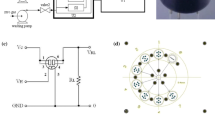
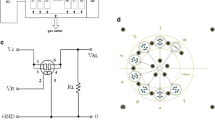
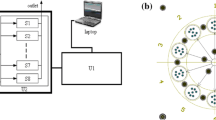
Abstract
In this paper, a portable electronic nose (E-nose) system was designed, and its application in K value prediction for large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) was also explored. E-nose responses to croaker samples were measured for 8 days. Microbiological and chemical indexes including total viable count (TVC), K value, and GC-MS were synchronously examined. Principal component analysis (PCA) and stochastic resonance (SR) were utilized for E-nose measurement data analysis. Results suggested that croaker’s K value increased rapidly due to microbial propagation. GC-MS results presented the information of volatile gas emitted by croaker samples, and provided reliable references for E-nose responses. PCA method could not discriminate all croaker samples, while SR signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) maximum (Max SNR ) values quantitatively discriminated all samples. Large yellow croaker K value predictive model was developed by linear fitting regression between K values and Max SNR values with a regression coefficient (R 2) of 0.96. Validating experiment results demonstrated that the forecasting accuracy of this model is 83 % the regression coefficient of the developed model was 0.83. E-nose is a useful tool for food quality examination. But, there are no such standard references for E-nose examination, which limits the applications of this technique. The method proposed here will promote the applications of E-nose in aquatic product quality rapid analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiana A et al (1981) The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J Phys A 14:L453–L456
Cai ZN, Li WJ, Mai KS, Xu W, Zhang YJ, Ai QH et al (2015) Effects of dietary size-fractionated fish hydrolysates on growth, activities of digestive enzymes and aminotransferases and expression of some protein metabolism related genes in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquaculture 440:40–47
Dang LJ, Tian FC, Zhang L, Kadri C, Yin X, Peng XW, Liu SQ et al (2014) A novel classifier ensemble for recognition of multiple indoor air contaminants by an electronic nose. Sensors Actuators A 207:67–74
Deshmukh S, Kamde K, Jana A, Korde S, Bandyopadhyay R, Sankar R, Bhattacharyya N, Pandey RA et al (2014) Application of electronic nose for industrial odors and gaseous emissions measurement and monitoring –an overview. Anal Chim Acta 841:58–67
Díaz Enrich MJ, Barcia R, Ramos Martínez JI, Ibarguren I et al (1999) Determination of adenine nucleotides in Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. by ion-pair high-performnce liquid chromatography with a diode array detector. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 22:1391–1402
Dragonieri S, Brinkman P, Mouw E, Zwinderman AH, Carratú P, Resta O, Sterk PJ, Jonkers RE (2013) An electronic nose discriminates exhaled breath of patients with untreated pulmonary sarcoidosis from controls. Respir Med 107:1073–1078
Dutta R, Das A, Stocks NG, Morgan D et al (2006) Stochastic resonance-based electronic nose: a novel way to classify bacteria. Sensors Actuators B 115:17–27
El Barbri N, Mirhisse J, Ionescu R, El Bari N, Correig X, Bouchikhi B, Llobet E et al (2009) An electronic nose system based on a micro-machined gas sensor array to assess the freshness of sardines. Sensors Actuators B 141:538–543
Fan HB, Luo YK, Yin XF, Bao YL, Feng LG et al (2014) Biogenic amine and quality changes in lightly salt- and sugar-salted black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) fillets stored at 4 °C. Food Chem 159:20–28
Gammaitoni L, Hanggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F et al (1998) Stochastic resonance. Rev Mod Phys 70:223–287
Gammaitoni L, Hanggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F et al (2009) Stochastic resonance: a remarkable idea that changed our perception of noise. Eur Phys J B 69:1–3
Gao MS, Feng LF, Jiang TJ, Zhu JL, Fu LL, Yuan DX, Li JR et al (2014) The use of rosemary extract in combination with nisin to extend the shelf life of pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) fillet during chilled storage. Food Control 37:1–8
Ginson J, Kamalakanth CK, Bindu J, Venkateswarlu R, Das S, Chauhan OP, Srinivasa Gopal TK (2013) Changes in K value, microbiological and sensory acceptability of high pressure processed Indian white prawn (Fenneropenaeus indicus). Food Bioprocess Technol 6:1175–1180
Godoy JL, Vega JR, Marchetti JL et al (2014) Relationships between PCA and PLS-regression. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 130:182–191
Hernández-Cázares AS, Aristoy M-C, Toldrá F et al (2011) Nucleotides and their degradation products during processing of dry-cured ham, measured by HPLC and an enzyme sensor. Meat Sci 87:125–129
Hui G, Jin J, Deng S, Ye X, Zhao M, Wang M, Ye D et al (2015) Winter jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Mill.) quality forecasting method based on electronic nose. Food Chem 170:484–491
Huo DQ, Wu Y, Yang M, Fa HB, Luo XG, Hou CJ (2014) Discrimination of Chinese green tea according to varieties and grade levels using artificial nose and tongue based on colorimetric sensor arrays. Food Chem 145:639–645
Li TT, Hu WZ, Li JR, Zhang XG, Zhu JL, Li XP et al (2012) Coating effects of tea polyphenol and rosemary extract combined with chitosan on the storage quality of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Control 25:101–106
Li QF, Ai QH, Mai KS, Xu W, Zhang YJ et al (2013a) A comparative study: In vitro effects of EPA and DHA on immune functions of head-kidney macrophages isolated from large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea). Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:933–940
Li TT, Li JR, Hu WZ et al (2013b) Changes in microbiological, physicochemical and muscle proteins of post mortem large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Control 34:514–520
Li TT, Li JR, Hu WZ, Li XP et al (2013c) Quality enhancement in refrigerated red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) fillets using chitosan coatings containing natural preservatives. Food Chem 138:821–826
Li TT, Li JR, Hu WZ, Chen JR, Li HJ et al (2014) Protein changes in post mortem large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) monitored by SDS-PAGE and proteome analysis. Food Control 41:49–55
Natale CD, Olafsdottir G, Einarsson S, Martinelli E, Paolesse R, D’Amico A et al (2001) Comparison and integration of different electronic noses for freshness evaluation of cod-fish fillets. Sensors Actuators B 77:572–578
National Food Safety Standard Food microbiological examination: Aerobic Plate Count. (2010) China standard protocols, GB 4789.2-2010, 2010
O’Connell M, Valdora G, Peltzer G, Martín Negri R et al (2001) A practical approach for fish freshness determinations using a portable electronic nose. Sensors Actuators B 80:149–154
Ozogul F, Taylor KDA, Quantick P, Ozogul Y et al (2000) Chemical, microbiological and sensory evaluation of Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) stored in ice, modified atmosphere and vacuum pack. Food Chem 71:267–273
Peng Q, Tian RG, Chen FR, Li BB, Gao HG et al (2015) Discrimination of producing area of Chinese Tongshan kaoliang spirit using electronic nose sensing characteristics combined with the chemometrics methods. Food Chem 178:301–305
Qiu XJ, Chen SJ, Liu GM, Yang QM et al (2014) Quality enhancement in the Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicas) fillets stored at 4 °C by chitosan coating incorporated with citric acid or licorice extract. Food Chem 162:156–160
Sato N, Usui K, Okuma H (2002) Development of a bienzyme reactor sensor system for the determination of ornithine. Anal Chim Acta 456:219–226
Verma P, Yadava RDS (2015) Polymer selection for SAW sensor array based electronic noses by fuzzy c-means clustering of partition coefficients: Model studies on detection of freshness and spoilage of milk and fish. Sensors Actuators B 209:751–769
Wei ZB, Wang J, Zhang WL et al (2015) Detecting internal quality of peanuts during storage using electronic nose responses combined with physicochemical methods. Food Chem 177:89–96
Westenbrink E, Arasaradnam RP, O’Connell N, Bailey C, Nwokolo C, Bardhan KD, Covington JA et al (2015) Development and application of a new electronic nose instrument for the detection of colorectal cancer. Biosens Bioelectron 67:733–738
Yi XW, Xu W, Zhou HH, Zhang YJ, Luo YW, Zhang WB, Mai KS et al (2014) Effects of dietary astaxanthin and xanthophylls on the growth and skin pigmentation of large yellow croaker Larimichthys croceus. Aquaculture 433:377–383
Zhang XD, Zhu YF, Cai LS, Wu TX et al (2008) Effects of fasting on the meat quality and antioxidant defenses of market-size farmed large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Aquaculture 280:136–139
Zhao J, Lv WJ, Wang JL, Li JR, Liu XX, Zhu JL et al (2013) Effects of tea polyphenols on the post-mortem integrity of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) fillet proteins. Food Chem 141:2666–2674
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Key Technology R&D Program (No. 2014BAD10B02-04), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61272313, 61302185), Zhejiang National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. LQ14F020014), Key Laboratory of Forestry Intelligent Monitoring and Information Technology Research of Zhejiang Province, Talent Startup Project of Zhejiang A & F University (Nos.2015FR020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work is supported by National Key Technology R&D Program (No. 2014BAD10B02-04), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61272313, 61302185), Zhejiang National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. LQ14F020014), Key Laboratory of Forestry Intelligent Monitoring and Information Technology Research of Zhejiang Province (Nos. 100151402), Talent Startup Project of Zhejiang A & F University (Nos.2015FR020).
Conflict of Interest
Author Jian Li has received research grant from Zhejiang National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. LQ14F020014). Author Hailin Feng has received research grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61272313, 61302185). Author Yuanyuan Gao has received research grant from Talent Startup Project of Zhejiang A & F University (Nos. 2015FR020). Author Guohua Hui has received research grant from National Key Technology R&D Program (Nos. 2014BAD10B02-04), and Talent Startup Project of Zhejiang A & F University (Nos. 2015FR020).
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
> E-nose combined with non-linear stochastic resonance was proposed for large yellow croaker K value prediction.
> Stochastic resonance SNR eigen values presented better quantitative discriminating effects than PCA.
> The proposed model presented good predicting accuracy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Feng, H., Liu, W. et al. Design of A Portable Electronic Nose system and Application in K Value Prediction for Large Yellow Croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Anal. Methods 9, 2943–2951 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0431-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0431-8