Abstract
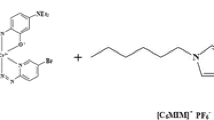
Conventional monitoring of metal ions in edible vegetable oils is crucial for assessing the quality and safety of consumers. In the current study, we developed a magnetic effervescence–enhanced emulsification microextraction (MEEM-DM) based on the employment of effervescent tablets composed of dicationic ionic liquids (DILs), MFe2O4 nanoparticles, and acidic and alkaline sources. The MEEM-DM pre-treatment was combined with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis for trace-level detection of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) in ten types of edible oil. It realized efficient preconcentration/extraction by DILs, vigorous dispersion by effervescent reaction, and rapid separation/collection by MFe2O4 in one synchronous step. As the DIL ([Cn(MIM)2]Br2) possesses two active centers, it provided superior adsorption/extraction performance for metal ions when compared with its corresponding monocationic form ([Cn(MIM)]Br). Four types of MFe2O4 were synthesized and characterized, in which NiFe2O4 nanoparticles presented a larger specific surface area and smaller particle diameter than others. The optimized parameters for ICP-MS were as follows: flow rate of carrier gas, 1.15 L/min, and ICP ratio frequency power, 1550 W. The optimized MEEM-DM conditions were as follows: 0.46 g Na2CO3, 60 mg [C4(MIM)2]Br2, 45 mg Na[N(CN)2], 10 mg NiFe2O4, 0.58 g for each tablet, and 0.50 M HCl solution. The newly developed method gave satisfactory detection limits (0.076–0.086 μg/kg) and recoveries (96.9–105.8%) for Cr(VI) and Cu(II) that were comparable with conventional ultrasound-assisted extraction and microwave-assisted acid-digestion methods. These superior performance metrics show an additive extraction action between DILs and MFe2O4 in an effervescent reaction–enhanced microextraction and great potential in the conventional monitoring of heavy metals in edible oil samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Alonso J, Barandiarán JM, Fernández Barquín L, García-Arribas A (2018) Chapter 1 - magnetic nanoparticles, synthesis, properties, and applications. In: Micro and Nano Technologies, Magnetic Nanostructured Materials. Elsevier, pp 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813904-2.00001-2
Altunay N, Yildirim E, Gurkan R (2018) Extraction and preconcentration of trace Al and Cr from vegetable samples by vortex-assisted ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Food Chem 245:586–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.134
Barreto IS, Andrade SIE, Cunha FAS, Lima MB, Araujo MCU, Almeida LF (2018) A robotic magnetic nanoparticle solid phase extraction system coupled to flow-batch analyzer and GFAAS for determination of trace cadmium in edible oils without external pretreatment. Talanta 178:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.09.063
Boros E, Pinkhasov OR, Caravan P (2018) Metabolite profiling with HPLC-ICP-MS as a tool for in vivo characterization of imaging probes EJNMMI. Radiopharm Chem 3:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41181-017-0037-5
Carneiro AF, Carneiro CN, de N Pires L, Teixeira LSG, Azcarate SM, de S Dias F (2020) D-optimal mixture design for the optimization of extraction induced by emulsion breaking for multielemental determination in edible vegetable oils by microwave-induced plasma optical emission spectrometry. Talanta 219:121218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121218
Cindric IJ, Zeiner M, Steffan I (2007) Trace elemental characterization of edible oils by ICP–AES and GFAAS. Microchem J 85:136–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2006.04.011
Fan C et al (2017) In-situ ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using a new anion-exchange reagent combined Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for determination of pyrethroid pesticides in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 975:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.036
Frizzo CP et al (2018) Impact of anions on the partition constant, self-diffusion, thermal stability, and toxicity of dicationic ionic liquids. ACS Omega 3:734–743. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01873
Gunduz S, Akman S (2015) Investigation of trace element contents in edible oils sold in Turkey using microemulsion and emulsion procedures by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry. LWT Food Sci Technol 64:1329–1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.032
Habila MA, Alothman ZA, El-Toni AM, Al-Tamrah SA, Soylak M, Labis JP (2017) Carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with surface amido groups for magnetic solid phase extraction of Cr(III), Co(II), Cd(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) prior to their quantitation by ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 184:2645–2651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2283-3
Habila MA, Alothman ZA, Yilmaz E, Alabdullkarem EA, Soylak M (2019) A new amine based microextraction of lead (II) in real water samples using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem J 148:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.078
He D, Zhu Z, Miao X, Zheng H, Li X, Belshaw NS, Hu S (2019) Determination of trace cadmium in geological samples by membrane desolvation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchem J 148:561–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.05.042
Herce-Sesa B, López-López JA, Moreno C (2021) Advances in ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents-based liquid phase microextraction of metals for sample preparation in Environmental Analytical Chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116398
Jagirani MS, Soylak M (2020) A review: recent advances in solid phase microextraction of toxic pollutants using nanotechnology scenario. Microchem J 159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105436
Jing Q, Chen L, Zhao Q, Zhou P, Li Y, Wang H, Wang X (2021) Effervescence-assisted dual microextraction of PAHs in edible oils using lighter-than-water phosphonium-based ionic liquids and switchable hydrophilic/hydrophobic fatty acids. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:1983–1997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03167-0
Lasarte-Aragonés G, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2014) Effervescence assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with extractant removal by magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 807:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.11.029
Lepri FG, Chaves ES, Vieira MA, Ribeiro AS, Curtius AJ, DeOliveira LCC, DeCampos RC (2011) Determination of trace elements in vegetable oils and biodiesel by atomic spectrometric techniques—a review applied spectroscopy. Reviews 46:175–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2010.529628
Li Q, Yang D, Yang Y (2021) Spectrofluorimetric determination of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by quenching effect of Cr(III) based on the Cu-CDs with peroxidase-mimicking activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 244:118882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118882
Liu T et al (2022) Enhanced adsorption/extraction of bisphenols by pyrrolic N-based 3D magnetic carbon nanocomposites for effervescence-assisted solid-phase microextraction of bisphenols from juices and the underlying interaction mechanisms. Chem Eng J 448:137690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137690
Llorent-Martinez EJ, Ortega-Barrales P, Fernandez-de Cordova ML, Dominguez-Vidal A, Ruiz-Medina A (2011) Investigation by ICP-MS of trace element levels in vegetable edible oils produced in Spain. Food Chem 127:1257–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.064
Manjusha R, Shekhar R, Kumar SJ (2019) Ultrasound-assisted extraction of Pb, Cd, Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn from edible oils with tetramethylammonium hydroxide and EDTA followed by determination using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometer. Food Chem 294:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.104
Mdluli NS, Nomngongo PN, Mketo N (2022) A critical review on application of extraction methods prior to spectrometric determination of trace-metals in oily matrices. Crit Rev Anal Chem 52:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2020.1781591
Mehdinia A, Shegefti S, Shemirani F (2015) A novel nanomagnetic task specific ionic liquid as a selective sorbent for the trace determination of cadmium in water and fruit samples. Talanta 144:1266–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.012
Mei M, Pang J, Huang X, Luo Q (2019) Magnetism-reinforced in-tube solid phase microextraction for the online determination of trace heavy metal ions in complex samples. Anal Chim Acta 1090:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.028
Reis BF, Knochen M, Pignalosa G, Cabrera N, Giglio J (2004) A multicommuted flow system for the determination of copper, chromium, iron and lead in lubricating oils with detection by flame AAS. Talanta 64:1220–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.03.070
Saad SM et al (2020) Magnetic nanoparticles assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of chloramphenicol in water samples. R Soc Open Sci 7:200143. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200143
Sabale S, Jadhav V, Khot V, Zhu X, Xin M, Chen H (2015) Superparamagnetic MFe2O4 (M = Ni Co, Zn, Mn) nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, induction heating and cell viability studies for cancer hyperthermia applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 26:127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5466-7
Saeed M, Mansha A, Hamayun M, Ahmad A, Ulhaq A, Ashfaq M (2018) Green synthesis of CoFe2O4 and investigation of its catalytic efficiency for degradation of dyes in aqueous medium. Z Phys Chem 232:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2017-1065
Shirkhanloo H, Arjomandi M (2019) A review: analytical methods for heavy metals determination in environment and human samples. Anal Methods Environ Chem J 97–126. https://doi.org/10.24200/amecj.v2.i03.73
Sripriya RC, Ezhil A, Madhavan J, Victor AR (2017) Synthesis and characterization studies of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles Mechanics. Mater Sci Eng J 9. https://doi.org/10.2412/mmse.81.85.882
Tan C, Li J, Liu W, Zhao Q, Wang X, Li Y (2020a) Core-shell magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites as an adsorbent for effervescent reaction-enhanced microextraction of endocrine disruptors in liquid matrices. Chem Eng J 396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125191
Tan C, Li J, Liu W, Zhao Q, Wang X, Li Y (2020) Core-shell magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites as an adsorbent for effervescent reaction-enhanced microextraction of endocrine disruptors in liquid matrices. Chem Eng J 396:125191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125191
Trujillo-Rodriguez MJ, Anderson JL (2019) In situ formation of hydrophobic magnetic ionic liquids for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1588:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.12.032
Wang H, Du L, Qu J, Li J, Wang J, Wang X (2019) Determination of bisphenolic pollutants in raw bovine milks and their derivative products using an in-situ metathesis reaction microextraction based on dicationic imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Microchem J 149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104028
Wu J et al (2019) Preconcentration/extraction of phthalate esters in milk samples using MFe2O4-based magnetic ionic liquid effervescent tablets consisting of accessory functional fillers. Food Anal Methods 12:2106–2119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01535-2
Wu J et al (2018) Combination of in situ metathesis reaction with a novel “magnetic effervescent tablet-assisted ionic liquid dispersive microextraction” for the determination of endogenous steroids in human fluids. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:2921–2935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0973-2
Wu J et al (2016) Optimization of a NH4PF6-enhanced, non-organic solvent, dual microextraction method for determination of phthalate metabolites in urine by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 1014:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.01.024
Yao L et al (2018) Ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction using a magnetic ionic liquid coupled with micro-solid phase extraction for the determination of cadmium and lead in edible vegetable oils. Food Chem 256:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.132
Zhang W, Zhou P, Liu W, Wang H, Wang X (2020) Enhanced adsorption/extraction of five typical polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from meat samples using magnetic effervescent tablets composed of dicationic ionic liquids and NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Mol Liquids 315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113682
Zhou P, Zheng R, Zhang W, Liu W, Li Y, Wang H, Wang X (2019) Development of an effervescent tablet microextraction method using NiFe2O4-based magnetic nanoparticles for preconcentration/extraction of heavy metals prior to ICP-MS analysis of seafood. J Anal Atom Spectrom 34:598–606. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ja00331a
Acknowledgements
The authors also thank the support by the Key Discipline of Zhejiang Province in Medical Technology (First Class, Category A).
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the Wenzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (Y20210086), the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students (202210343004), Science and Technology Innovation Program of Zhejiang Province College Students and the Sprout Talents Plan (2022R413A004), and Jiangsu Provincial Key Research & Development Program (BE2022733).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jia Wu: overall design; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing; Shuning Lan: preparation and characterization of the METs; Jiaju Sun and Hui She: optimization of the MEEM-DM procedures. Gang Wang and Xingfu Wen: validation of method performance; Shanle Zhou and Bingxia Ying: sample collection and detection; Xuedong Wang: management and supervision of experiment process; Huili Wang: methodology, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
Jia Wu declares no conflict of interest. Shuning Lan declares no conflict of interest. Jiaju Sun declares no conflict of interest. Hui She declares no conflict of interest. Gang Wang declares no conflict of interest. Xingfu Wen declares no conflict of interest. Shanle Zhou declares no conflict of interest. Bingxia Ying declares no conflict of interest. Xuedong Wang declares no conflict of interest. Huili Wang declares no conflict of interest.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Lan, S., Sun, J. et al. Trace-Level Detection of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) in Edible Vegetable Oils Using Dicationic Ionic Liquids and MFe2O4-Based Effervescence-Enhanced Emulsification Microextraction Followed by ICP-MS Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 16, 1655–1672 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02528-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02528-y