, 428–433 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-012-1023-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-012-1023-z