Abstract
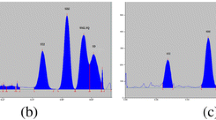
A high-performance thin-layer chromatographic (HPTLC) method was developed and validated according to the protocol on Validation of Analytical Procedures: methodology, Veterinary International Cooperation on Harmonization for simultaneous determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in broiler chicken tissues viz. liver, kidney, muscle-breast, muscle-thigh, and skin. Chromatography was performed on thin-layer chromatography (TLC) silica gel 60F254, aluminum sheets (10 × 10 cm) by Camag Linomat-5 applicator. The isolation of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin was attained by two development stages, initially with diethyl ether followed by dichloromethane/methanol/aqueous ammonia/acetonitrile (2:3:2:3) as mobile phase. The developed TLC plates were exposed to hydrochloric acid fumes and fluorescent densitometric evaluation was performed at 366 nm using Camag TLC Scanner-3 with WinCAT 1.4.4 software. The RF value was 0.60 and 0.44 for enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin, respectively. The detection limits were 2 and 3 ng/band for enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin, respectively, and 5 ng/band as limit of quantification for both the compounds. Enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin showed wide linear range from 2 to 110 ng/band and 3 to 110 ng/band with high correlation coefficient values of 0.99997 and 0.99990 for peak area, respectively. An exemplary precision was observed for individual compounds. The percent recovery for ciprofloxacin was 82.0–86.8% when compared to enrofloxacin 83.4–90.3%. The observed results were within the acceptable values as a function of the analyte concentration, suggested by the Association of Official Analytical Chemists peer-verified methods program. The present validated HPTLC method can be used as screening technique for antibiotics residue monitoring program in broiler chicken tissues to promulgate food safety.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anadon A, Martinez-Larranaga MR, Diaz MJ, Bringas P, Martinez MA, Fernandez-Cruz ML, Fernandez MC, Fernandez R (1995) Pharmacokinetics and residues of enrofloxacin in chickens. Am J Vet Res 56:501–506
Anderson AD, Nelson JM, Rossiter S, Angulo FJ (2003) Public health consequences of use of antimicrobial agents in food animals in the United States. Microb Drug Resist 9:373–379
Angulo FJ, Johnson KR, Tuxe RV, Cohen ML (2000) Origins and consequences of antimicrobial-resistant nontyphoidal salmonella: implications for the use of fluoroquinolones in food animals. Microb Drug Resist 6:77–83
AOAC Peer Verified Methods Program (1993) Manual on policies and procedures; Arlington
Bober K (2008) Determination of selected quinolones and fluoroquinolones by use of TLC. Anal Lett 41:1909–1913
Choma IM (2003) TLC separation of fluoroquinolones: searching for better selectivity. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 26:2673–2685
Choma IM, Choma A, Komaniecka I, Pilorz K, Staszczuk K (2005) Semiquantitative estimation of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin by thin-layer chromatography-direct bioautography. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 27:2071–2085
Dorofeev VL, Konovalov AA, Kochin VY, Arzamastsev AP (2004) TLC analysis of drugs of the fluoroquinolone group. Pharmaceut Chem J 38:510–512
Ellakany HF, Abu El-Azm IM, Bekhit AA, Shehawy MM (2007) Studies on the effects of enrofloxacin overdose on different health parameters in broiler chickens. In: BS Vet Med J., 5th Scientific Conference. pp 176–186
EMEA (2002) The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines and Inspections. Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products, Enrofloxacin (Extension to all food producing species), Summary report (5), EMEA/MRL/820/02-FINAL
EMEA (2006) Use of fluoroquinolones in food producing animals: precautions for use in the SPC regarding prudent use guidance. Committee for medicinal products for veterinary use. (EMEA/CVMP/416168/2006)
FAO/WHO (1995) Codex Alimentarius, residues of veterinary drugs in foods, volume 3, 2nd edition, section 3, part II. FAO, Rome
Garcia MA, Solans C, Calvo A, Hernandez E, Rey R, Bregante MA, Puig M (2005) Determination of enrofloxacin and its primary metabolite ciprofloxacin in pig tissues. application to residue studies. Biomed Chromatogr 19:27–31
Garcia Ovando H, Gorla N, Weyers A, Ugnia L, Magnoli A (2004) Simultaneous quantification of ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin and balofloxacin in broiler chicken muscle. Arch Med Vet 36:93–98
Gorla N, Chiostri E, Ugnia L, Weyers A, Giacomelli N, Davicino R, Garcia Ovando H (1997) HPLC residues of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in eggs of laying hens. Int J Antimicrob Agents 8:253–256
Herndndez-Arteseros JA, Boronat I, Compan R, Prat MD (2000) Liquid chromatographic separation of fluoroquinolone antibacterials used as veterinary drugs. Chromatographia 52:295–300
Humphrey TJ, Jorgensen F, Frost JA, Wadda H, Domingue G, Elviss NC, Griggs DJ, Piddock LJ (2005) Prevalence and subtypes of ciprofloxacin resistant Campylobacter spp. in commercial poultry flocks before, during and after treatment with fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:690–698
Juhel-Gaugain M, Abjean JP (1998) Screening of quinolone residues in pig muscle by planar chromatography. Chromatographia 47:101–104
Khan AA, Nawaz MS, Summage West C, Khan SA, Lin J (2005) Isolation and molecular characterization of fluoroquinolones resistant Escherichia coli from poultry litter. Poult Sci 84:61–66
Krzek J, Hubicka U, Szczepanczyk J (2005) High-performance thin-layer chromatography with densitometry for the determination of ciprofloxacin and impurities in drugs optimized chromatographic conditions. J AOAC Int 88:1530–1536
Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan (2005) Specifications and standards for food, food additives. Notification no. 499. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Tokyo
Norstrom M, Hofshagen M, Stavnes T, Schau J, Lassen J, Kruse K (2006) Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter jejuni from humans and broilers in Norway. Epidemiol Infect 134:127–130
Petrovic J, Baltic M, Stefanovic S, Milanov D, Ratajac R (2009) Determination of flumequine residues in broiler chickens with HPLC and screening method. Acta Vet (Beograd) 59:547–555
Posyniak A, Zmudzki J, Semeniuk S, Niedzielska J, Eblis R (1999) Determination of fluoroquinolone residues in animal tissues by liquid chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr 13:279–285
Prescott JF, Baggot JD, Walker RD (2000) Fluoroquinolones. In: Prescott JF, Baggot JD, Walker RD (eds) Antimicrobial therapy in veterinary medicine, 3rd edn. Iowa State University Press, Iowa, pp 315–339
Ramos M, Aranda A, Garcia E, Reuvers T, Hooghuis H (2003) Simple and sensitive determination of five quinolones in food by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B 789:373–381
Saleh GA, Askal HF, Refaat IH, Abdel-aal FAM (2013) Review on recent separation methods for determination of some fluoroquinolones. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 36:1401–1420
Schneider MJ (2004) Rapid fluorescence screening assay for enrofloxacin and tetracyclines in chicken muscle. J Agric Food Chem 52:7809–7813
Thangadurai S, Shukla SK, Anjaneyulu Y (2002) Separation and detection of certain beta lactam and fluoroquinolones antibiotic drugs by thin layer chromatography. Anal Sci 18:97–100
Tollefson L, Karp BE (2004) Human health impact from antimicrobial use in food animals. Med Mal Infect 34:514–521
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2005) Enrofloxacin for poultry: final decision of withdrawal of new animal drug application following formal evidentiary public hearing availability. Fed Regist 70:44105
Verdon E, Couedor P, Roudaut B, Sanders P (2005) Multiresidue method for simultaneous determination of ten quinolones antibacterials residues in multimatrix/multispecies animal tissues by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection: single laboratory validation study. J AOAC Int 88:1179–1192
VICH Guideline on Validation of Analytical Procedures (1998) Methodology, Veterinary International Cooperation on Harmonization, EMEA/CVMP/590/98-Final, London, UK
Wang PL, Chen L, Fan YF (2001) Selective separation and simultaneous determination of trace levels of five types of fluorinated quinolone drugs by thin layer chromatography/fluorescence densitometry. J AOAC Int 84:684–688
Wegner HC (1999) The consequences for food safety of the use of fluoroquinolones in food animals. N Engl J Med 340:1525–1532
WHO (1998) Use of quinolones in food animals and potential impact on human health. Report of a WHO meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 2–5 June, 1998. WHO/EMC/2DI/98
Wilson ID (1999) The state of the art in thin-layer chromatography-mass spectrometry: a critical appraisal. J Chromatogr A 856:429–442
Zhao L, Dong YH, Wang H (2010) Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. Sci Total Environ 408:1069–1075
Acknowledgements
The Authors are highly thankful to the Drugs and Pharmaceutical Research Programme, Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, New Delhi, for the financial assistance in conducting the experiment as part of the DST scheme entitled “A National Facility for Pharmacovigilance on Drug Residue and other Toxic Xenobiotics including Genetically Manipulated Organisms in Veterinary Products” at Pharmacovigilance Laboratory for Animal Feed and Food Safety, Directorate of Centre for Animal Health Studies, Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai-600 051.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Veerapandian Sureshkumar declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ghadevaru Sarathchandra declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Part of Ph.D. thesis submitted to Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Tamil Nadu State, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sureshkumar, V., Sarathchandra, G. A HPTLC-Fluorescent Densitometry Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Broiler Chicken Tissues. Food Anal. Methods 11, 1076–1085 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1077-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1077-x