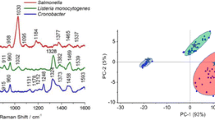
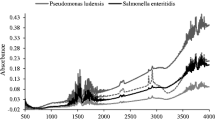
Abstract
Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes are three of the most common foodborne pathogens found in pork. SERS technology enables the rapid acquisition of molecular information by harnessing the synergistic effect of Raman scattering and enhanced substrate surface plasmonics. However, because of the similar chemical composition between bacteria and between pathogens and pork, it is difficult to discriminate pork contaminated with different pathogens. In view of this problem, Raman spectra of three bacteria, bacteria mixtures, and fresh pork contaminated with three pathogens were obtained by using Au @Ag NPs as the enhancement substrate. After data pretreatment, Raman characteristics of pathogens were analyzed by the PCA. PLS-DA and SVM-DA classifiers were employed to discriminate the feature data. To reduce the impact of sample variations on the modeling results, the influence of three data standardization methods, SNV, max-normalization, and area-normalization, on the predictive ability of the models was discussed. The predicted results demonstrated that SVM-DA, combining with SNV, achieved superior discrimination for bacteria mixtures. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of prediction validation were all above 0.93. When PLS-DA was combined with normalization techniques, better results were obtained for discriminating pork contaminated with different bacteria. In the predictive discriminant analysis, the classification accuracy reached 0.85. This work not only achieved rapid discrimination of biological cells in complex environments but also improved the accuracy of the classification model, providing a feasible idea for the analysis of pork contaminated with microorganism based on SERS by incorporating stoichiometric methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad W, Wang J, Li H, Jiao T, Chen Q (2021) Trends in the bacterial recognition patterns used in surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 142:116310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116310
Ahn S, Walt DR (2005) Detection of salmonella spp. using microsphere-based, fiber-optic DNA microarrays. Anal Chem 77(15):5041–5047. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0505270
Artemyev DN, Shatskaya AA (2022) Study of spurious optical signals in a fiber-optic Raman spectroscopy system. Opt Laser Technol 152:108184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108184
Bashir S, Nawaz H, Majeed MI, Mohsin M, Abdullah S, Ali S, Rashid N, Kashif M, Batool F, Abubakar M, Ahmad S, Abdulraheem A (2021) Rapid and sensitive discrimination among carbapenem resistant and susceptible Escherichia coli strains using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy combined with chemometric tools. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 34:102280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102280
Carpentier B, Cerf O (2011) Review — persistence of Listeria monocytogenes in food industry equipment and premises. Int J Food Microbiol 145(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.005
Chen Y, Yang H, Shi X, He Z, Peng H, Chen Y, Gu G, Pang X, Chen H, Wang Y, Guo L (2023) Au@4-MBA@Ag NPs labeled SERS lateral flow immunoassay for ultrasensitive and quantitative detection of Salmonella enteritidis. Microchem J 193:109134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2023.109134
Choi SY, Rhie GE, Jeon JH (2019) Development of a double-antibody sandwich ELISA for sensitive detection ofYersinia pestis. Microbiol Immunol 64(1):72–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/1348-0421.12751
Deng B, Luo X, Zhang M, Ye L, Chen Y (2020) Corrigendum to “Quantitative detection of acyclovir by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy using a portable Raman spectrometer coupled with multivariate data analysis”. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 190:110942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110942
Dimopoulou M, Kefalloniti V, Tsakanikas P, Papanikolaou S, Nychas E, G. (2021) Assessing the biofilm formation capacity of the wine spoilage yeast Brettanomyces bruxellensis through FTIR spectroscopy. Microorganism 9(587). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030587
Du Y, Han D, Liu S, Sun X, Ning B, Han T, Wang J, Gao Z (2022) Raman spectroscopy-based adversarial network combined with SVM for detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Talanta 237:122901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122901
Ghosh S, Sarkar T, Chakraborty R (2021) Formation and development of biofilm- an alarming concern in food safety perspectives. Biocatalysis and Agricultural. Biotechnology 38:102210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102210
Gu M, Li C, Su Y, Chen L, Li S, Li X, Zheng X (2023) Novel insights from protein degradation: deciphering the dynamic evolution of biogenic amines as a quality indicator in pork during storage. Food Res Int 167:112684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112684
Hang Y, Boryczka J, Wu N (2022) Visible-light and near-infrared fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman scattering point-of-care sensing and bio-imaging: a review. Chem Soc Rev 51:329–375. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00621d
Hua Z, Yu T, Liu D, Xianyu Y (2021) Recent advances in gold nanoparticles-based biosensors for food safety detection. Biosens Bioelectron 179:113076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113076
Jiang W, Saxena A, Song B, Ward BB, Beveridge TJ, Myneni S (2004) Elucidation of functional groups on gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial surfaces using infrared spectroscopy. Langmuir 20:11433–11442. https://doi.org/10.1021/la049043
Kao P, Malvadkar NA, Cetinkaya M, Wang H, Allara DL, Demirel MC (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman detection on metalized nanostructured poly (p-xylylene) films. Adv Mater 20(18):3562–3565. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200800936
Kadadou D, Tizani L, Wadi VS, Banat F, Alsafar H, Yousef AF, Hasan SW (2022) Recent advances in the biosensors application for the detection of bacteria and viruses in wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 10(1):107070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.107070
Kashif M, Majeed MI, Nawaz H, Rashid N, Abubakar M, Ahmad S, Ali S, Hyat H, Bashir S, Batool F, Akbar S, Anwar MA (2021) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for identification of food processing bacteria. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 261:119989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119989
Kern L, Abdeen SK, Kolodziejczyk AA, Elinav E (2021) Commensal inter-bacterial interactions shaping the microbiota. Curr Opin Microbiol 63:158–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2021.07.011
Lee S, Khoo VSL, Medriano CAD, Lee T, Park SY, Bae S (2019) Rapid and in-situ detection of fecal indicator bacteria in water using simple DNA extraction and portable loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) PCR methods. Water Res 160:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.watres.2019.05.049
Li N, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Gu Q, Chen M, Zhang Y, Sun X, Zhang J (2019) High-throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial community composition and quality characteristics in refrigerated pork during storage. Food Microbiol 83:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.6b00282
Li Y, Church JS (2014) Raman spectroscopy in the analysis of food and pharmaceutical nanomaterials. J Food Drug Anal 22(1):29–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.003
Liu TT, Lin YH, Hung CS, Liu TJ, Chen Y, Huang YC, Tsai TH, Wang HH, Wang DW, Wang JK, Wang YL, Lin CH (2009) A high speed detection platform based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering for monitoring antibiotic-induced chemical changes in bacteria cell wall. PLoS One 4(5):e5470. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005470
Liu Y, Pu H, Sun D (2017) Hyperspectral imaging technique for evaluating food quality and safety during various processes: a review of recent applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 69(A):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.08.013
Liu Y, Zhu W, Yuan Q, Hu J, Zhang X, Shen A (2022) Photo-reduced Ag+ surrounding single poly(4-cyanostyrene) nanoparticles for undifferentiated SERS sensing and killing of bacteria. Talanta 245:123450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123450
Meisel S, Stöckel S, Rösch P, Popp J (2014) Identification of meat-associated pathogens via Raman microspectroscopy. Food Microbiol 38:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2013.08.007
Mushtaq A, Nawaz H, Irfan Majeed M, Rashid N, Tahir M, Zaman Nawaz M, Shahzad K, Dastgir G, Bari ZA, R., Ul Haq, A., Saleem, M., & Akhtar, F. (2022) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for monitoring colistin-resistant and susceptible Escherichia coli strains. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 278:121315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.121315
Olson AP, Spies KB, Browning AC, Soneral PAG, Lindquist NC (2017) Chemically imaging bacteria with super-resolution SERS on ultra-thin silver substrates. Sci Rep 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08915-w
Olson TY, Schwartzberg AM, Orme CA, Talley CE, O’Connell B, Zhang JZ (2008) Hollow gold−silver double-shell nanospheres: structure, optical absorption, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Phys Chem C 112(16):6319–6329. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp7116714
Premasiri WR, Lee JC, Sauer-Budge A, Théberge R, Costello CE, Ziegler LD (2016) The biochemical origins of the surface-enhanced Raman spectra of bacteria: a metabolomics profiling by SERS. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(17):4631–4647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9540-x
Qu C, Li Y, Du S, Geng Y, Su M, Liu H (2022) Raman spectroscopy for rapid fingerprint analysis of meat quality and security: principles, progress and prospects. Food Res Int 161:111805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111805
Riu J, Giussani B (2020) Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. Trends Anal Chem 126:115863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115863
Ramachandran K, Daoudi K, Hadj Kacem H, Cloumbus S, Benaoum H, Gaidi M (2022) Rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of pork DNA with surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for onsite food quality inspection. Sens Bio-sensing Res 38:100524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2022.100524
Schuster KC, Reese I, Urlaub E, Gapes JR, Lendl B (2000) Multidimensional information on the chemical composition of single bacterial cells by confocal Raman micro-spectroscopy. Anal Chem 72(22):5529–5534. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac000718x
Wang C, Wang J, Li M, Qu X, Zhang K, Rong Z, Xiao R, Wang S (2016) A rapid SERS method for label-free bacteria detection using polyethylenimine-modified Au-coated magnetic microspheres and Au@Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 141(22):6226–6238. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6an01105e
Wiercigroch E, Szafraniec E, Czamara K, Pacia MZ, Majzner K, Kochan K, Kaczor A, Baranska M, Malek K (2017) Raman and infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates: a review. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 185:317–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.045
Witkowska E, Korsak D, Kowalska A, Janeczek A, Kamińska A (2018) Strain-level typing and identification of bacteria - a novel approach for SERS active plasmonic nanostructures. Anal Bioanal Chem 410(20):5019–5031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1153-0
Witkowska E, Niciński K, Korsak D, Szymborski T, Kamińska A (2019) Sources of variability in SERS spectra of bacteria: comprehensive analysis of interactions between selected bacteria and plasmonic nanostructures. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(10):2001–2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01609-4
Xu Y, Hassan MM, Zhu A, Li H, Chen Q (2021) Dual-mode of magnetic assisted Au @Ag SERS tags and cationic conjugated UCNPs for qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple foodborne pathogens. Sensors Actuators B Chem 344:130305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130305
Yamamoto T, Taylor JN, Koseki S, Koyama K (2021) Classification of food spoilage bacterial species and their sodium chloride, sodium acetate and glycine tolerance using chemometrics analysis and Raman spectroscopy. J Microbiol Methods 190:106326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106326
Yang S, Lin C, Aljuffali IA, Fang J (2017) Current pathogenic Escherichia coli foodborne outbreak cases and therapy development. Arch Microbiol 199(6):811–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1393-y
Zhu A, Ali S, Xu Y, Ouyang Q, Wang Z, Chen Q (2022a) SERS-based Au @Ag NPs solid-phase substrate combined with chemometrics for rapid discrimination of multiple foodborne pathogens. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 270:120814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120814
Zhu G, Zhu X, Fan Q, Wan X (2011) Raman spectra of amino acids and their aqueous solutions. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 78(3):1187–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.12.079
Zhu Y, Liu S, Li M, Liu W, Wei Z, Zhao L, Liu Y, Xu L, Zhao G, Ma Y (2022b) Preparation of an AgNPs@Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) multi-hole filter membrane chip for the rapid identification of food-borne pathogens by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 267:120456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120456
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 32172287).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yahui Chen conduct data analysis and wrote the main manuscript text. Yankun Peng: conceptualization. Qinghui Guo, Jiewen Zuo, Xinlong Zhao, and Qibin Zhuang: formal analysis and investigation; all authors reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Peng, Y., Guo, Q. et al. Rapid Discrimination of Pork Contaminated with Different Pathogens by Using SERS. Food Anal. Methods 17, 309–321 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02567-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02567-5