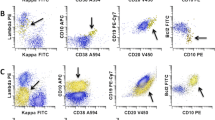
Abstract
We report two cases of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), both occurring in the small bowel, which coexpress PAX5, weak or no CD20 and the CD4 antigen. The CD4 was initially identified by flow cytometry and then confirmed by immunohistochemistry. CD4 is a representative marker for helper T-lymphocytes and is present on a subset of thymocytes, peripheral T cells and monocytes or macrophages. Unlike CD2 and CD5, no B cell fractions are known to express CD4. It might be hypothesized that the deregulated control of gene expression in malignant B cells, in particular PAX5, leads to the activation of some silent or repressed genes of T cell differentiation. Although lineage infidelity is described in some B lymphomas, it remains as an uncommon phenomenon; to our knowledge, cases reported here are the first two cases of DLBCL of the gastrointestinal tract coexpressing the CD4 antigen to be described to date.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swerdlow H, Campos E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Wardiman JW, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours of haemopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008. 439 pp.
Wong MT, Eu KW. Primary colorectal lymphomas. Colorectal Dis. 2006;8:586–91.
Bairey O, Ruchlemer R, Shpilberg O. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas of the colon. Israel Med Assoc J. 2006;8:832–5.
Inaba T, Shimazaki C, Sumikuma T, Akano A, Hatsuse M, Okamoto A, et al. Expression of T-cell-associated antigens in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2000;109:592–9.
Kaleem Z, White G, Zutter M. Aberrant expression of T-cell-antigens on B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001;115:396–403.
Carulli G, Stacchini A, Marini A, Ciriello M, Zucca A, Cannizzo E, et al. Aberrant expression of CD8 in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a multicenter study of 951 bone marrow samples with lymphomatous infiltration. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:186–90.
Wang J, Chen C, Lau S, Raghavan RI, Rowsell EH, Said J, et al. CD3-positive large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:505–12.
Wallentine JC, Perkins SL, Tripp SR, Bruggman RD, Bayer MG. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with coexpression of CD3 in a pediatric patient: a case report, review of the literature, and tissue microarray study. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2009;31:124–7.
Wang E, Stoecker M. Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B cell lymphoma with aberrant expression of CD3: a case report with review of the literature. Int J Hematol. 2010; [Epub ahead of print].
Nakazato T, Suzuki K, Mihara A, Sanada Y, Kakimoto T, Yoshida S. CD4-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2009;50:568–73.
Jani P, Qi XY, Chang H. Aberrant expression of T-cell-associated markers CD4 and CD7 on B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:73–6.
Vega F, Chang C, Medeiros LJ, Udden MM, Cho-Vega JH, Lau C, et al. Plasmablastic lymphomas and plasmablastic plasma cell myelomas have nearly identical immunophenotypic profiles. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:806–15.
Onciu M, Behm FG, Downing JR, Shurtleff SA, Raimondi SC, Morris SW, et al. ALK-positive plasmablastic B-cell lymphoma with expression of the NPM-ALK fusion transcript. Report of 2 cases. Blood. 2003;102:2642–4.
Reichard KK, McKenna RW, Kroft S. ALK-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: report of four cases and review of the literature. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:310–9.
Yoshino T, Miyake K, Ichimura K, Mannami T, Ohara N, Hamazaki S, et al. Increased incidence of follicular lymphoma in the duodenum. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:688–93.
Amer M, el-Akkad S. Gastrointestinal lymphoma in adults: clinical features and management of 300 cases. Gastroenterology. 1994;106:846–58.
Petitjean B, Jardin F, Joly B, Martin-Garcia N, Tilly H, Picquenot JM, et al. Pyothorax-associated lymphoma: a peculiar clinicopathologic entity derived from B cells at late stage of differentiation and with occasional aberrant dual B and T-cell phenotype. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:724–32.
Ozdemirli M, Cheson B, Jaffe ES. What is anaplastic large cell lymphoma? Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:1664–5.
Delsol G, Lamant L, Mariamè B, Pulford K, Dastugue N, Brousset P, et al. A new subtype of large B-cell lymphoma expressing the ALK kinase and lacking the 2;5 translocation. Blood. 1997;89:1483–90.
Chikatsu N, Kojima H, Suzukawa K, Shinagawa A, Nagasawa T, Ozawa H, et al. ALK+, CD30, CD20- large B-cell lymphoma containing anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fused to clathrin heavy chain gene (CLTC). Mod Pathol. 2003;16:828–32.
Gascoyne RD, Lamant L, Martin-Subero JI, Lestou VS, Harris NL, Müller-Hermelink HK, et al. ALK-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is associated with clathrin-ALK rearrangements: reports of 6 cases. Blood. 2003;102:2568–73.
Aisenberg AC, Bloch KJ, Wilkes BM. Malignant lymphoma with dual B and T cell markers. Analysis of the neoplastic cells with monoclonal antibodies directed against T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1981;154:1709–14.
Torlakovic E, Torlakovic G, Nguyen PL, Brunning RD, Delabie J. The value of anti-pax-5 immunostaining in routinely fixed and paraffinembedded sections: a novel pan pre-B and B-cell marker. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:1343–50.
Nutt SL, Heavey B, Rolink AG, Busslinger M. Commitment to the B-lymphoid lineage depends on the transcription factor Pax5. Nature. 1999;401:556–62.
Poppe B, De Paepe P, Michaux L, Dastugue N, Bastard C, Herens C, et al. PAX5/IGH rearrangement is a recurrent finding in a subset of aggressive B-NHL with complex chromosomal rearrangements. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2005;44:218–23.
Hansson M, Jerkeman M, Dictor M. Biphenotypic bigenotypic lymphoma with simultaneous expression of PAX5/BSAP and B- and T-cell markers. Eur J Haematol. 2007;79:159–65.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Arrondini, M., Barreca, A., Aliberti, S. et al. CD4-positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma identified by flow cytometry: two case reports. Int J Hematol 92, 198–203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0631-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0631-8