Abstract
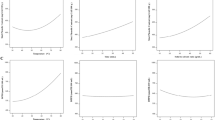
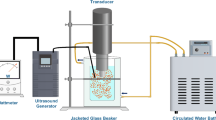
Interest in extracting mucilage from natural sources like taro corms stems from its potential applications in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, while traditional extraction methods are often inefficient and time-consuming. Hence, the critical purposes of the current research trends are to use an efficient and sustainable extraction method, optimize the process conditions for maximum yield and quality. Nevertheless, this research aimed to optimize the conditions for ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) of mucilage from taro corms and compare its extraction efficacy and functional properties with conventional methods like heat extraction and Soxhlet extraction. As a consequence, the extraction conditions were optimized with fifteen experimental trials using response surface methodology (RSM) combined with a Box-Behnken design (BBD) (three-factor-three-level), considering ultrasonic temperature (X1, 40–60 °C), ultrasonic time (X2, 15–45 min), and water-to-solvent ratio (X3: 3:1–7:1). Moreover, a second-order polynomial model predicted the responses, and model validity was confirmed through analysis of variance (ANOVA). Briefly, the results revealed the optimal extraction parameters for maximizing taro mucilage extraction (14.315 ± 0.015%) were 60 °C ultrasonic temperature, 45 min ultrasonic time, and a 5:1 water-to-solid ratio. This outperformed heating extraction (4.15 ± 0.029%) and Soxhlet extraction (6.05 ± 0.011%). Furthermore, the UAE extracted mucilage exhibited superior functional properties, including higher emulsion stability against heat (92 ± 0.023%), water holding capacity (65 ± 0.013%), oil holding capacity (41 ± 0.01%), foaming capacity (38 ± 0.041%), and foaming stability (87 ± 0.021%) compared to the heating and Soxhlet methods. In addition, the experimental results supported the predicted values, confirming the appropriateness of the model and the efficacy of RSM in optimizing UAE extraction conditions. These results not only provide a practical solution for efficient taro mucilage extraction but also underscore the effectiveness of RSM in optimizing extraction conditions. Ultimately, the study’s findings have the potential to significantly impact various industries by enhancing product quality, reducing waste, and conserving valuable resources.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, NG, upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmed T, Rana MR, Zzaman W, Ara R, Aziz MG (2021) Optimization of substrate composition for pectinase production from satkara (Citrus macroptera) Peel using aspergillus Niger-ATCC 1640 in solid-state fermentation. Heliyon 7:e08133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08133
Ahmed T, Rana MR, Maisha MR, Sayem ASM, Rahman M, Ara R (2022) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic content & antioxidant activity of hog plum (Spondias pinnata L. f. Kurz) pulp by response surface methodology. Heliyon 8:e11109
Ahmed T, Rana MR, Hossain MA, Ullah S, Suzauddula M (2023) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction using response surface methodology for total anthocyanin content, total phenolic content, and antioxidant activities of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) calyces and comparison with conventional soxhlet extrac. Biomass Convers Biorefin 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03881-y
Andrade LA, Nunes CA, Pereira J (2015) Relationship between the chemical components of Taro rhizome mucilage and its emulsifying property. Food Chem 178:331–338
Andrade LA, deOliveira Silva DA, Nunes CA, Pereira J (2020) Experimental techniques for the extraction of Taro mucilage with enhanced emulsifier properties using chemical characterization. Food Chem 327:127095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127095
Andrade LA, Nunes CA, Pereira J (2021) Physical and chemical analysis in crude taro mucilage obtained by simple extraction technique. Bol do Cent Pesqui Process Aliment 37:68–82. https://doi.org/10.5380/bceppa.v37i2.78875
Anwar MA (2020) Taro (Colocasia Esculenta) Water-Soluble Non-Starch Polysaccharide: Extraction, Characteristics, Properties, and Biological Activities. University of Otago
Anwar M, Babu G, Bekhit AE-D (2021) Utilization of ultrasound and pulse electric field for the extraction of water-soluble non-starch polysaccharide from Taro (Colocasia esculenta) Peel. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 70:102691
Babamoradi N, Yousefi S, Ziarati P (2018) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of functional polysaccharides from common mullein (Verbascum thapsus L.) flowers. J Food Process Eng 41:e12851
Basiony AM, Atta MB, Abd-Elazim EI, Mohamed AS (2022) Chemical composition and functional properties of egyptian Taro (Colocasia esculenta) mucilage. Al-Azhar J Agric Res 47:185–1901
Bernardo CO, Ascheri JLR, Chávez DWH, Carvalho CWP (2018) Ultrasound assisted extraction of yam (Dioscorea bulbífera) starch: effect on morphology and functional properties. Starch-Stärke 70:1700185
Brzezińska R, Wirkowska-Wojdyła M, Piasecka I, Górska A (2023) Application of response surface methodology to optimize the extraction process of bioactive compounds obtained from coffee silverskin. Appl Sci 13:5388
Castejon N, Luna P, Senorans FJ (2017) Ultrasonic removal of mucilage for pressurized liquid extraction of Omega-3 rich oil from chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.). J Agric Food Chem 65:2572–2579
Chalapud MC, Carrín ME (2023) Ultrasound-assisted extraction of oilseeds—Sustainability processes to obtain traditional and non-traditional food ingredients: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 22:2161–2196
Chao Z, Ri-fu Y, Tai-qiu Q (2013) Ultrasound-enhanced subcritical water extraction of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum L. Sep Purif Technol 120:141–147
Ebrahimi Hemmati Kaykha M, Jooyandeh H, Behbahani BA, Noshad M (2022) Optimization of mucilage extraction from sepestan fruit and evaluation of its physicochemical and antioxidant activity. J Food Meas Charact 16:4331–4344
Emadzadeh MK, Aarabi A, Aarabi Najvani F, Chiani M, Mehrabi MR (2022) The effect of extraction method on physicochemical properties of mucilage extracted from yellow and brown flaxseeds. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod 17(4):e123952. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjnpp-123952
Gheybi N, Pirouzifard MK, Almasi H (2021) Ornithogalum cuspidatum mucilage as a new source of plant-based polysaccharide: physicochemical and rheological characterization. J Food Meas Charact 15:2184–2201
Goksen G, Demir D, Dhama K, Kumar M, Shao P, Xie F, Echegaray N, Lorenzo JM (2023) Mucilage polysaccharide as a plant secretion: potential trends in food and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 230:123146
Govender S, Pillay V, Chetty DJ, Essack SY, Dangor CM, Govender T (2005) Optimisation and characterisation of bioadhesive controlled release tetracycline microspheres. Int J Pharm 306:24–40
Granato D, DeCastro IA, Ellendersen LSN, Masson ML (2010) Physical stability assessment and sensory optimization of a dairy-free emulsion using response surface methodology. J Food Sci 75:S149–S155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01514.x
Hamad D, El-Sayed H, Ahmed W, Sonbol H, Ramadan MAH (2022) GC-MS analysis of potentially volatile compounds of pleurotus ostreatus polar extract: in vitro antimicrobial, cytotoxic, immunomodulatory, and antioxidant activities. Front Microbiol 13:834525
Hamzah AFA, Hamzah MH, Mazlan NI, Man HC, Jamali NS, Siajam SI, Show PL (2022) Optimization of subcritical water pre-treatment for biogas enhancement on co-digestion of pineapple waste and cow dung using the response surface methodology. Waste Manag 150:98–109
Hassan I, Gani A, Ahmad M, Banday J (2022) Extraction of polysaccharide from Althea rosea and its physicochemical, anti-diabetic, anti-hypertensive and antioxidant properties. Sci Rep 12:17116
Hossain MA, Ahmed T, Hossain MS, Dey P, Ahmed S, Hossain MM (2022) Optimization of the factors affecting BT-2 black tea fermentation by observing their combined effects on the quality parameters of made tea using response surface methodology (RSM). Heliyon 8:e08948
Hussain N, Ishak I, Sulaiman R, Fauzi WM, Coorey R (2020) Influence of processing conditions on rheological properties of aqueous extract chia (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage. Food Res 4:227–236
Kalkan E, Maskan M (2023) Mucilage in okra: extraction, modelling, optimization and application. J Food Meas Charact 17:4812–4822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01979-5
Koocheki A, Mortazavi SA, Shahidi F, Razavi SMA, Kadkhodaee R, Milani JM (2010) Optimization of mucilage extraction from qodume shirazi seed (Alyssum homolocarpum) using response surface methodology. J Food Process Eng 33:861–882
Lianfu Z, Zelong L (2008) Optimization and comparison of ultrasound/microwave assisted extraction (UMAE) and ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE) of lycopene from tomatoes. Ultrason Sonochem 15:731–737
Lira MM, de Oliveira Filho JG, de Sousa TL, da Costa NM, Lemes AC, Fernandes SS, Egea MB (2023) Selected plants producing mucilage: overview, composition, and their potential as functional ingredients in the development of plant-based foods. Food Res Int 169:112822
Morales-Tovar ME, Ramos-Ramírez EG, Salazar-Montoya JA (2020) Modeling and optimization of the parameters affecting extraction of the Chan seed mucilage (Hyptis suaveolens (L.) poit) by mechanical agitation (MA) and ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) in a multiple variables system. Food Bioprod Process 120:166–178
Nguimbou RM, Boudjeko T, Njintang NY, Himeda M, Scher J, Mbofung CMF (2014) Mucilage chemical profile and antioxidant properties of Giant swamp Taro tubers. J Food Sci Technol 51:3559–3567
Njintang NY, Boudjeko T, Tatsadjieu LN, Nguema-Ona E, Scher J, Mbofung CMF (2014) Compositional, spectroscopic and rheological analyses of mucilage isolated from Taro (Colocasia esculenta L. schott) corms. J Food Sci Technol 51:900–907
Oh S, Kim D-Y (2022) Characterization, antioxidant activities, and functional properties of mucilage extracted from Corchorus olitorius L. Polymers (Basel) 14:2488
Öncü Glaue Ş, Akcan T, Tavman Ş (2023) Thermal properties of ultrasound-extracted okra mucilage. Appl Sci 13:6762
Pereira GA, Silva EK, Araujo NMP, Arruda HS, Meireles MAA, Pastore GM (2019) Mutamba seed mucilage as a novel emulsifier: stabilization mechanisms, kinetic stability and volatile compounds retention. Food Hydrocoll 97:105190
Puligundla P, Lim S (2022) A review of extraction techniques and food applications of flaxseed mucilage. Foods 11:1677
Rashid F, Ahmed Z, Hussain S, Huang J-Y, Ahmad A (2019) Linum usitatissimum L. seeds: flax gum extraction, physicochemical and functional characterization. Carbohydr Polym 215:29–38
Samavati V, Manoochehrizade A (2013) Polysaccharide extraction from Malva sylvestris and its anti-oxidant activity. Int J Biol Macromol 60:427–436
Shiehnezhad M, Zarringhalami S, Malekjani N et al (2023) Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of mucilage from Ocimum basilicum var. album (L.) seed. J Food Process Preserv 2023:1–15
Silva LA, Sinnecker P, Cavalari AA, Sato ACK, Perrechil FA (2022) Extraction of chia seed mucilage: effect of ultrasound application. Food Chem Adv 1:100024
Tomasi IT, Santos SCR, Boaventura RAR, Botelho CMS (2023) Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from chestnut processing waste using response surface methodology. J Clean Prod 395:136452
Tosif MM, Najda A, Klepacka J, Bains A, Chawla P, Kumar A, Sharma M, Sridhar K, Gautam SP, Kaushik R (2022) A concise review on Taro mucilage: extraction techniques, chemical composition, characterization, applications, and health attributes. Polymers (Basel) 14:1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061163
Tripathi S, Prakash V, Morya V (2022) An overview of natural medicinal plant extraction, isolation and characterization methods in improvement of medicinal research. Int J Sci Dev Res 7:842–856
Wang W-H, Lu C-P, Kuo M-I (2022) Combination of ultrasound and heat in the extraction of chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage: impact on yield and technological properties. Processes 10:519
Yang Y, Gupta VK, Du Y, Aghbashlo M, Show PL, Pan J, Tabatabaei M, Rajaei A (2023) Potential application of polysaccharide mucilages as a substitute for emulsifiers: A review. Int J Biol Macromol 242(Pt 2):124800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124800
Yin G, Dang Y (2008) Optimization of extraction Technology of the Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides by box-behnken statistical design. Carbohydr Polym 74:603–610
Yusoff IM, Taher ZM, Rahmat Z, Chua LS (2022) A review of ultrasound-assisted extraction for plant bioactive compounds: phenolics, flavonoids, thymols, saponins and proteins. Food Res Int 157:111268
Zhang H, Li H, Netala VR, Hou T, Zhang Z (2022) Optimization of complex enzyme-ultrasonic synergistic extraction of water-soluble polysaccharides from perilla frutescens seed meal: purification, characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity. J Food Process Preserv 46:e16201
Zheng J, Zhang X, Herrera-Balandrano DD, Wang J, Chai Z, Beta T, Huang W, Li Y (2022) Extraction optimization of arctium lappa L. polysaccharides by box-behnken response surface design and their antioxidant capacity. Starch-Stärke 74:2100305
Acknowledgements
The authors express gratitude to the Food Engineering and Tea Technology (FET) laboratory of Shahjalal University of Science and Technology (SUST) for technical assistance and other supports throughout the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Saydul Md Safwa: Formal analysis, Writing—Original Draft; *Md Rahmatuzzaman Rana: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition; Tanvir Ahmed: Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Review & Editing; Shahriar Rahman: Writing—Review & Editing; Md. Akib Bin Kabir: Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Saydul Md Safwa declares no conflict of interest. Md Rahmatuzzaman Rana declares no conflict of interest. Tanvir Ahmed declares no conflict of interest. Shahriar Rahman declares no conflict of interest. Md. Akib Bin Kabir declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Safwa, S.M., Rana, M.R., Ahmed, T. et al. Maximization and Characterization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Taro Corms Mucilage Using Response Surface Optimization and Comparison with Conventional Methods. Food Anal. Methods 16, 1724–1737 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02539-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02539-9