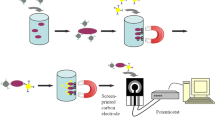
Abstract
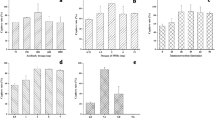
Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella choleraesuis are two important foodborne pathogens that cause illnesses and even deaths. Rapid and convenient methods, such as immunochromatographic assays (ICAs), are useful for detecting these two pathogens. Herein, we developed a highly sensitive ICA for the simultaneous quantitative analysis of these two foodborne pathogens. Silver nanoplates (AgNPs) and gold nanospheres (AuNSs) were synthesized as two probes for simultaneous detection. In this method, Escherichia coli O157:H7 (E. coli O157:H7) and Salmonella choleraesuis (S. choleraesuis) were specifically detected at concentrations as low as 2.16 × 104 and 1.18 × 105 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL, respectively, in 30 min. Subsequently, a method for separately detecting these two targets with the same test strips was developed. The tests achieved specific detections of E. coli O157:H7 and S. choleraesuis, with detection limits of 1.07 × 104 and 9.85 × 104 CFU/mL, respectively. By comparing the intensity of the test lines (T) in the two methods, we found an interesting phenomenon in which the intensity of T in the simultaneous detection method was lower than that in the separate detection method. RGB analysis of the test lines demonstrated that the two probe–target compounds influenced each other. We believe that this phenomenon is an important factor to consider when building a simultaneous quantitative ICA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer ED, Rijkelt RB (1999) Methodology for detection and typing of foodborne microorganisms. Int J Food Microbiol 50:119–130
Cao L, Cui X, Hu J, Li Z, Choi JR, Yang Q, Lin M, Ying Hui L, Xu F (2017) Advances in digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) and its emerging biomedical applications. Biosens Bioelectron 90:459–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.082
CDC (2017) Multistate outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections linked to I.M. Healthy brand SoyNut butter (final update). https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/2017/o157h7-03-17/index.html. Accessed 4 May 2017
CDC (2018) Reports of active Salmonella outbreak investigations. https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/outbreaks-active.html. Accessed 7 Dec 2018
Charlermroj R, Himananto O, Seepiban C, Kumpoosiri M, Warin N, Gajanandana O, Elliott CT, Karoonuthaisiri N (2014) Antibody array in a multiwell plate format for the sensitive and multiplexed detection of important plant pathogens. Anal Chem 86:7049–7056. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501424k
Cohen JI, Bartlett JA, Ralph Corey G (1987) Extra-intestinal manifestations of salmonella infections. Medicine 66:349–388
Guo Q, Han JJ, Shan S, Liu DF, Wu SS, Xiong YH, Lai WH (2016) DNA-based hybridization chain reaction and biotin-streptavidin signal amplification for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 through ELISA. Biosens Bioelectron 86:990–995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.049
Hsu HL, Huang HH, Liang CC, Lin HC, Liu WT, Lin FP, Kau JH, Sun KH (2013) Suspension bead array of the single-stranded multiplex polymerase chain reaction amplicons for enhanced identification and quantification of multiple pathogens. Anal Chem 85:5562–5568. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400778b
Hsu CK, Huang HY, Chen WR, Nishie W, Ujiie H, Natsuga K, Fan ST, Wang HK, Lee JYY, Tsai WL, Shimizu H, Cheng CM (2014) Paper-based ELISA for the detection of autoimmune antibodies in body fluid-the case of bullous pemphigoid. Anal Chem 86:4605–4610. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500835k
Li Y, Li Z, Gao Y, Gong A, Zhang Y, Hosmane NS, Shen Z, Wu A (2014) “red-to-blue” colorimetric detection of cysteine via anti-etching of silver nanoprisms. Nanoscale 6:10631–10637. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr03309d
Morales-Narvaez E, Naghdi T, Zor E, Merkoci A (2015) Photoluminescent lateral-flow immunoassay revealed by graphene oxide: highly sensitive paper-based pathogen detection. Anal Chem 87:8573–8577. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02383
NORS (2018) National Outbreak Reporting System Dashboard https://wwwn.cdc.gov/norsdashboard/. Accessed 7 Dec 2018
Park J, Park S, Kim Y-K (2010) Multiplex detection of pathogens using an immunochromatographic assay strip. BioChip J 4:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-010-4407-2
Park J, Shin JH, Park JK (2016) Pressed paper-based dipstick for detection of foodborne pathogens with multistep reactions. Anal Chem 88:3781–3788. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04743
Raeisossadati MJ, Danesh NM, Borna F, Gholamzad M, Ramezani M, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2016) Lateral flow based immunobiosensors for detection of food contaminants. Biosens Bioelectron 86:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.06.061
Shan S, Lai W, Xiong Y, Wei H, Xu H (2015) Novel strategies to enhance lateral flow immunoassay sensitivity for detecting foodborne pathogens. J Agric Food Chem 63:745–753. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5046415
Shu B, Zhang C, Xing D (2017) A sample-to-answer, real-time convective polymerase chain reaction system for point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 97:360–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.06.014
Wei T, Du D, Zhu MJ, Lin Y, Dai Z (2016) An improved ultrasensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using hydrangea-like antibody-enzyme-inorganic three-in-one nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6329–6335. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b11834
Xie X, Wang S, Jiang SC, Bahnemann J, Hoffmann MR (2016) Sunlight-activated propidium monoazide pretreatment for differentiation of viable and dead bacteria by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Environ Sci Technol Lett 3:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00348
Xue S, Li HP, Zhang JB, Liu JL, Hu ZQ, Gong AD, Huang T, Liao YC (2013) Chicken single-chain antibody fused to alkaline phosphatase detects Aspergillus pathogens and their presence in natural samples by direct sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Chem 85:10992–10999. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac402608e
Zhao Y, Wang H, Zhang P, Sun C, Wang X, Wang X, Yang R, Wang C, Zhou L (2016) Rapid multiplex detection of 10 foodborne pathogens with an up-converting phosphor technology-based 10-channel lateral flow assay. Sci Rep 6:21342. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21342
Funding
This work was supported by the free explore issue of State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology of Nanchang University (SKLF-ZZB-201719), the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University (SKLF-KF-201616), earmarked fund for Jiangxi Agriculture Research System (JXARS-03), and Jiangxi Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Collaborative Innovation (JXXTCX201703-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Ganggang Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Youju Huang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Juan Peng declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jiaojiao Han declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ping Guo declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lei Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jiawei Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Weihua Lai declares that he has no conflict of interest. Tao Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2358 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Huang, Y., Peng, J. et al. Silver Nanoplates and Gold Nanospheres as Probesfor Revealing an “Interference” Phenomenon in a Simultaneous Quantitative Immunochromatographic Assay. Food Anal. Methods 12, 1666–1673 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01509-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01509-4