Abstract
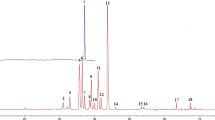
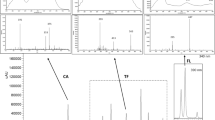
The process to develop a chromatographic method for fingerprinting complex matrices should be performed through a multiparameter approach that could lead to the desired separation and save environmental resources such as organic solvents and energy. In other words, this process should be pursued by employing an optimized experimental design and having a response function which takes into consideration separation parameters together with environmental parameters. Green Analytical Chemistry principles should be pursued during all steps of the research. This work presents a heuristic approach to develop a high-performance liquid chromatography method for fingerprinting an extract from leaves of Cynara scolymus L., a food plant consumed worldwide. A fractional factorial design was used to identify relevant chromatographic variables followed by a comprehensive design for optimization purposes (Doehlert design). A response function called green chromatographic fingerprinting response was employed to obtain a compromise between fingerprint quality and low environmental impact of the method. This optimized approach led to the development of a robust and green method for fingerprinting C. scolymus by HPLC-PAD. This method proved to be greener than the reference method reported in literature and compatible even with no state of art HPLC instruments because the system backpressure did not exceed 15 MPa and the column temperature was 35 °C.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaerts G, Dejaegher B, Smeyers-Verbeke J, Heyden YV (2010) Recent developments in chromatographic fingerprints from herbal products: set-up and data analysis. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 13:900–922. https://doi.org/10.2174/138620710793360284
Bundy R, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Wallis C, Simpson HCR (2008) Artichoke leaf extract (Cynara scolymus) reduces plasma cholesterol in otherwise healthy hypercholesterolemic adults: a randomized, double blind placebo controlled trial. Phytomedicine 15:668–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2008.03.001
Dolan JW (2002) Temperature selectivity in reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 965:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01321-8
Fantini N, Colombo G, Giori A, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Bombardelli E, Carai MAM (2011) Evidence of glycemia-lowering effect by a Cynara scolymus L. extract in normal and obese rats. Phytoter Res 25:463–466. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3285
Fritsche J, Beindorff CM, Dachtler M, Zhang H, Lammers JG (2002) Isolation, characterization and determination of minor artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) leaf extract compounds. Eur Food Res Technol 215:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-002-0507-0
Fritz R, Ruth W, Kragl U (2009) Assessment of acetone as an alternative to acetonitrile in peptide analysis by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:2139–2145. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.4122
Funari CS, Carneiro RL, Andrade AM, Hilder EF, Cavalheiro AJ (2014) Green chromatographic fingerprinting: an environmentally friendly approach for the development of separation methods for fingerprinting complex matrices. J Sep Sci 37:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201300955
Gaber Y, Törnvall U, Kumar MA, Amin MA, Hatti-Kaul R (2011) HPLC-EAT (environmental assessment tool): a tool for profiling safety, health and environmental impacts of liquid chromatography methods. Green Chem 13:2021–2025. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0gc00667j
Gałuszka A, Migaszewski Z, Namieśnik J (2013) The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. Trends. Anal Chem 50:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2013.04.010
Gong F, Liang YZ, Xie PS, Chau FT (2003) Information theory applied to chromatographic fingerprint of herbal medicine for quality control. J Chromatogr A 1002:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00648-4
Heinisch S, Rocca JL (2009) Sense and nonsense of high-temperature liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1216:642–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.11.079
Holtmann G, Adam B, Haag S, Collet W, Grünewald E, Windeck T (2003) Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia: a six-week placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 18:1099–1105. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01767.x
Hutchinson JP, Remenyi T, Nesterenko P, Farrell W, Groeber E, Szucs R, Dicinoski G, Haddad PR (2012) Investigation of polar organic solvents compatible with corona charged aerosol detection and their use for the determination of sugars by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 750:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.04.002
ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline (2005) Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology Q2(R1). ICH. https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf. Accessed 12 July 2017
Ji Y, Xu Q, Hu Y, Heyden YV (2005) Development, optimization and validation of a fingerprint of Ginkgo biloba extracts by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1066:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.01.035
Klein EJ, Rivera SL (2000) A review of criteria functions and response surface methodology for the optimization of analytical scale HPLC separations. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 23:2097–2121. https://doi.org/10.1081/JLC-100100475
Li Y, Wu T, Zhu J, Wan L, Yu Q, Li X, Cheng Z, Guo C (2010) Combinative method using HPLC fingerprint and quantitative analyses for quality consistency evaluation of an herbal medicinal preparation produced by different manufacturers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 52:597–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2010.01.018
Liang Y, Xie P, Chan K (2004) Quality control of herbal medicines. J Chromatogr B 812:53–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.08.041
Liang Y, Xie P, Chau F (2010) Chromatographic fingerprinting and related chemometric techniques for quality control of traditional Chinese medicines. J Sep Sci 33:410–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200900653
López-Molina D, Navarro-Martínez MD, Rojas-Melgarejo F, Hiner ANP, Chazarra S, Rodríguez-López JN (2005) Molecular properties and prebiotic effect of inulin obtained from artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) Phytochemistry 66:1476–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.04.003
Lutz M, Henríquez C, Escobar M (2011) Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of mature and baby artichokes (Cynara scolymus L.), raw and cooked. J Food Compos Anal 24:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2010.06.001
Marakis G, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Booth JCL, Wright J, Pike DJ (2002) Artichoke leaf extract reduces mild dyspepsia in an open study. Phytomedicine 9:694–699. https://doi.org/10.1078/094471102321621287
Montgomery DC (2017) Design and analysis of experiments. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Myers RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-Cook CM (2016) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Negro D, Montesano V, Grieco S, Crupi P, Sarli G, Lisi A, Sonnante G (2012) Polyphenol compounds in artichoke plant tissues and varieties. J Food Sci 77:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02531.x
Pandino G, Lombardo S, Mauromicale G, Williamson G (2011) Profile of polyphenols and phenolic acids in bracts and receptacles of globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus) germplasm. J Food Compos Anal 24:148–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2010.04.010
Pereira Filho ER (2015) Planejamento fatorial em química: maximizando a obtenção de resultados. EdUfscar, São Carlos
Qian G, Wang Q, Leung KS, Qin Y, Zhao Z, Jiang Z (2007) Quality assessment of Rhizoma et radix Notopterygii by HPTLC and HPLC fingerprinting and HPLC quantitative analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 44:812–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2007.03.029
Rodriguez TS, Giménez DG, Vásquez RP (2002) Choleretic activity and biliary elimination of lipids and bile acids induced by an artichoke leaf extract in rats. Phytomedicine 9:687–693. https://doi.org/10.1078/094471102321621278
Romani A, Pinelli P, Cantini C, Cimato A, Heimler D (2006) Characterization of Violetto di Toscana, a typical Italian variety of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) Food Chem 95:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.01.013
Schütz K, Persike M, Carle R, Schieber A (2006) Characterization and quantification of anthocyanins in selected artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) cultivars by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. Anal Bioanal Chem 384:1511–1517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0316-6
Snyder LR, Kirkland JJ, Glajch JL (1997) Practical HPLC method development. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products (2006) Note for guidance on quality of herbal medicinal products/traditional herbal medicinal products. EMEA, London
Tistaert C, Dejaegher B, Heyden YV (2011) Chromatographic separation techniques and data handling methods for herbal fingerprints: a review. Anal Chim Acta 690:148–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.023
United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization (2010) UNESCO Intangible Heritage Lists. https://ich.unesco.org/en/lists. Accessed 12 Aug 2017
US Food and Drug Administration (2004) Guidance for industry botanical drug product. US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville
World Health Organization (1991) Guidelines for the Assessment of Herbal Medicines. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/58865/1/WHO_TRM_91.4.pdf. Accessed 12 Aug 2017
Wu J, Qian Y, Mao P, Chen L, Lu Y, Wang H (2013) Separation and identification of phenolic compounds in canned artichoke by LC/DAD/ESI-MS using core-shell C18 column: a comparative study. J Chromatogr B 927:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.11.026
Xie Y, Jiang Z, Zhou H, Cai X, Wong Y, Liu Z, Bian Z, Xu H, Liu L (2007) Combinative method using HPLC quantitative and qualitative analyses for quality consistency assessment of a herbal medicine preparation. J Pharm Biomed Anal 43:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2006.07.008
Zapolska-Downar D, Zapolski-Downar A, Naruszewicz M, Siennicka A, Krasnodębska B, Kolodziej B (2002) Protective properties of artichoke (Cynara scolymus) against oxidative stress induced in cultured endothelial cells and monocytes. L Sci 71:2897–2908. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(02)02136-7
Zhu X, Zhang H, Lo R (2004) Phenolic compounds from the leaf extract of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and their antimicrobial activities. J Agric Food Chem 52:7272–7278. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0490192
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for financial support (grants 15-20639/1, 16/08179-8, and 45398 2014-5). The authors also thank Dr. Valdecir Farias Ximenes of the Department of Chemistry of São Paulo State University for the use of the HPLC-PAD instrument.
Funding
This study was funded by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (grants 15/20639-1, 16/08179-8) and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (grant 45398 2014-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Otávio Aguiar Souza declares that he has no conflict of interest. Renato Lajarim Carneiro declares that he has no conflict of interest. Thiago Henrick Martins Vieira declares that he has no conflict of interest. Cristiano Soleo Funari declares that he has no conflict of interest. Daniel Rinaldo declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souza, O.A., Carneiro, R.L., Vieira, T.H.M. et al. Fingerprinting Cynara scolymus L. (Artichoke) by Means of a Green Statistically Developed HPLC-PAD Method. Food Anal. Methods 11, 1977–1985 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1159-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1159-4