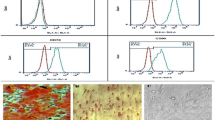
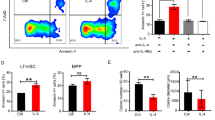
Abstract
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection is usually implicated in thrombocytopenia occurring in newborns and immunocompromised patients. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of HCMV infection on the viability of megakaryocytic CHRF-288-11 cells and the underlying mechanisms involved. RT-PCR for determining mRNA expression of HCMV immediate early gene 1 and Western blot for measuring protein expression of late HCMV gene pp65 showed that CHRF-288-11 cells were susceptible to HCMV infection. HCMV infection reduced the viability of CHRF-288-11 cells via apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Both caspase 3 and c-Jun terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway were activated in the HCMV-treated CHRF-288-11 cells. z-DEVD-fmk (a caspase inhibitor) and SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor) significantly prevented the death of CHRF-288-11 cells induced by HCMV, respectively. Furthermore, inhibition of JNK activity could reduce the formation of active caspase 3 induced by HCMV. Interestingly, the co-application of antivirus drug ganciclovir and SP600125 synergistically prevented the death of CHRF-288-11 cells induced by HCMV. Collectively, these findings suggest that HCMV infection may induce the caspase-dependent apoptosis of megakaryocytic CHRF-288-11 cells by the activation of JNK signaling pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crapnell K, Zanjani ED, Chaudhuri A, Ascensao JL, St Jeor S, Maciejewski JP. In vitro infection of megakaryocytes and their precursors by human cytomegalovirus. Blood. 2000;95:487–93.
Britt W. Manifestations of human cytomegalovirus infection: proposed mechanisms of acute and chronic disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:417–70.
Lilleri D, Fornara C, Chiesa A, Caldera D, Alessandrino EP, Gerna G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell reconstitution in adult allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients and immune control of viral infection. Haematologica. 2008;93:248–56.
Sindre H, Rollag H, Olafsen MK, Degré M, Hestdal K. Human cytomegalovirus induces apoptosis in the hematopoietic cell line MO7e. APMIS. 2000;108:223–30.
DiMaggio D, Anderson A, Bussel JB. Cytomegalovirus can make immune thrombocytopenic purpura refractory. Br J Haematol. 2009;146:104–12.
Movassagh M, Gozlan J, Senechal B, Baillou C, Petit JC, Lemoine FM. Direct infection of CD34+ progenitor cells by human cytomegalovirus: evidence for inhibition of hematopoiesis and viral replication. Blood. 1996;88:1277–83.
Goodrum F, Jordan CT, Terhune SS, High K, Shenk T. Differential outcomes of human cytomegalovirus infection in primitive hematopoietic cell subpopulations. Blood. 2004;104:687–95.
Pleskoff O, Casarosa P, Verneuil L, Ainoun F, Beisser P, Smit M, et al. The human cytomegalovirus-encoded chemokine receptor US28 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis. FEBS J. 2005;272:4163–77.
Thorburn A. Apoptosis and autophagy: regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes. Apoptosis. 2008;13:1–9.
McCormick AL. Control of apoptosis by human cytomegalovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:281–95.
Clarke P, Meintzer SM, Widmann C, Johnson GL, Tyler KL. Reovirus infection activates JNK and the JNK-dependent transcription factor c-Jun. J Virol. 2001;75:11275–83.
Beckham JD, Goody RJ, Clarke P, Bonny C, Tyler KL. Novel strategy for treatment of viral central nervous system infection by using a cell-permeating inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J Virol. 2007;81:6984–92.
Yeh CJ, Lin PY, Liao MH, Liu HJ, Lee JW, Chiu SJ, et al. TNF-alpha mediates pseudorabies virus-induced apoptosis via the activation of p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK signaling. Virology. 2008;381:55–66.
Moon MS, Lee GC, Kim JH, Yi HA, Bae YS, Lee CH. Human cytomegalovirus induces apoptosis in promonocyte THP-1 cells but not in promyeloid HL-60 cells. Virus Res. 2003;94:67–77.
Kong XL, Wang QW, Chen ML, Cai Y, He ZX, Yang M. Human cytomegalovirus aggravates apoptosis of human megakaryocytes via direct infection in vitro. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004;12:70–3.
Chan G, Guilbert LJ. Ultraviolet-inactivated human cytomegalovirus induces placental syncytiotrophoblast apoptosis in a Toll-like receptor-2 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha dependent manner. J Pathol. 2006;210:111–20.
Ma C, Ying C, Yuan Z, Song B, Li D, Liu Y, et al. Dp5 is a c-Jun target gene and required for apoptosis induced by potassium deprivation in cerebellar granule neurons. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:30901–9.
Correa GT, Veranio GA, Silva LE, Hirata Junior R, Coil JM, Scelza MF. Cytotoxicity evaluation of two root canal sealers and a commercial calcium hydroxide paste on THP1 cell line by Trypan Blue assay. J Appl Oral Sci. 2009;17:457–61.
Li W, Pi R, Chan HH, Fu H, Lee NT, Tsang HW, et al. Novel dimeric acetylcholinesterase inhibitor bis(7)-tacrine, but not donepezil, prevents glutamate-induced neuronal apoptosis by blocking N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18179–88.
Loos B, Engelbrecht AM. Cell death: a dynamic response concept. Autophagy. 2009;5:590–603.
Hengartner MO. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature. 2000;40:770–6.
Malhi H, Gores GJ, Lemasters JJ. Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver: a tale of two deaths. Hepatology. 2006;43:S31–44.
Chiou SH, Liu JH, Chen SS, Liu WT, Lin JC, Wong WW, et al. Apoptosis of human retina and retinal pigment cells induced by human cytomegalovirus infection. Ophthalmic Res. 2002;34:77–82.
Briceño J, de la Torre-Cisneros J, Alvarez-Kindelan A, Sanchez-Guijo P, Pera C. Antiviral drugs can inhibit lymphocyte apoptosis induced by cytomegalovirus antigens. Transplant Proc. 2001;33:1799–800.
Fugman DA, Witte DP, Jones CL, Aronow BJ, Lieberman MA. In vitro establishment and characterization of a human megakaryoblastic cell line. Blood. 1990;75:1252–61.
Fuhrken PG, Chen C, Miller WM, Papoutsakis ET. Comparative, genome-scale transcriptional analysis of CHRF-288-11 and primary human megakaryocytic cell cultures provides novel insights into lineage-specific differentiation. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:476–89.
Villeneuve J, Block A, Le Bousse-Kerdilès MC, Lepreux S, Nurden P, Ripoche J, et al. Tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in platelets and megakaryocytes: a novel organization for these secreted proteins. Exp Hematol. 2009;37:849–56.
Fuhrken PG, Apostolidis PA, Lindsey S, Miller WM, Papoutsakis ET. Tumor suppressor protein p53 regulates megakaryocytic polyploidization and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:15589–600.
Odeberg J, Wolmer N, Falci S, Westgren M, Seiger A, Söderberg-Nauclér C. Human cytomegalovirus inhibits neuronal differentiation and induces apoptosis in human neural precursor cells. J Virol. 2006;80:8929–39.
Krogerus L, Soots A, Loginov R, Bruggeman C, Lautenschlager I. CMV increases tubular apoptosis through the TNF-alpha-TNF-R1 pathway in a rat model of chronic renal allograft rejection. Transpl Immunol. 2008;18:232–6.
Takada E, Hata K, Mizuguchi J. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) following engagement of membrane immunoglobulin on WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104:1927–36.
Bachis A, Colangelo AM, Vicini S, Doe PP, De Bernardi MA, Brooker G, et al. Interleukin-10 prevents glutamate-mediated cerebellar granule cell death by blocking caspase-3-like activity. J Neurosci. 2001;21:3104–12.
Choi JH, Kim DW, Cho SG, Yoo JH, Jeong DC, et al. Pre-emptive ganciclovir treatment can play a role in restoration of hematopoiesis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997;19:187–90.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30872219), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (6300658 and 07001505), Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (PolyU660807, 560909; N_PolyU61807 and AoE/B15/01) and Hong Kong PolyU (G-YX96, G-U439). The authors sincerely thank Dr. Yijun Huang for his kind assistance in the flow cytometry assay and Professor Mingtao Li for kindly providing materials used in the experiments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest including any financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, J., Li, X., Cai, Y. et al. Human cytomegalovirus induces caspase-dependent apoptosis of megakaryocytic CHRF-288-11 cells by activating the JNK pathway. Int J Hematol 91, 620–629 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0560-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0560-6