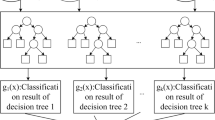
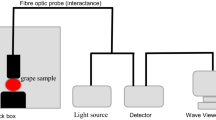
Abstract
In this study, we aimed to develop rapid, nondestructive methods for fig fruit quality prediction after picking. Visible and near-infrared spectroscopy and the random forest (RF) method were used to develop prediction models for the color (L*a*b*, △E), soluble solid content (SSC), and firmness of three fresh fig varieties. The RF method had better predictive capacity than the partial least squares (PLS) method for L*, a*, △E, and firmness. The selection of characteristic wavelengths by the SPA algorithm improved the predictive performance of the models. For the Orphan fig variety, the R2p for firmness and L* increased from 0.8215 and 0.8605 to 0.9173 and 0.9000, respectively. For LvMi, the R2p for SSC, b* and △E increased from 0.5165, 0.5617, and 0.3405 to 0.7518, 0.7172, and 0.5483. For Bojihong, the R2p for SSC a* and △E increased to 0.6106, 0.6573, and 0.4184, respectively. The accuracy of firmness, L*, and △E prediction models for the Orphan variety and that of the firmness prediction model for LvMi were high. This study provides a new technical means for rapidly determining the quality of figs in the early stages of production and evaluating the processing quality of fig products.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Vis-NIR:
-
Visible and near-infrared
- RF:
-
Random forest method
- SSC:
-
Soluble solid content
- PLS:
-
Partial least squares
- SPA:
-
Successive projections algorithm
- S-G:
-
Savitzky-Golay
- MSC:
-
Multiplicative scatter correction
- FD:
-
First derivative
- RMSEC:
-
Root mean standard error of calibration
- RMSEP:
-
Root mean square error of prediction
- RMSECV:
-
Root mean standard error of cross-validation
- RPD:
-
Residual predictive deviation
References
Alamar PD, Caramês ETS, Poppi RJ, Pallone JAL (2016) Quality evaluation of frozen guava and yellow passion fruit pulps by NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Res Int 85:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.04.027
Albanell E, Martínez M, De Marchi M, Manuelian CL (2021) Prediction of bioactive compounds in barley by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS). J Food Compos Anal 97:103763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103763
Arvaniti OS, Samaras Y, Gatidou G et al (2019) Review on fresh and dried figs: chemical analysis and occurrence of phytochemical compounds, antioxidant capacity and health effects. Food Res Int 119:244–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.055
Azarmdel H, Jahanbakhshi A, Mohtasebi SS, Muñoz AR (2020) Evaluation of image processing technique as an expert system in mulberry fruit grading based on ripeness level using artificial neural networks (ANNs) and support vector machine (SVM). Postharvest Biol Technol 166:111201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111201
Benalia S, Cubero S, Prats-Montalbán JM et al (2016) Computer vision for automatic quality inspection of dried figs (Ficus carica L.) in real-time. Comput Electron Agric 120:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.11.002
Byeon S-E, Lee J (2020) Fruit quality and major primary metabolites differ across production systems in cold-stored figs (Ficus carica L.). Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 274:109669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109669
Cai H-T, Liu J, Chen J-Y et al (2021) Soil nutrient information extraction model based on transfer learning and near infrared spectroscopy. Alexandria Eng J 60:2741–2746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.01.014
Chen H-Z, Xu L-L, Tang G-Q et al (2016) Rapid detection of surface color of Shatian pomelo using Vis-NIR spectrometry for the identification of maturity. Food Anal Methods 9:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0188-5
de Brito AA, Campos F, dos ReisNascimento A et al (2021) Determination of soluble solid content in market tomatoes using near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Control 126:108068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108068
Flores P, Zhang Z, Igathinathane C et al (2021) Distinguishing seedling volunteer corn from soybean through greenhouse color, color-infrared, and fused images using machine and deep learning. Ind Crops Prod 161:113223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113223
Herrero-Langreo A, Fernández-Ahumada E, Roger J-M et al (2012) Combination of optical and non-destructive mechanical techniques for the measurement of maturity in peach. J Food Eng 108:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.07.004
Hu R, Zhang LX, Yu ZY et al (2019) Optimization of soluble solids content prediction models in ‘Hami’ melons by means of Vis-NIR spectroscopy and chemometric tools. Infrared Phys Techn 102:102999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2019.102999
Kamiloglu S, Capanoglu E (2015) Polyphenol content in figs (Ficus carica L.): effect of sun-drying. Int J Food Prop 18:521–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2013.833522
Khodabakhshian R, Bayati M, Emadi B (2022) Adulteration detection of Sudan Red and metanil yellow in turmeric powder by NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics: the role of preprocessing methods in analysis. Vib Spectrosc 120:103372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2022.103372
Li J, Zhang H, Zhan B et al (2020) Nondestructive firmness measurement of the multiple cultivars of pears by Vis-NIR spectroscopy coupled with multivariate calibration analysis and MC-UVE-SPA method. Infrared Phys Technol 104:103154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2019.103154
Li Z, Yang Y, Liu M et al (2021) A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, bioactivities, toxicity studies, and clinical studies on Ficus carica Linn. leaves. Biomed Pharmacother 137:111393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111393
Maniwara P, Nakano K, Ohashi S et al (2019) Evaluation of NIRS as non-destructive test to evaluate quality traits of purple passion fruit. Sci Hortic (amsterdam) 257:108712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108712
Mishra P, Marini F, Brouwer B et al (2021) Sequential fusion of information from two portable spectrometers for improved prediction of moisture and soluble solids content in pear fruit. Talanta 223:121733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121733
Munera S, Besada C, Aleixos N et al (2017) Non-destructive assessment of the internal quality of intact persimmon using colour and VIS/NIR hyperspectral imaging. LWT 77:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.11.063
Ncama K, Opara UL, Tesfay SZ et al (2017) Application of Vis/NIR spectroscopy for predicting sweetness and flavour parameters of ‘Valencia’ orange (Citrus sinensis) and ‘Star Ruby’ grapefruit (Citrus x paradisi Macfad). J Food Eng 193:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.08.015
Nordey T, Joas J, Davrieux F et al (2017) Robust NIRS models for non-destructive prediction of mango internal quality. Sci Hortic 216:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.12.023
Nturambirwe JFI, Opara UL (2020) Machine learning applications to non-destructive defect detection in horticultural products. Biosyst Eng 189:60–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.11.011
Olarewaju OO, Bertling I, Magwaza LS (2016) Non-destructive evaluation of avocado fruit maturity using near infrared spectroscopy and PLS regression models. Sci Hortic (amsterdam) 199:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.12.047
Onwude DI, Hashim N, Abdan K et al (2018) Combination of computer vision and backscattering imaging for predicting the moisture content and colour changes of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) during drying. Comput Electron Agric 150:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.04.015
Ouyang Q, Liu Y, Chen Q et al (2017) Intelligent evaluation of color sensory quality of black tea by visible-near infrared spectroscopy technology: A comparison of spectra and color data information. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 180:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.03.009
Pissard A, Marques EJN, Dardenne P et al (2021) Evaluation of a handheld ultra-compact NIR spectrometer for rapid and non-destructive determination of apple fruit quality. Postharvest Biol Technol 172:111375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111375
Sanaeifar A, Bakhshipour A, de la Guardia M (2016) Prediction of banana quality indices from color features using support vector regression. Talanta 148:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.10.073
Sánchez M-T, Torres I, De la Haba M-J, Pérez-Marín D (2014) First steps to predicting pulp colour in whole melons using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosyst Eng 123:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2014.04.010
Santos Pereira LF, Barbon S, Valous NA, Barbin DF (2018) Predicting the ripening of papaya fruit with digital imaging and random forests. Comput Electron Agric 145:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2017.12.029
Tsouvaltzis P, Babellahi F, Amodio ML, Colelli G (2020) Early detection of eggplant fruit stored at chilling temperature using different non-destructive optical techniques and supervised classification algorithms. Postharvest Biol Technol 159:111001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111001
Uwadaira Y, Sekiyama Y, Ikehata A (2018) An examination of the principle of non-destructive flesh firmness measurement of peach fruit by using VIS-NIR spectroscopy. Heliyon 4:e00531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00531
Valente M, Leardi R, Self G et al (2009) Multivariate calibration of mango firmness using vis/NIR spectroscopy and acoustic impulse method. J Food Eng 94:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.02.020
Vieira LS, Assis C, de Queiroz MELR et al (2021) Building robust models for identification of adulteration in olive oil using FT-NIR. PLS-DA and Variable Selection Food Chem 345:128866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128866
Wang NN, Sun DW, Yang YC et al (2015) Recent advances in the application of hyperspectral imaging for evaluating fruit quality. Food Anal Methods 9:178–191
Wu D, Sun DW, He Y (2012) Application of long-wave near infrared hyperspectral imaging for measurement of color distribution in salmon fillet. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 16:361–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2012.08.003
Yuan L, Mao F, Huang G et al (2020) Models fused with successive CARS-PLS for measurement of the soluble solids content of Chinese bayberry by vis-NIRS technology. Postharvest Biol Technol 169:111308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111308
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Mingguan Yang, Prof. Chengzhong Wang, Prof. Xiuhe Liu, and Prof. Zhiguo Zhang for their support of the research work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Qinghai Province Science and Technology Project [grant number 2021-NK-127]; Jinan 20 Rules of High School [grant number 2020GXRC024]; Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province [grant number ZR2017MC063]; and Shandong Province Key Research & Development Program [grant number 2019GNC106139].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
Jingyu Zhou declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xinyu Liu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Rui Sun declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lei Sun declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Liu, X., Sun, R. et al. Rapid Nondestructive Detection of the Pulp Firmness and Peel Color of Figs by NIR Spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 15, 2575–2593 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02314-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02314-2