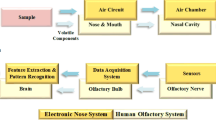
Abstract
Food quality is a fundamental requirement for consumers, and there is growing interest in food quality assessment. An electronic nose is a machine that is designed to mimic biological olfaction and detect and discriminate among complex odors using an array of chemical sensors. Electronic noses have been widely applied for food quality evaluations because they are rapid, sensitive, and non-destructive. In the present paper, we review important applications of electronic noses to meat analysis. First, we briefly describe the components, working principle, and data processing for an electronic nose. Then, we discuss the applications of electronic noses to meat freshness evaluations, quality classification, and authenticity assessments using different pattern recognition algorithms. Despite many successful results, sensor technology limitations still restrict electronic nose applications at the industrial scale. Finally, we discuss existing problems and prospects for electronic noses in food analysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alimelli A, Pennazza G, Santonico M, Paolesse R, Filippini D, D’Amico A, Lundström I, Di Natale C (2007) Fish freshness detection by a computer screen photoassisted based gas sensor array. Anal Chim Acta 582:320–328
Baby R, Cabezas M, Castro E, Filip R, Walsöe de Reca NE (2005) Quality control of medicinal plants with an electronic nose. Sensors Actuators B Chem 106:24–28
Cai BB (2013) Gas sensor array pattern recognition algorithms and hardware implementation [M]. Optical Engineening Institute. University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu
Canhoto O, Pinzari F, Fanelli C, Magan N (2004) Application of electronic nose technology for the detection of fungal contamination in library paper. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 54:303–309
Casalinuovo I, Di Pierro D, Coletta M, Di Francesco P (2006) Application of electronic noses for disease diagnosis and food spoilage detection. Sensors 6:1428–1439
Chang ZY (2013) Study on the multi-intelligence fusion technology for the meat freshness identification based on bionic nose [M]. Biological and Agricultural Engineering Institute. Jilin University, Jilin
Chen J, Sun Y, Shen L (2015a) Application of electronic nose in detecting the quality of agriculture products. J Anhui Agric Sci 43:364–366
Chen XW, Wang J, Shen RQ (2015b) Wireless electronic nose based on GPRS and its application on mangos. T Chin Soc Agric Mach 46:238–245
Deshmukh S, Bandyopadhyay R, Bhattacharyya N, Pandey RA, Jana A (2015) Application of electronic nose for industrial odors and gaseous emissions measurement and monitoring—an overview. Talanta 144:329–340
Di Rosa AR, Leone F, Cheli F, Chiofalo V (2017) Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment—a review. J Food Eng 210:62–75
Dymerski T, Gębicki J, Wardencki W, Namieśnik J (2013) Quality evaluation of agricultural distillates using an electronic nose. Sensors 13:15954–15967
El Barbri N, Llobet E, El Bari N, Correig X, Bouchikhi B (2008) Application of a portable electronic nose system to assess the freshness of Moroccan sardines. Mater Sci Eng C 28:666–670
Falasconi M, Comini E, Concina I, Sberveglieri V, Gobbi E (2014) Electronic nose and its application to microbiological food spoilage screening. In: Mason A, Mukhopadhyay SC, Jayasundera KP, Bhattacharyya N (eds) Sensing technology: current status and future trends II. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 119–140
Gao XQ, Shen XL (2015) Research and implementation of electronic nose pattern recognition algorithm. Sci Technol Innov 132:173–182
García M, Aleixandre M, Gutiérrez J, Horrillo MC (2006) Electronic nose for ham discrimination. Sensors Actuators B Chem 114:418–422
Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti M, Lozano J (2016) Electronic nose as an innovative measurement system for the quality assurance and control of bakery products: a review. Eng Agric Environ Food 9:365–374
Gliszczyńska-Świgło A, Chmielewski J (2017) Electronic nose as a tool for monitoring the authenticity of food. A review. Food Anal Methods 10:1800–1816
Gu SQ, Wang XC, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Zhang JJ, Xie J, Zheng JZ (2010) Electronic nose for measurement of freshness change of chilled pork during storage at different temperatures. Food Sci Technol 31:172–176
Hansen T, Petersen MA, Byrne DV (2005) Sensory based quality control utilising an electronic nose and GC-MS analyses to predict end-product quality from raw materials. Meat Sci 69:621–634
Herrero JL, Lozano J, Santos JP, Suárez JI (2016) On-line classification of pollutants in water using wireless portable electronic noses. Chemosphere 152:107–116
Hong XZ, Wei ZB, Hai Z, Li JK, Zhang P (2014) Application of electronic nose and neural network in beef freshness. Mod Food Sci Technol 30:279–285
Hu Y (2013) The develop of wireless electronic nose based on Zigbee [M]. Biological Engineering and Food Science Institute. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou
Huang L, Zhao J, Chen Q, Zhang Y (2014) Nondestructive measurement of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) in pork meat by integrating near infrared spectroscopy, computer vision and electronic nose techniques. Food Chem 145:228–236
Jia HF, Zhan Y, He JH, Pan T, Xiao L, Zhang ZY, Zhu LM (2011) Recognition of yak meat, beef and pork by electronic nose. T Chin Soc Agric Mach 27:358–363
Kiani S, Minaei S, Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti M (2016) Application of electronic nose systems for assessing quality of medicinal and aromatic plant products: a review. J App Res Med Aromat Plants 3:1–9
Kovács Z, Dalmadi I, Lukács L, Sipos L, Szántai-Kőhegyi K, Kókai Z, Fekete A (2010) Geographical origin identification of pure Sri Lanka tea infusions with electronic nose, electronic tongue and sensory profile analysis. J Chemom 24:121–130
Lei L (2011) Study on detection methods freshness of meat [M]. Biological and Agricultural Engineering Institute Jilin: Jilin University
Li HY (2008) Research and evaluation on the hardware of electronic nose [M]. Nanoscale Science and Technology. Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Hubei
Li HT (2010) Special electronic nose system for agriculture products quality detection [M]. Institute of Biological Instruments. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou
Li F, Sun J, Huang QY (2014a) Establish poultry meat detection and identification model with the electronic nose. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol 14:255–260
Li H, Chen Q, Zhao J, Ouyang Q (2014b) Non-destructive evaluation of pork freshness using aportable electronic nose (e-nose) based on acolorimetric sensor array. Anal Methods 6:6271–6277
Liang G, Liu XH, Li XH (2013) Highly sensitive detection of α-naphthol based on G-DNA modified gold electrode by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 45:46–51
Liang G, Man Y, Jin X, Pan L, Liu X (2016) Aptamer-based biosensor for label-free detection of ethanolamine by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 936:222–228
Liu SC, Zhao CJ, Yang XT (2015) Progress of electronic nose system on agricultural products safety and quality identification and control in the logistics. Mod. Food Sci Technol 40:306–309
Loutfi A, Coradeschi S, Mani GK, Shankar P, Rayappan JBB (2015) Electronic noses for food quality: a review. J Food Eng 144:103–111
Ning K (2014) Fusion technique of electronic nose and electronic tongue and its application [M]. College of Automation Engineering Jilin: Northeast Dianli University
Nurjuliana M, Che Man YB, Mat Hashim D, Mohamed AKS (2011) Rapid identification of pork for halal authentication using the electronic nose and gas chromatography mass spectrometer with headspace analyzer. Meat Sci 88:638–644
Pan LL, Yang SX (2009) An electronic nose network system for online monitoring of livestock farm odors: IEEE-ASME transactions on mechatronics. IEEE/ASME T Mech 14:371–376
Peris M, Escuder-Gilabert L (2009) A 21st century technique for food control: electronic noses. Anal Chim Acta 638:1–15
Peris M, Escuder-Gilabert L (2013) On-line monitoring of food fermentation processes using electronic noses and electronic tongues: a review. Anal Chim Acta 804:29–36
Rong JH, Xiong S, Zhang LZ (2015) Analysis of volatile flavor components in crisp grass carp muscle by electronic nose and SPME-GC-MS [J]. Food Sci Technol 36(10):124–128
Sanaeifar A, ZakiDizaji H, Jafari A, Guardia MDL (2017) Early detection of contamination and defect in foodstuffs by electronic nose: a review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 97:257–271
Santos JP, Garcı́a M, Aleixandre M, Horrillo MC, Gutiérrez J, Sayago I, Fernández MJ, Arés L (2004) Electronic nose for the identification of pig feeding and ripening time in Iberian hams. Meat Sci 66:727–732
Shi ZB (2004) Study on intelligent bionic nose system and its application [D]. Biological and Agricultural Engineering Institute. Jilin University, Jilin
Shi ZB, Tong YY, Chen DH (2009) Identification of beef freshness with electronic nose. T Chin Soc Agric Mach 40:184–188
Shi H, Zhang M, Adhikari B (2017) Advances of electronic nose and its application in fresh foods: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr:1–11
Śliwińska M, Wiśniewska P, Dymerski T, Namieśnik J, Wardencki W (2014) Food analysis using artificial senses. J Agric Food Chem 62:1423–1448
Song X, Gao ST, Hang MX, Chen W, Chen L, Liu Y, Zhang JJ (2015) Application of electronic nose on origin identification and quality grade evaluation of Jinhua and Xuanwei ham. Food Mach 31:114–118
Sun TL, Yue XQ, Zhang P (2014) The electronic nose usage in predicting the freshness of beef at freezing point storage. Food Ferm Ind 4:185–189
Sun QX, Dong FJ, Chen Q (2015) Application of electronic nose technique detect the flavor and quality of meat and meat products. Food Res Dev 36:123–126
Tian XY, Cai Q, Zhang YM (2012) Rapid classification of hairtail fish and pork freshness using an electronic nose based on the PCA method. Sensors 12:260–277
Tian XJ, Wang J, Cui SQ (2013a) Analysis of pork adulteration in minced mutton using electronic nose of metal oxide sensors. J Food Eng 119:744–749
Tian XJ, Wang J, Cui SQ (2013b) Fast discriminating of chicken adulteration in minced mutton by electronic nose. Mod Food Sci Technol 29:2997–3001
Tian HX, Li FH, Qin L (2015a) Quality evaluation of beef seasonings using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and electronic nose: correlation with sensory attributes and classification according to grade level. Food Anal Methods 8:1522–1534
Tian XJ, Wang J, Qiu SS (2015b) Review of data fusion methods for electronic nose and electronic tongue signal and its application in food quality detection. Food Sci Technol Int 36:386–389
Wang YC (2010) Pattern recognition algorithms in the test of agricultural products used e-nose [M]. The colloge of electronics and information. Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou
Wang M, Wang ZY, Ma CW (2009) Evaluation of aroma quality of pork from different castrated pigs using an electronic nose. Meat Res 23:45–49
Wang D, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Gu S, Xie J, Pan Y (2010) Estimation of total bacterial count in pork using electronic nose. Food Sci 31:148–150
Wang D, Wang X, Liu T, Liu Y (2012) Prediction of total viable counts on chilled pork using an electronic nose combined with support vector machine. Meat Sci 90:373–377
Wang J, Cui SQ, Chen XW (2013) Advanced technology and new application in electronic nose. T Chin Soc Agric Mach 44:160–167
Wojnowski W, Majchrzak T, Dymerski T, Gębicki J, Namieśnik J (2017a) Electronic noses: powerful tools in meat quality assessment. Meat Sci 131:119–131
Wojnowski W, Majchrzak T, Dymerski T, Gębicki J, Namieśnik J (2017b) Portable electronic nose based on electrochemical sensors for food quality assessment. Sensors 17:2715
Wu H, Liu Y, Gu S, Fu N, Chen W, Wang X (2013) Category distinction of different surimis by electronic nose, electronic tongue and sensory evaluation. Food Sci Technol Int 34:80–83
Wu SG, Zhang YH, Meng Y, Chen JD, Zhang YM, Zhang YL (2015) Analysis of chicken quality deterioration by electronic nose. Food Sci Technol Int 36:53–56
Xin SL, Li C, Xiao L, Chi FM, Fu G, Zhang Y (2018) Quality evaluation of black pepper duck breast by electronic nose. Food Sci 33:191–194
Xiong Z, Sun D-W, Pu H, Xie A, Han Z, Luo M (2015) Non-destructive prediction of thiobarbituricacid reactive substances (TBARS) value for freshness evaluation of chicken meat using hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem 179:175–181
Xu S, Zhou Z, Lu H, Luo X, Lan Y, Zhang Y, Li Y (2014) Estimation of the age and amount of brown rice plant hoppers based on bionic electronic nose use. Sensors 14:18114–18130
Yan MY, Lu YQ, Chen DW (2015) Application of electronic nose in freshness evaluation of tilapia fillets as affected by ozone treatment. Food Sci Technol 36:265–269
Zhang HM (2007) Quality detection of several kinds of agricultural products based on gas sensor array [D]. Biological engineering and food science institute [D]. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou
Zhang LY, Wen LJ, Zhou F, Zhang S, Yang PY (2003) Electronic nose for the determination of formaldehyde in air. Chem J Chin Univ 24:184–188
Zou XB, Zhao JW (2006) Electronic nose preprocessing and its application. T Chin Soc Agric Mach 37:83–86
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support from the Project of Beijing Science and Technology (grant number Z171100001517017), the Special Projects of Construction of Science and Technology Innovation Ability of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (grant numbers KJCX20170420), the Project of Beijing Excellent Talents (grant number 2017000020060G127), the International Cooperation Fund of Beijing Agricultural Forestry Academy (grant number GJHZ2018-05), the Beijing Agricultural Forestry Academy Youth Fund (grant number QNJJ201630), the Open Project of Hubei Engineering Technology Research Center for Farmland Environmental Monitoring (grant number 201601), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number 2016YFD0400902). We also thank Gabrielle David, Ph. D, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Wenshen Jia declares that he has no conflict of interest. Gang Liang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yalei Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jihua Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, W., Liang, G., Wang, Y. et al. Electronic Noses as a Powerful Tool for Assessing Meat Quality: a Mini Review. Food Anal. Methods 11, 2916–2924 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1283-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1283-1