Abstract
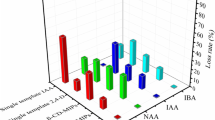
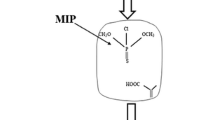
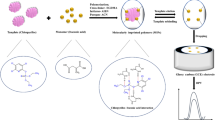
In this work, we first reported molecularly imprinted polymers-surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (MIP-SERS) for rapid detection and quantification of bitertanol in cucumber and peaches. In order to remove interference-mitigation effects and avoid template leakage, MIPs were successfully synthesized based on triadimefon molecules as the dummy template, methacrylic acid (MAA) as a functional monomer, trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TRIM) as a cross-linker, and 2,2-azobis-isobutyronitrile (AIBN) as an initiator. Static adsorption experiments and Scatchard analysis were then conducted and results showed that the synthesized MIPs could rapidly and selectively adsorb and separate bitertanol from cucumber and peaches due to their predetermined recognition sites. The capacity of MIPs for absorbing bitertanol (∼ 2.21 mg/g) was approximately 1.5 times that of non-imprinted polymers (NIPs) (∼ 1.55 mg/g). Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) synthesized by sodium citrate reduction method were validated as a suitable SERS colloid for enhancing Raman signals. SERS spectral peaks (760, 985, 1190, and 1279 cm−1) were used to develop quantitative analysis based on partial least-squares regression (PLSR) for bitertanol in cucumber and peaches. The LODs for this method were 0.041 and 0.029 mg/kg in cucumber and peaches, respectively. The entire analysis process required 15 min or less. More importantly, the MIP-SERS system provided not only a rapid, sensitive, and reliable method for bitertanol detection, but also a routine for overcoming the interference-mitigation effects in the SERS technology.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos C, Miliadis GE (2013) Development and validation of an easy multiresidue method for the determination of multiclass pesticide residues using GC–MS/MS and LC–MS/MS in olive oil and olives. Talanta 112:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.03.051
Basozaba I, Guerreiro A, Aranzazu Goicolea M, Barrio RJ (2014) Direct potentiometric quantification of histamine using solid-phase imprinted nanoparticles as recognition elements. Biosens Bioelectron 58:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.02.054
Cao XL, Hong SH, Jiang ZJ, She YX, Wang SS, Zhang C, Li H, Jin F, Jin MJ, Wang J (2017) SERS-active metal-organic frameworks with embedded gold nanoparticles. Analyst 142(14):2640–2647. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AN00534B
Chen SN, Li X, Zhao YY, Chang LM, Qi JY (2014) High performance surface-enhanced Raman scattering via dummy molecular imprinting onto silver microspheres. Chem Commun 50(92):14331–14333. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC06535B
Dong N, Hu YJ, Yang K, Liu JZ (2016) Development of aptamer-modified SERS nanosensor and oligonucleotide chip to quantitatively detect melamine in milk with high sensitivity. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 228:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.12.089
Feng SL, Gao F, Chen ZW, David D, Wang S, Lu XN (2013) Determination of α-tocopherol in vegetable oils using a molecularly imprinted polymers–surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic biosensor. J Agric Food Chem 61(44):10467–10475. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4038858
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nature Phys Sci 241(105):20–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/physci241020a0
Haynes CL, McFarland AD, Van Duyne RP (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 77:338–346
He L, Lamont E, Veeregowda B, Sreevatsan S, Haynes CL, Diez-Gonzalez F (2011) Aptamer-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of ricin in liquid foods. Chem Sci 2(8):1579–1582. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1sc00201e
Hu YL, Li JW, Li GK (2011) Synthesis and application of a novel molecularly imprinted polymer-coated stir bar for microextraction of triazole fungicides in soil. J Sep Sci 34(10):1190–1197. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100068
Huang Z, Zhang Y, Wang L, Ding L, Wang M, Zhu SH (2009) Simultaneous determination of 103 pesticide residues in tea samples by LC-MS/MS. J Sep Sci 32(9):1294–1301. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800605
Li JF, Huang Y, Ding Y, Li SB, Yang ZL, Zhou XH, Ren B, Wang ZL, Tian ZQ (2010) Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464(7287):392–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08907
Li J, Zhang XB, Liu YX, Tong HW, Xu YP, Liu SM (2013) Preparation of a hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymer using tetrabromobisphenol A as a dummy template and its application as SPE sorbent for determination of bisphenol A in tap water. Talanta 117:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.09.022
Liu B, Zhou P, Liu X, Sun X, Li H, Lin M (2013) Detection of pesticides in fruits by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with gold nanostructures. Food Bioprocess Technol 6(3):710–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0774-5
Lu X, Rasco BA, Kang DH, Jabal JM, Aston DE, Konkel ME (2011) Infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies of the antimicrobial effects of garlic concentrates and diallyl constituents on foodborne pathogens. Anal Chem 83(11):4137–4146. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac2001498
Lu X, Huang Q, Miller WG, Aston DE, Xu J, Xue F, Zhang HW, Rascoi BA, Wang S, Konkel ME (2012) Comprehensive detection and discrimination of Campylobacter species by use of confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy and multilocus sequence typing. J Clin Microbiol 50(9):2932–2946. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01144-12
Maria VC, Alessandro F (2013) Surface-enhanced Raman spectra of the neonicotinoid pesticide thiacloprid. J Raman Spectrosc 44:1126–1135
Müller C, David L, Chis V, Cintă Pînzaru S (2014) Detection of thiabendazole applied on citrus fruits and bananas using surface enhanced Raman scattering. Food Chem 145:814–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.136
Pissuwan D, Hobro AJ, Pavillon N, Smith NI (2014) Distribution of label free cationic polymer-coated gold nanorods in live macrophage cells reveals formation of groups of intracellular SERS signals of probe nanoparticles. RSC Adv 4(11):5536–5541. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra45556d
Rejczak T, Tuzimski T (2017) QuEChERS-based extraction with dispersive solid phase extraction clean-up using PSA and ZrO 2-based sorbents for determination of pesticides in bovine milk samples by HPLC-DAD. Food Chem 217:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.095
Restrepo AR, Ortiz AFG, Ossa DEH, Mesa GAP (2014) QuEChERS GC–MS validation and monitoring of pesticide residues in different foods in the tomato classification group. Food Chem 158:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.121
Temur E, Zengin A, Boyacı ISH, Dudak FC, Torul H, Tamer UU (2012) Attomole sensitivity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B detection using an aptamer-modified surface-enhanced Raman scattering probe. Anal Chem 84(24):10600–10606. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301924f
Tuzimski T (2008) Application of SPE-HPLC-DAD and SPE-TLC-DAD to the determination of pesticides in real water samples. J Sep Sci 31(20):3537–3542. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800368
Tuzimski T (2012) Determination of pesticides in wines samples by HPLC-DAD and HPTLC-DAD. J Liq Chromatogr R T 35:1415–1428
Wang L, Zang XH, Chang QY, Zhang GJ, Wang C, Wang Z (2014) Determination of triazole fungicides in vegetable samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction with graphene-coated magnetic nanocomposite as adsorbent followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry detection. Food Anal Methods 7(2):318–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9629-1
Wang AX, Lu HZ, Xu SF (2016) Preparation of magnetic hollow molecularly imprinted polymers for detection of triazines in food samples. J Agric Food Chem 64(24):5110–5116. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b01197
Wiest L, Buleté A, Giroud B, Fratta C, Amic S, Lambert O, Pouliquen H, Arnaudguilhem C (2011) Multi-residue analysis of 80 environmental contaminants in honeys, honeybees and pollens by one extraction procedure followed by liquid and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1218(34):5743–5756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.079
Xi S, Zhang K, Xiao DL, He H (2016) Computational-aided design of magnetic ultra-thin dummy molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction and determination of morphine from urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1473:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.09.074
Xiao XH, Yan KL, Xu XF, Li GK (2015) Rapid analysis of ractopamine in pig tissues by dummy-template imprinted solid-phase extraction coupling with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 138:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.02.003
Xie XF, Mukamurezi G, Sun YY, Wang HY, Qian H, Yao WR (2012) Establishment of rapid detection method of methamidophos in vegetables by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Eur Food Res Technol 234(6):1091–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1724-9
Zhang J, Zhuang S, Tong C, Liu W (2013) Probing the molecular interaction of triazole fungicides with human serum albumin by multispectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling. J Agric Food Chem 61(30):7203–7211. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf401095n
Zhao F, She Y, Zhang C, Cao X, Jin F, Jin M,Wang, J (2017) Selective solid-phase extraction based on molecularly imprinted technology and simultaneous determination of 20 triazole pesticides in cucumber samples by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B, In Press
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (201209094), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Contract No. 31471654), and National Key Technology R&D Program for the 12th five-year plan (2014BAD13B05–05) are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Xiaolin Cao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Fengnian Zhao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Zejun Jiang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Sihui Hong declares that she has no conflict of interest. Chao Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yongxin She declares that he has no conflict of interest. Fen Jin declares that he has no conflict of interest. Maojun Jin declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jing Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable in this study.
Additional information
Fengnian Zhao is co-first author.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 765 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Zhao, F., Jiang, Z. et al. Rapid Analysis of Bitertanol in Agro-products Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers-Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 11, 1435–1443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1125-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1125-6