Abstract
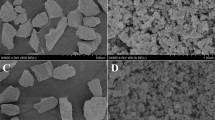
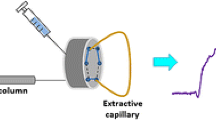
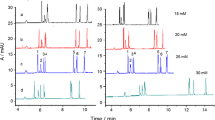
Capillary liquid chromatography with UV detection is proposed for the determination of 5-nitroimidazole residues in aquaculture products. The separation was carried out in a C18 column at 20 °C, using a mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile, at 7 μL/min and 320 nm as detection wavelength. Furthermore, full loop injection mode (8 μL) was selected and water was considered as injection solvent. The optimized method was applied to the monitoring of nine 5-nitroimidazoles, including three metabolites, in crab, salmon, prawn, and velvet swimming crab. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction has been evaluated for sample cleanup. The method was characterized in all the matrices in terms of linearity (R 2 ≥ 0.9964), precision (repeatability, RSD ≤ 7.9%, and reproducibility, RSD ≤ 11.1%) and trueness (recoveries between 80.4 and 108.7%). Decision limits, CCα, ranging from 0.2 to 1.5 μg/kg and detection capabilities, CCβ, from 0.2 to 1.8 μg/kg, were obtained.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCβ:
-
Detection capability
- CCα:
-
Decision limit
- DMZ:
-
Dimetridazole
- EURLs:
-
European Union Reference Laboratories
- HMMNI:
-
2-Hydroxymethyl-1-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazole
- IPZ:
-
Ipronidazole
- IPZ-OH:
-
Hydroxyl-ipronidazole
- MISPE:
-
Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction
- MNZ:
-
Metronidazole
- MNZ-OH:
-
Hydroxyl-metronidazole
- MRLs:
-
Maximum residue levels
- 5-NDZ:
-
5-Nitroimidazole
- ORZ:
-
Ornidazole
- RNZ:
-
Ronidazole
- SCZ:
-
Secnidazole
- SPE:
-
Solid-phase extraction
- TNZ:
-
Tinidazole
- TRZ:
-
Ternidazole
References
Antignac J, Marchand P, Bizec BL (2002) Identification of ractopamine residues in tissue and urine samples at ultra-trace level using liquid chromatography-positive electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 774:59–66
Bendesky A, Menéndez D, Ostrosky-Wegman P (2002) Is metronidazole carcinogenic? Mutat Res 511(2):133–144
Cháfer-Pericás C, Maquieira Á, Puchades R (2010) Fast screening methods to detect antibiotic residues in food samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 29(9):1038–1049
Cronly M, Behan P, Foley B, Malone E, Regan L (2009) Development and validation of a rapid method for the determination and confirmation of 10 nitroimidazoles in animal plasma using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 877(14–15):1494–1500
Dolan JW (2012) When should an internal standard be used? LCGC N Am 30:474–480
European Commission (2002) Commission Decision (2002/657/EC) of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off J Eur Communities L221:8–36
European Union Reference Laboratories (2007) CRL guidance paper (7 December 2007). CRLs view on state of the art analytical methods for national residue control plans. http://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/digitaaldepot/crlguidance2007.pdf. Accessed on 16th October 2016
Fanali C, Dugo L, Dugo P, Mondello L (2013) Capillary-liquid chromatography (CLC) and nano-LC in food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 52:226–238
Granja RHMM, Nino AMM, Reche KVG, Giannotti FM, de Lima AC, Wanschel ACBA, Salerno AG (2013) Determination and confirmation of metronidazole, dimetridazole, ronidazole and their metabolites in bovine muscle by LC-MS/MS. Food Additives & Contaminants. Part A 30(6):970–976
Hernández-Mesa M, García-Campaña AM, Cruces-Blanco C (2014) Novel solid phase extraction method for the analysis of 5-nitroimidazoles and metabolites in milk samples by capillary electrophoresis. Food Chem 145:161–167
Hernández-Mesa M, Lara FJ, Cruces-Blanco C, García-Campaña AM (2015) Determination of 5-nitroimidazole residues in milk by capillary electrochromatography with packed C18 silica beds. Talanta 144:542–550
Leiros H-KS, Kozielski-Stuhrmann S, Kapp U, Terradot L, Leonard GA, McSweeney SM (2004) Structural basis of 5-nitroimidazole antibiotic resistance: the crystal structure of NimA from Deinococcus radiodurans. J Biol Chem 279(53):55840–55849
Mahugo-Santana C, Sosa-Ferrera Z, Torres-Padrón ME, Santana-Rodríguez JJ (2010) Analytical methodologies for the determination of nitroimidazole residues in biological and environmental liquid samples: a review. Anal Chim Acta 30:113–122
Martín-Esteban A (2013) Molecularly-imprinted polymers as a versatile, highly selective tool in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 45:169–181
Mitrowska K, Posyniak A, Zmudzki J (2014) Selective determination of fourteen nitroimidazoles in honey by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Lett 47(10):1634–1649
Mohamed R, Mottier P, Treguier L, Richoz-Payot J, Yilmaz E, Tabet J-C, Guy PA (2008) Use of molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction sorbent for the determination of four 5-nitroimidazoles and three of their metabolites from egg-based samples before tandem LC-ESIMS/MS analysis. J Agric Food Chem 56(10):3500–3508
Płotka J, Tobiszewski M, Sulej AM, Kupska M, Górecki T, Namieśnik J (2013) Green chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1307:1–20
Rodríguez Ferreiro G, Cancino Badías L, Lopez-Nigro M, Palermo A, Mudry M, González Elio P, Carballo MA (2002) DNA single strand breaks in peripheral blood lymphocytes induced by three nitroimidazole derivatives. Toxicol Lett 132(2):109–115
Saito Y, Jinno K, Greibrokk T (2004) Capillary columns in liquid chromatography: between conventional columns and microchips. J Sep Sci 27(17–18):1379–1390
Sams MJ, Strutt PR, Barnes KA, Damant AP, Rose MD (1998) Determination of dimetridazole, ronidazole and their common metabolite in poultry muscle and eggs by high performance liquid chromatography with UV detection and confirmatory analysis by atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. Analyst 123(12):2545–2549
Shimelis O, Wihlborg A, Rudolfsson M, Boyd B, Trinh A (2009) Extraction of nitroimidazoles from milk and egg samples using SupelMIP SPE Nitroimidazoles and LC-MS-MS (Technical Note—Sigma-Aldrich®)
Sorensen LK, Hansen H (2000) Determination of metronidazole and hydroxymetronidazole in trout by a high-performance liquid chromatographic method. Food Additives & Contaminants 17(3):197–203
Sun H-W, Wang F-C, Ai L-F (2007) Simultaneous determination of seven nitroimidazole residues in meat by using HPLC-UV detection with solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr B 857(2):296–300
The European Commission (2010) Commission Regulation (EU) No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off J Eur Union L15(2377):1–72
Tölgyesi A, Sharma VK, Fekete S, Fekete J, Simon A, Farkas S (2012) Development of a rapid method for the determination and confirmation of nitroimidazoles in six matrices by fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 64-65:40–48
Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A (2010) Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation: a review. Anal Chim Acta 668(2):87–99
Xia X, Li X, Zhang S, Ding S, Jiang H, Li J, Shen J (2008) Simultaneous determination of 5-nitroimidazoles and nitrofurans in pork by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1208(1–2):101–108
Xia X, Li X, Ding S, Zhang S, Jiang H, Li J, Shen J (2009) Determination of 5-nitroimidazoles and corresponding hydroxy metabolites in swine kidney by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 637(1–2):79–86
Zelnícková H, Rejtharová M (2013) Determination of 5-nitroimidazoles in various types of matrices using molecular imprinted polymer purification. Food Additives & Contaminants, Part A 30(6):1123–1127
Zhou J, Shen J, Xue X, Zhao J, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang S (2007) Simultaneous determination of nitroimidazole residues in honey samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J AOAC Int 90(3):872–878
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Andalusian Government (Junta de Andalucía) for Excellence Project Ref: P12-AGR-1647. M. Hernández-Mesa thanks the “Plan Propio” of University of Granada for a pre-doctoral fellowship. D. Moreno-González acknowledges the program to strengthen research groups of the University of Granada for his postdoctoral contract.
Conflict of Interest
M. Hernández-Mesa declares that he has no conflict of interest. D. Moreno-González declares that he has no conflict of interest. C. Cruces-Blanco declares that she has no conflict of interest. A.M. García-Campaña declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 453 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Mesa, M., Moreno-González, D., Cruces-Blanco, C. et al. Evaluation of a Selective Approach for the Determination of 5-Nitroimidazoles in Aquaculture Products by Capillary Liquid Chromatography Using Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction. Food Anal. Methods 10, 3647–3657 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0928-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0928-9